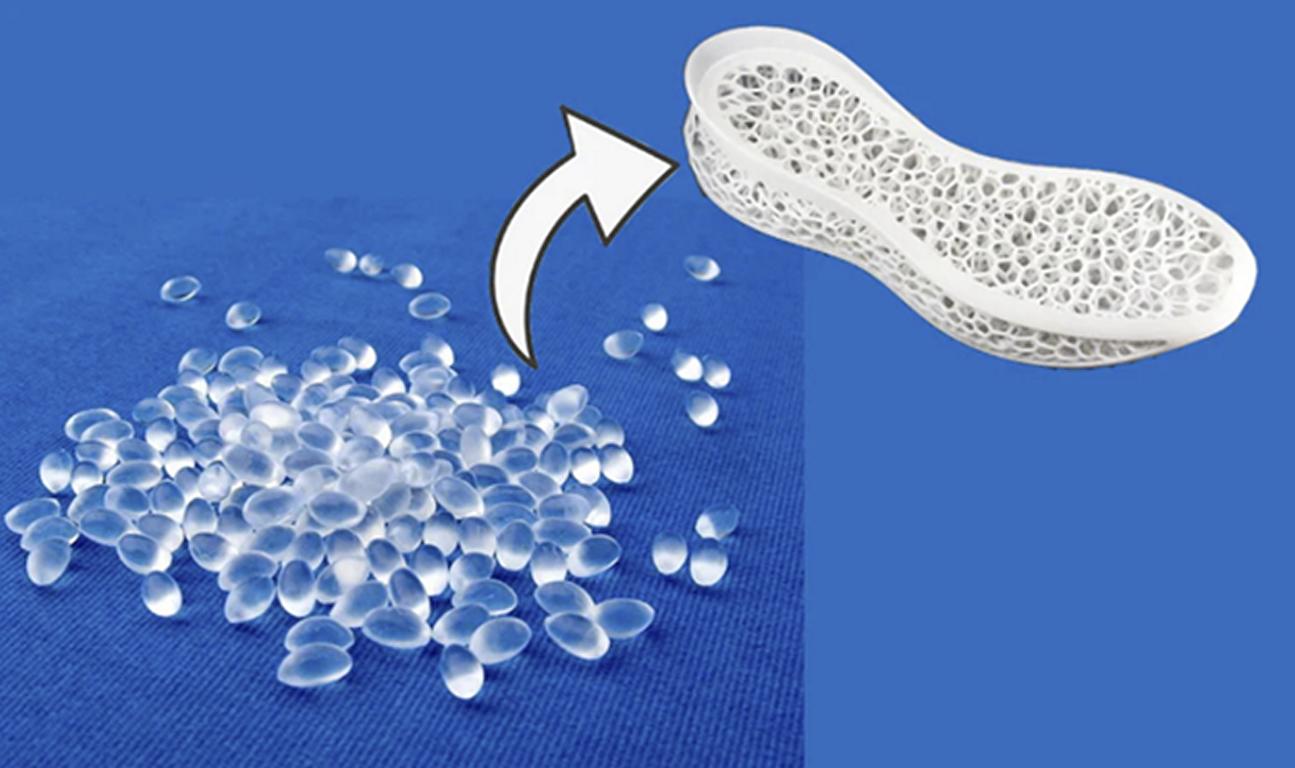
Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych to wyspecjalizowany proces produkcyjny wykorzystywany również w produkcji wysokiej jakości przezroczystych elementów z tworzyw sztucznych dla wielu branż. Technika ta różni się od standardowego formowania tworzyw sztucznych tym, że materiały, konstrukcja formy i wszystkie zmienne muszą być precyzyjnie kontrolowane, aby zapewnić wyjątkową przejrzystość optyczną i trwałość. Przezroczyste plastikowe części pojawiają się w instrumentach medycznych i soczewkach samochodowych, elektronice użytkowej i oświetleniu architektonicznym wszędzie i wszędzie indziej. Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych udaje się w zależności od wyboru odpowiedniego materiału, takiego jak akryl, poliwęglan i optyczna guma silikonowa, z ich specyficznymi właściwościami, takimi jak odporność na uderzenia, stabilność UV i przepuszczalność światła.
Sam proces wymaga delikatnego przygotowania formy, suszenia materiału, wtryskiwania w kontrolowany sposób, a następnie powolnego chłodzenia w celu uniknięcia wad, takich jak pęcherzyki, smugi i zamglenia. Ponadto techniki obróbki końcowej i zaawansowane powłoki dodatkowo poprawiają właściwości optyczne optycznie przezroczystych elementów z tworzyw sztucznych. Przy wszystkich tych zaletach, formowanie przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych stoi przed wyzwaniami, takimi jak idealna przezroczystość, unikanie defektów powierzchni i wrażliwość materiału. Niemniej jednak tempo postępu w dziedzinie formowania rośnie, a firmy z branży wykorzystują innowacje, takie jak optymalizacja formowania oparta na sztucznej inteligencji, konfigurowalne formy do druku 3D i samonaprawiające się tworzywa sztuczne w celu poprawy wydajności i wytwarzanych produktów.
W tym artykule omówiono proces formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych, kluczowe stosowane materiały, wyzwania, zastosowania, a także ich przyszłe postępy. Jeśli pracujesz w branży medycznej, motoryzacyjnej, elektronicznej lub oświetleniowej, jeśli chcesz poznać tajemnicę tworzenia przezroczystych narzędzi z tworzyw sztucznych, ta wiedza może pomóc Ci wybrać wysokowydajny i przyjemny wizualnie element z tworzywa sztucznego.
Czym jest formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych?

Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych to rodzaj produkcji, w którym przezroczysty lub półprzezroczysty materiał z tworzywa sztucznego jest topiony i wtryskiwany do formy w celu ostatecznego utworzenia określonych kształtów. W przeciwieństwie do zwykłego formowania wtryskowego, proces ten jest bardzo wrażliwy na dobór materiału (w tym wybór rodzajów przepływów), projekt formy i techniki chłodzenia, aby uniknąć takich wad, jak zmętnienie, pęcherzyki i zniekształcenia.
Jest szeroko stosowany do wytwarzania produktów, które powinny mieć doskonałe właściwości optyczne, takich jak instrumenty medyczne, oświetlenie samochodowe i wyświetlacze elektroniczne.
Proces formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych

Jest to bardzo precyzyjny proces uzyskiwania przezroczystych plastikowych elementów. Oto zestawienie niektórych istotnych kroków w tym kursie online.
1. Projektowanie i przygotowanie formy
Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych wymaga dobrze zaprojektowanej formy. Forma musi posiadać:
- Polerowane do bardzo wysokiego poziomu, aby zapobiec powstawaniu śladów lub zniekształceń dźwięku.
- Można go odpowietrzyć, aby usunąć pęcherzyki powietrza i uniknąć uwięzienia gazów.
- Mechanizmy kontroli temperatury w celu regulacji szybkości chłodzenia
2. Suszenie materiału
Żywice z tworzyw sztucznych o zbyt dużej zawartości wilgoci powodują zmętnienie, powstawanie pęcherzyków lub słabych punktów. Materiały poliwęglanowe i akrylowe muszą być suszone w kontrolowanych temperaturach przed wtryskiem w celu usunięcia wilgoci.
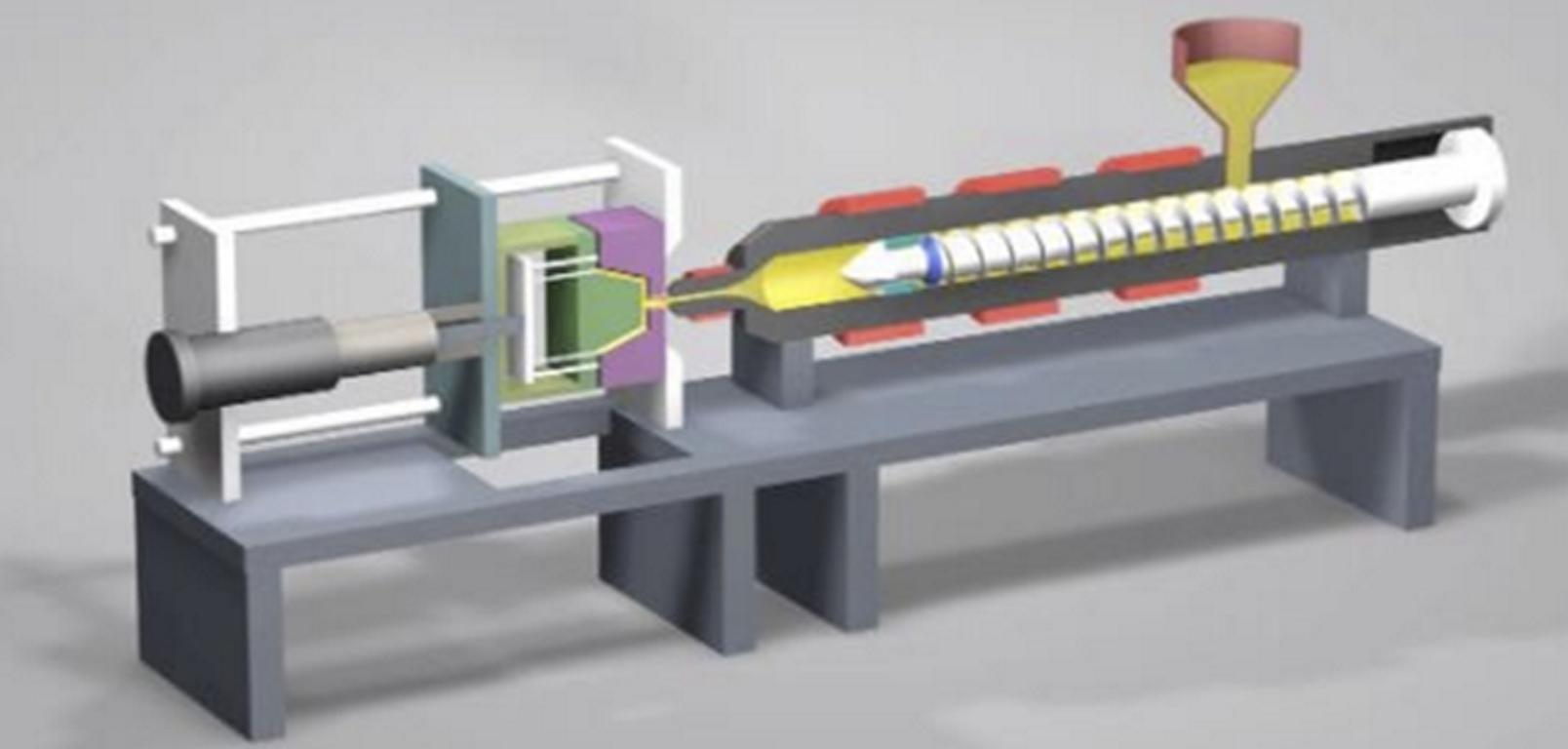
3. Topienie i wtryskiwanie
Wnęka formy jest wypełniana pod wysokim ciśnieniem wysuszoną żywicą podgrzaną do temperatury topnienia. Kluczowe kwestie obejmują:
- Zapobiega powstawaniu śladów przepływu i pęknięć naprężeniowych dzięki prędkości wtrysku i ciśnieniu.
- Wyższa temperatura pomaga zachować przejrzystość optyczną
- Równomierne chłodzenie i zapobieganie kurczeniu się: Jednolite wypełnienie
4. Chłodzenie i krzepnięcie
Chłodzenie musi być powolne i równomierne, aby uniknąć wypaczenia lub zniekształcenia materiału. Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne często wymagają:
- Stopniowe chłodzenie w celu utrzymania klarowności
- Możliwe jest zastosowanie zaawansowanych kanałów chłodzących wewnątrz formy.
- W niektórych przypadkach wyżarzanie po formowaniu zmniejsza naprężenia wewnętrzne.
5. Wyrzucanie i przetwarzanie końcowe
Część jest ostrożnie wyrzucana po zestaleniu, aby uniknąć zadrapań lub śladów. Techniki obróbki końcowej, takie jak:
Polerowanie
- Powłoka chroniąca przed promieniowaniem UV
- Cięcie laserowe zapewniające precyzję
- Może to również poprawić wygląd i trwałość produktu.
Przezroczyste formowanie wtryskowe Wykorzystuje kluczowe materiały.
Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne formowane wtryskowo wymagają wyboru materiału, który jest ważny dla zapewnienia wysokiej wytrzymałości i wysokiej przejrzystości. Poniżej przedstawiono najczęściej stosowane materiały:
Akryl (PMMA)

