Messingindsatsernes rolle i sprøjtestøbning af plast
Plastsprøjtestøbning gør brug af messingindsatser for at tilbyde stærke, pålidelige og genanvendelige gevindforbindelser. De præcisionsfremstillede komponenter er indlejret i plastdele for at forbedre den strukturelle pålidelighed, så de kan modstå højere stress- og belastningsforhold. Sammenlignet med andre metaller kan messing bearbejdes, er korrosionsbestandigt og har en god varmeledningsevne, hvilket gør det til et foretrukket materiale til fremstilling af sprøjtestøbeindsatser i forskellige industrier som bilindustrien, elektronik, medicinsk udstyr og rumfart. Forskellige slags messingindsatser er velegnede til forskellige anvendelser. Elektroniske kabinetter og bildele kræver sikker fastgørelse med gevindindsatser; indpresningsindsatser bruges, hvor omkostningerne er vigtigere, og til anvendelser med lav belastning. Varmestøbte og ultralydsindsatser giver stærk fastholdelse ved termisk binding, støbte indsatser giver maksimal styrke ved at blive indkapslet under plaststøbning. Dette inkluderer et format af riflede indsatser, mønstret med riller, der giver et forbedret greb og en bedre udtrækningsmodstand til fastgørelse med høj styrke.
Der kræves