Polimetakrylan metylu (PMMA), lub jak jest naukowo znany jako akryl, jest jednym z najczęściej stosowanych materiałów do formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych ze względu na doskonałą przejrzystość optyczną. Dzięki współczynnikowi przepuszczalności światła wynoszącemu około 92%, jest on przeznaczony do zastosowań wymagających wysokiej przezroczystości, takich jak oprawy oświetleniowe, gabloty i komponenty samochodowe.
Oprócz doskonałej odporności na promieniowanie UV, co skutkuje brakiem żółknięcia z upływem czasu i wysoką odpornością na zarysowania, akryl jest również nietoksyczny w wielu zastosowaniach. Akryl jest jednak bardzo kruchy i podatny na pęknięcia lub pęknięcia przy uderzeniu. Ponadto jest bardzo wrażliwy na wilgoć i wymaga wstępnego suszenia, aby mógł być stosowany w formowaniu bez wad.
Polietylen o wysokiej gęstości (HDPE)

Polietylen o wysokiej gęstości (HDPE) to stosunkowo niedrogi i wszechstronny materiał o półprzezroczystej przejrzystości, dzięki czemu nadaje się do produktów, które nie wymagają pełnej przezroczystości. Ze względu na swoją odporność na promieniowanie UV, jest to dobry wybór do użytku na zewnątrz, ponieważ może tolerować długą ekspozycję na słońce bez degradacji.
HDPE ma większą odporność na uderzenia w porównaniu z akrylem, więc jest mniej podatny na pękanie. Najczęściej stosowany jest w produkcji butelek, rur i pojemników opakowaniowych ze względu na niski koszt produkcji i niesamowitą trwałość. Z drugiej strony, HDPE nie jest wystarczająco sztywny jak inne przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne, co czyni go nieodpowiednim do zastosowań wymagających wysokiej wytrzymałości strukturalnej.
Poliwęglan (PC)

Poliwęglan (PC) to wysokowydajne, przezroczyste tworzywo sztuczne o dobrych właściwościach optycznych i bardzo wysokiej wytrzymałości mechanicznej. Jest szeroko stosowany w aplikacjach wymagających przezroczystości i trwałości, np. w okularach ochronnych, reflektorach samochodowych, oknach kuloodpornych.
W przeciwieństwie do akrylu, poliwęglan jest wyjątkowo odporny na uderzenia i nie pęka pod wpływem dużych sił. Co więcej, jest odporny na promieniowanie UV, dzięki czemu nie żółknie przez długi czas. Jedną z wad jest jednak to, że powierzchnia poliwęglanu jest podatna na zarysowania powierzchni i zwykle wymaga kolejnej warstwy czegoś, aby faktycznie była trwała. PC wymaga również wstępnego domieszkowania przed formowaniem wtryskowym, aby zapobiec wadom związanym z wilgocią (jak akryl).
Polieteroimid (PEI)

Wysokowydajne tworzywo konstrukcyjne Polieteroimid (PEI) to wyjątkowe tworzywo sztuczne odporne na promieniowanie UV, ciepło i chemikalia. Stop ten znajduje zastosowanie przede wszystkim w branżach wymagających wysokiej wytrzymałości mechanicznej, a także wysokiej stabilności termicznej, takich jak przemysł lotniczy, motoryzacyjny i produkcja sprzętu medycznego.
W rezultacie PEI ma doskonałą odporność na ciepło dla wszystkiego, co będzie narażone na ekstremalne temperatury. Chociaż jest droższy i trudniejszy do formowania na powierzchni produktu, jest sporadycznie stosowany w produktach konsumenckich. W wielu przypadkach formowanie wtryskowe PEI wymaga użycia stalowych form, aby zachować precyzję i trwałość.
Polipropylen (PP)

Polipropylen (PP) jest szeroko stosowanym tworzywem termoplastycznym charakteryzującym się elastycznością, odpornością chemiczną oraz przewodnością elektryczną. Jest szeroko stosowany w materiałach opakowaniowych, tekstyliach i komponentach samochodowych ze względu na swoją trwałość i wszechstronność.
Najważniejszą zaletą PP jest jego zdolność do wielokrotnego zamykania i otwierania bez pękania. Jest więc szczególnie odpowiedni do takich zastosowań, jak zakrętki do butelek typu flip-top i zawiasy. Niemniej jednak, polipropylen nie jest tak przezroczysty jak akryl czy poliwęglan - jest bardziej półprzezroczysty niż przezroczysty. Dodatkowo, nie jest wystarczająco sztywny, aby można go było wykorzystać jako element konstrukcyjny lub nośny.
Płynna guma silikonowa (LSR)

Płynna guma silikonowa (LSR) to wysokowydajny elastomer, który znany jest z bardzo dobrej biokompatybilności, doskonałej stabilności termicznej i odporności chemicznej. Pod względem mechanicznym jest dość mocny i elastyczny i jest szeroko stosowany w zastosowaniach medycznych, motoryzacyjnych i elektronicznych.
Wyjątkową zaletą LSR jest jego zdolność do zachowania kształtu i właściwości w warunkach ekstremalnych cykli termicznych lub ekspozycji na chemikalia lub rozpuszczalniki i ciepło. LSR charakteryzuje się elastycznością i trwałością, dzięki czemu nadaje się do uszczelnień, uszczelek i rurek medycznych. Dzięki odporności na wysoką temperaturę i chemikalia LSR może być również stosowany w wymagających środowiskach.
Optyczna guma silikonowa (OSLR)

Ta optyczna guma silikonowa (OSLR) została opracowana specjalnie z myślą o wysokiej przepuszczalności światła i wysokiej przejrzystości optycznej. W soczewkach optycznych, oświetleniu LED, urządzeniach do obrazowania medycznego i innych dziedzinach, w których wymagana jest wyższa przepuszczalność światła i wyjątkowo niskie zniekształcenia, np. w telewizji przemysłowej.
OSLR charakteryzuje się wyjątkową odpornością na niekorzystne warunki pogodowe i nie żółknie przez cały oczekiwany okres eksploatacji. Jest to odpowiedni wybór dla zewnętrznych opraw oświetleniowych i precyzyjnych elementów optycznych ze względu na jego zdolność do utrzymywania stabilności optycznej w czasie.
Polietylen (PE)

Polietylen (PE) to tworzywo termoplastyczne, które powstaje z materiałów na bazie ropy naftowej w wyniku obróbki cieplnej i ciśnieniowej. Używany ze względu na swoją opłacalność i możliwość formowania, jest powszechnie stosowany w butelkach, rurach, opakowaniach i towarach konsumpcyjnych.
Jest odporny na promieniowanie UV, dzięki czemu doskonale nadaje się do użytku na zewnątrz. Chociaż nie może zbliżyć się do przejrzystości optycznej akrylu lub poliwęglanu, jest lepszy do zastosowań półprzezroczystych niż w pełni przezroczystych.
Żywice elastomerowe (TPR)

Kauczuk termoplastyczny (TPR) to elastyczny materiał łączący w sobie cechy plastiku i gumy. Jest on często stosowany w medycynie, przemyśle i konsumenckich zastosowaniach wymagających odporności chemicznej i elastyczności.
TPR jest używany w typowych zastosowaniach, takich jak dozowniki płynów, cewniki medyczne i węże elastyczne. Jest to idealny materiał do produktów wymagających odporności na kwasy i agresywne chemikalia, ponieważ może wytrzymać trudne warunki.
Termoplastyczny poliuretan (TPU)

Termoplastyczny poliuretan (TPU) to elastomer o wysokiej wytrzymałości, często stosowany w artykułach sportowych, częściach samochodowych i ergonomicznych uchwytach. Jako materiał jest znany ze swojej miękkiej tekstury, doskonałej elastyczności, a także doskonałej odporności na rozdarcie.
TPU daje wrażenie gumy w swoim składzie, dlatego jest szeroko stosowany w uchwytach i elastycznych częściach. Chociaż ta wersja tworzywa sztucznego jest droższa niż standardowe tworzywa sztuczne, jej trwałość i odporność na uderzenia sprawiają, że jest to dobry wybór tworzywa sztucznego do zastosowań o wysokiej wydajności.
Przepuszczalność światła i jej cechy oraz najlepsze wykorzystanie
Poniższa tabela pomaga porównać różne przezroczyste i półprzezroczyste materiały pod względem przepuszczalności światła oraz ich cech i najlepszego zastosowania.
| Materiał | Transmisja światła (%) | Kluczowe cechy | Typowe zastosowania |
| Akryl (PMMA) | ~92% | Jest to przezroczysty, odporny na promieniowanie UV i zarysowania kruchy materiał. | Oprawy oświetleniowe, ekrany wyświetlaczy, soczewki optyczne |
| Poliwęglan (PC) | 88-90% | Wysoka odporność na uderzenia, odporność na promieniowanie UV, nieco niższa przejrzystość niż PMMA | Okulary ochronne, reflektory samochodowe, kuloodporne szyby |
| Optyczna guma silikonowa (OSLR) | ~90-94% | Przejrzystość zbliżona do szkła, elastyczność, odporność na wysokie temperatury | Oświetlenie LED, soczewki optyczne, urządzenia do obrazowania medycznego |
| Płynna guma silikonowa (LSR) | ~85-90% | Elastyczny, biokompatybilny, odporny na ciepło i chemikalia | Urządzenia medyczne, elektronika, specjalistyczne oświetlenie |
| Polipropylen (PP) | ~80-85% | Przezroczyste, odporne na chemikalia, elastyczne, tanie | Szronione pokrywy, pojemniki, rozwiązania opakowaniowe |
| Polietylen o wysokiej gęstości (HDPE) | ~75-85% | Przezroczyste, trwałe, ekonomiczne, odporne na uderzenia | Butelki, rury, opakowania, towary konsumpcyjne |
Wyzwania związane z przezroczystym formowaniem wtryskowym

Chociaż przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne oferują szereg korzyści, nadal mają wady:
1. Osiągnięcie wysokiej przejrzystości optycznej
Przezroczystość może być zmniejszona przez jakiekolwiek niedoskonałości formy lub chłodzenia. Forma musi być gładka i wysoce wypolerowana, a przetwarzanie musi odbywać się w precyzyjnych temperaturach.
2. Unikanie pęcherzyków i linii przepływu
Pęcherzyki lub linie przepływu powietrza uwięzione podczas procesu wtrysku mogą być widoczne w produkcie końcowym. Aby temu zapobiec:
Konieczne jest odpowiednie odpowietrzenie formy. Pomaga to utrzymać płynny przepływ dzięki powolnym, kontrolowanym prędkościom wtrysku.
3. Wrażliwość materiału
Poliwęglan i akryl to przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne, które są bardzo wrażliwe na wilgoć, ciepło i promieniowanie UV. Jeśli suszenie i przechowywanie odbywa się w odpowiedni sposób, wydajność jest wysokiej jakości.
4. Zadrapania i wady powierzchni
Wynika to z faktu, że niedoskonałości są wyraźnie widoczne w przezroczystych tworzywach sztucznych, więc producenci muszą ich używać:
- Powłoki zapobiegające zarysowaniom
- Opakowanie ochronne podczas transportu
Typowe wady przezroczystych części plastikowych i ich rozwiązania

Do produkcji przezroczystych części z tworzyw sztucznych wymagana jest idealna przezroczystość i gładkość. Istnieje jednak wiele wad, które mogą wpływać na przejrzystość i ogólną jakość produktu końcowego. Oto kilka typowych problemów związanych z formowaniem wtryskowym przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych i sposoby ich rozwiązywania.
1. Bąbelki
Przyczyna
Uwięzione powietrze lub gaz, który nie może wydostać się podczas procesu formowania, jest zwykle przyczyną powstawania pęcherzyków. Może się to zdarzyć z powodu:
- Niepełne wypełnienie formy.
- Szybkie chłodzenie na powierzchni kondensacji.
- Żywica z wilgocią powodująca powstawanie oparów.
Rozwiązanie
- Upewnij się, że forma jest odpowiednio wentylowana, aby gazy mogły się ulatniać.
- Zwiększ ciśnienie wtrysku, aby poprawić przepływ materiału.
- Nadmiar wilgoci należy usunąć z żywicy przed formowaniem.
2. Srebrne smugi
Przyczyna
Wewnętrzne zmiany naprężeń podczas przepływu materiału powodują powstawanie srebrnych smug. Poprzez wywieranie nacisku na żywicę, jest ona popychana w różnych kierunkach, tworząc układ o nierównym współczynniku załamania światła i powodując efekt smug lub jedwabiu. Jeśli naprężenia te będą narastać, ostatecznie doprowadzi to do pęknięć.
Rozwiązanie
- Aby zapewnić równomierne chłodzenie, należy zoptymalizować temperaturę formy.
- Zwiększyć prędkość wtrysku i ciśnienie, aby zminimalizować wzrost naprężeń.
- Zapobieganie kierunkowemu wyrównaniu materiału podczas formowania za pomocą technik formowania z niskim naprężeniem.
3. Wzorce sejsmiczne
Przyczyna
Wada ta charakteryzuje się rowkowanymi lub falistymi wzorami na powierzchni wynikającymi z wysokiej lepkości stopu. Jeśli żywica nie przepływa płynnie i skrapla się zbyt wcześnie w zagłębieniu, niszczy to jednorodność materiału.
Rozwiązanie
- Zwiększ temperaturę topnienia, aby zwiększyć przepływ materiału.
- Lepkość jest zmniejszana poprzez dostosowanie warunków plastyfikacji.
- Zmień konstrukcję wlewu i prowadnicy, aby uzyskać lepszą dystrybucję materiału.
4. Słaby połysk powierzchni
Przyczyna
Przyczyną matowego lub nierównego wykończenia powierzchni jest zazwyczaj szorstka powierzchnia formy lub zbyt szybkie zestalenie się żywicy, zanim całkowicie dopasuje się ona do formy.
Rozwiązanie
- Aby uzyskać gładsze wykończenie, należy wypolerować gniazdo formy.
- Zwiększenie temperatury formy w celu poprawy przepływu materiału.
- Należy stosować żywice wysokiej jakości o lepszej charakterystyce przepływu.
5. Biały dym / czarne plamy
Przyczyna
Degradacja żywicy wewnątrz cylindra formowania wtryskowego z powodu nadmiernego ciepła jest przyczyną powstawania tych wad. Czarne plamy mogą pojawić się, gdy przegrzany materiał może się palić, a biały dym może pojawić się, gdy gaz jest emitowany ze zdegradowanej żywicy.
Rozwiązanie
- Zapobieganie przegrzaniu lufy poprzez obniżenie temperatury.
- Finnerzy powinni regularnie czyścić i konserwować wtryskarkę, aby uniknąć gromadzenia się żywicy.
- Gwarantuje stałe czasy cykli, dzięki czemu materiał nie ulega degradacji.
6. Wybielanie / zamglenie
Przyczyna
Gdy wilgoć lub cząsteczki kurzu zanieczyszczają tworzywo sztuczne, pojawia się zamglenie lub zmętnienie. Dyfrakcja światła spowodowana niewłaściwym suszeniem lub zanieczyszczeniami unoszącymi się w powietrzu zmniejsza przezroczystość.
Rozwiązanie
- Przetwarzanie surowców po ich dokładnym wysuszeniu.
- Zanieczyszczenia można uniknąć, przechowując materiały w czystym, kontrolowanym środowisku.
- Należy chronić powietrze przed pyłem, stosując filtry i oczyszczacze powietrza w obszarze produkcji.
Zalety formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych
Jednak formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych ma wiele zalet pomimo swoich wad.
1. Doskonała przezroczystość optyczna
Wysoka przepuszczalność światła dobrze nadaje się do przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych formowanych wtryskowo, stosowanych w takich elementach jak soczewki, sprzęt medyczny i ekrany wyświetlaczy.
2. Precyzja i spójność
Formowanie wtryskowe jest bardzo dokładne i powtarzalne, co skutkuje identycznymi częściami o bardzo niewielu wadach w każdej z nich.
3. Ekonomiczna produkcja masowa
Po stworzeniu formy koszty produkcji znacznie spadają w porównaniu z kolejnymi, dzięki czemu jest to skuteczny sposób, jeśli chodzi o produkcję masową.
4. Lekkość i trwałość
Ponieważ przezroczyste plastikowe części są lżejsze niż większość szkła, odporne na stłuczenia i uderzenia, doskonale nadają się do zastosowań związanych z bezpieczeństwem.
Zastosowania przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych formowanych wtryskowo
Tworzywa sztuczne z przezroczystymi formami wtryskowymi są powszechnie stosowane w przemyśle, ponieważ charakteryzują się przejrzystością optyczną, trwałością, odpornością chemiczną i mniejszą wagą. Są to tworzywa sztuczne, które mogą tworzyć przezroczyste, precyzyjne komponenty zwiększające funkcjonalność i estetykę. Poniżej przedstawiono niektóre z głównych branż, w których stosuje się przezroczyste formowanie wtryskowe tworzyw sztucznych.
1. Przemysł medyczny

Rynek medyczny wymaga przezroczystych elementów z tworzyw sztucznych, gdzie sterylność i precyzja mają kluczowe znaczenie, a także potrzeba widoczności. Typowe zastosowania obejmują:
- Obejmują przezroczyste strzykawki i rurki infuzyjne lub narzędzia chirurgiczne, które pozwalają personelowi monitorować lub sprawdzać przepływ płynów i zapobiegać przedawkowaniu.
- Sztywność przezroczystej osłony ochronnej na maskę na twarz lub gogle medyczne w celu ochrony bez ograniczania widoczności.
- Obudowy sprzętu diagnostycznego do urządzeń rentgenowskich, rezonansu magnetycznego i skanerów ultradźwiękowych, w których tak ważna jest przejrzystość.
2. Przemysł motoryzacyjny

Tworzywa sztuczne formowane wtryskowo mogą sprawić, że pojazdy będą bardziej funkcjonalne i przyjazne w projektowaniu. Są one stosowane w:
- Soczewki o wysokiej przejrzystości optycznej i trwałości do reflektorów przednich i tylnych, odporne na trudne warunki pogodowe.
- Przezroczyste górne pokrywy deski rozdzielczej i panele prędkościomierza zapewniają widoczność elementów sterujących i wyświetlaczy.
- W niektórych lekkich konstrukcjach samochodowych, które wymagają szyberdachów i szyb bocznych, wspomina się o odpornych na uderzenia przezroczystych tworzywach sztucznych.
3. Elektronika użytkowa

Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne do produkcji lekkich, trwałych i estetycznych części są wykorzystywane w przemyśle elektronicznym.
- Do ochronnych i ekonomicznych zastosowań dotykowych na ekranach smartfonów i osłonach wyświetlaczy.
- Obejmuje również przezroczyste ekrany telewizorów i laptopów o odporności na zarysowania i wysokiej przejrzystości.
- Elementy ekranów urządzeń do noszenia, takich jak smartwatche i monitory fitness, są również elastyczne i odporne na uderzenia.
4. Przemysł opakowań

Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne są powszechnie stosowane w opakowaniach, ponieważ można je myć, są lekkie i estetyczne. Niektóre kluczowe zastosowania obejmują:
- Wybór przezroczystych pojemników i butelek przeznaczonych do kontaktu z żywnością, zapewniających świeżość i widoczność zawartości.
- Rodzaj przezroczystego opakowania kosmetycznego i farmaceutycznego, dzięki któremu klienci mogą bezpiecznie zobaczyć produkt podczas przechowywania.
- Odporne na manipulacje i hermetyczne przezroczyste opakowania, stosowane w przypadku leków, suplementów lub produktów spożywczych wysokiej jakości.
5. Przemysł oświetleniowy

Tworzywa sztuczne, które są najczęściej stosowane jako materiały elektroizolacyjne, zwane przezroczystymi tworzywami sztucznymi lub tworzywami sztucznymi, są niezbędne w nowoczesnych zastosowaniach oświetleniowych, zapewniając zwiększoną wydajność i funkcjonalność. Są one stosowane w:
- Osłony LED i dyfuzory lamp zapewniają równomierny rozsył światła, a także chronią komponenty LED.
- Przezroczyste panele do oświetlenia architektonicznego, takie jak przezroczyste panele, mogą być używane jako niestandardowe rozwiązania oświetleniowe do projektowania wnętrz i na zewnątrz.
- Wysokowydajne soczewki optyczne są stosowane w latarniach ulicznych, oświetleniu stadionów i reflektorach samochodowych, zapewniając elastyczność kierunku i skupienia światła.
6. Przemysł lotniczy i obronny
Co więcej, lekkie i odporne na uderzenia przezroczyste materiały są wymagane do wielu zastosowań w przemyśle lotniczym i obronnym, takich jak
- Wysoka przejrzystość optyczna i odporność na zmiany ciśnienia, które są wymagane w oknach samolotów i panelach kokpitu.
- Przezroczyste wizjery do kasków, które chronią tyle, ile widzą oczy.
- Soczewki optyczne do sprzętu obronnego, takiego jak gogle noktowizyjne i dalmierze.
7. Sprzęt optyczny i naukowy
Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne są potrzebne w precyzyjnych zastosowaniach optycznych do dokładnej transmisji światła bez zniekształceń. Przykłady obejmują:
- Co za tym idzie, ich soczewki były używane w mikroskopach i teleskopach, dając duże powiększenie jasnowidzenia.
- Czujniki optyczne i komponenty laserowe są wykorzystywane w badaniach naukowych i automatyce przemysłowej.
- Osłony zapobiegawcze przyrządów laboratoryjnych do ochrony podczas pracy z materiałami niebezpiecznymi.
Przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne formowane wtryskowo są niezastąpione, ze względu na ich wszechstronność i zaawansowane właściwości, w wielu branżach, takich jak medycyna, motoryzacja, elektronika, opakowania, oświetlenie, lotnictwo i kosmonautyka oraz w dziedzinach naukowych, w których innowacje są wspomagane przez dostępność tych tworzyw sztucznych.
Przyszłe trendy w formowaniu wtryskowym przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych
W branży formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych nastąpi znaczny postęp wraz z postępem technologicznym. W nadchodzących latach konieczna będzie poprawa trwałości materiałów, ich zrównoważonego rozwoju i produkcji, a także wydajności produktu. Branża będzie definiowana przez kilka kluczowych trendów, które wymieniono poniżej.
1. Ulepszone innowacje materiałowe
Dziedzina przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych rozwija się w szybkim tempie, aby opracować bardziej trwałe, zrównoważone i funkcjonalne tworzywa sztuczne. Kluczowe innowacje obejmują:
- Automatyczne naprawy drobnych zadrapań wykonanych z samoregenerujących się przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych wydłużają żywotność produktów, takich jak soczewki samochodowe i ekrany smartfonów.
- Wysokowytrzymałe, lekkie kompozyty, które są wysoce przezroczyste i mają kombinację dobrej odporności na uderzenia i pozwalają na odporność na wstrząsy, gdy materiały termoplastyczne są niemożliwe lub trudne do zastosowania.
2. Zaawansowane technologie formowania
Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych podlega różnym nowym technikom produkcyjnym, które umożliwiają większą wydajność i precyzję:
- Integracja z drukiem 3D w celu dostosowania formy do szybkiego prototypowania oraz taniej i masowej produkcji złożonych części, takich jak przezroczysta.
- Optymalizacja formowania w czasie rzeczywistym za pomocą sztucznej inteligencji, zdolna do dynamicznego dostosowywania się w celu powodowania mniejszej liczby defektów, wytwarzania bardziej spójnych produktów i krótszego czasu cyklu.
- Wykorzystywany do formowania wtryskowego wzmocnionego nanotechnologią w tworzeniu tworzyw sztucznych, które były w stanie lepiej wpływać na przejrzystość optyczną, odporność na zarysowania i tolerancję na ciepło.
3. Powłoki odporne na promieniowanie UV i przeciwmgielne
Aby w przyszłości produkować przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne o lepszej funkcjonalności w różnych zastosowaniach, będą one wyposażane w specjalistyczne powłoki.
- Ulepszona ochrona przed promieniowaniem UV, dzięki czemu nie powoduje żółknięcia ani degradacji materiałów narażonych na działanie światła słonecznego, takich jak reflektory samochodowe lub panele oświetlenia zewnętrznego.
- Zapewnia właściwości przeciwmgielne, poprawiając widoczność na szybach samochodowych, urządzeniach medycznych i urządzeniach optycznych.
- Powłoki odporne na zarysowania zwiększające trwałość ekranów smartfonów, okularów, przemysłowego sprzętu ochronnego itp.
4. Inteligentne i funkcjonalne przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne
Ponieważ przezroczysty plastik staje się coraz bardziej pożądany jako materiał wielofunkcyjny, inteligentne technologie, takie jak siatka, zostaną z nim zintegrowane.
- Również czujniki osadzone w przezroczystych tworzywach sztucznych do zastosowań przemysłowych i medycznych do monitorowania temperatury, ciśnienia i narażenia chemicznego w czasie rzeczywistym.
- Cięcia, które umożliwiają formowanie przewodzących przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych do przezroczystych wyświetlaczy elektronicznych i powierzchni wrażliwych na dotyk w urządzeniach nowej generacji.
- A także powłoki samoczyszczące, które wymagają mniej konserwacji w zastosowaniach medycznych, optycznych i motoryzacyjnych.
Jeśli te postępy zostaną osiągnięte, będziemy mieć gwarancję wyraźniejszego formowania wtryskowego tworzyw sztucznych, które z pewnością spełni rosnące wymagania dzisiejszych branż w jeszcze bardziej inteligentny i zrównoważony sposób.
Wnioski
Przezroczyste formowanie wtryskowe tworzyw sztucznych jest ważną funkcją, która przekształciła branże produkcyjne wymagające wysokiej przejrzystości i dokładności. Zaawansowane materiały, takie jak poliwęglan, akryl i optyczna guma silikonowa, umożliwiają producentom projektowanie komponentów, które są lekkie, trwałe i optycznie przejrzyste, zastępując jednocześnie starsze rozwiązania szklane. Wszystko to doprowadziło do rosnącego zapotrzebowania na przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne ze względu na ich zastosowanie w urządzeniach medycznych, oświetleniu samochodowym, elektronice i opakowaniach. Jednak pomimo kwestii takich jak wrażliwość na wilgoć, defekty na powierzchni obiektu i surowe wymagania dotyczące przetwarzania, technologia formowania znacznie się rozwinęła, zwiększając wydajność i poprawiając jakość produktu. Sztuczna inteligencja, druk 3D i nanotechnologia nadal rozwijają technologię, integrując proces na tańszym i bardziej precyzyjnym poziomie, a przenoszenie powłok odpornych na promieniowanie UV i samonaprawiających się tworzyw sztucznych dodatkowo zwiększyło trwałość przezroczystych formowanych produktów.
Przyszłość formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych jest ukierunkowana na zrównoważony rozwój, inteligentne materiały i większe możliwości funkcjonalne. Biodegradowalne i nadające się do recyklingu przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne będą coraz bardziej pożądane przez branże poszukujące przyjaznych dla środowiska alternatyw dla swoich zwykłych produktów. Co więcej, zastosowania w medycynie i elektronice mogą być realizowane za pomocą inteligentnych tworzyw sztucznych, które mają wbudowane czujniki i właściwości przewodzące. Podsumowując, formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych pozostaje bardzo ważną technologią, która wciąż się rozwija i zapewnia kreatywne rozwiązania dla takich branż, jak te, które wymagają przejrzystości, wytrzymałości i estetyki.
Najczęściej zadawane pytania
1. Jakie są najczęściej stosowane materiały w formowaniu wtryskowym przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych?
PMMA jest materiałem o wysokiej przejrzystości optycznej, stosowanym najczęściej, PC dla wysokiej odporności na uderzenia, OSLR dla najwyższej dostępnej przepuszczalności światła, a PP dla półprzezroczystych, najtańszych zastosowań. Wybór każdego materiału jest dokonywany w odniesieniu do jego odpowiednich właściwości i potrzeb przemysłowych.
2. Jakie są główne trudności w formowaniu wtryskowym przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych?
Główne problemy to zapewnienie wysokiej przejrzystości optycznej materiału, brak defektów w postaci pęcherzyków lub smug, radzenie sobie z wrażliwością na wilgoć i powierzchnie odporne na zarysowania. Aby sprostać tym wyzwaniom, wymagane są precyzyjne warunki formowania, dobre suszenie i bardzo dobre formy.
3. Które branże najczęściej korzystają z formowania wtryskowego przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych?
Formowanie wtryskowe przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych jest jednym z podstawowych elementów w branżach produkcyjnych, takich jak zastosowania medyczne (strzykawki, rurki dożylne, sprzęt diagnostyczny) i motoryzacyjne (soczewki reflektorów, osłony deski rozdzielczej), elektronika użytkowa (ekrany smartfonów, panele wyświetlaczy), opakowania (pojemniki spożywcze, butelki kosmetyczne) i oświetlenie (osłony LED, dyfuzory lamp).
4. Jaką rolę odgrywa technologia w formowaniu wtryskowym przezroczystych tworzyw sztucznych?
Usprawnienie procesów dzięki sztucznej inteligencji, druk 3D do dostosowywania form, samoregenerujące się tworzywa sztuczne, ulepszone powłoki odporne na promieniowanie UV poprawiają wydajność produkcji i trwałość produktu. Redukcje te umożliwiają bardziej niezawodne procesy, lepszą wydajność materiałów i bardziej zrównoważone procesy.
5. Czy przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne są przyjazne dla środowiska?
Wydaje się, że tradycyjne przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne z ropy naftowej poprawiły się pod względem zrównoważonego rozwoju, chociaż w ostatnich latach opracowano biodegradowalne i pochodzące z recyklingu przezroczyste tworzywa sztuczne. Producenci badają również alternatywy biologiczne i przyjazne dla środowiska techniki produkcji, aby zmniejszyć wpływ na środowisko.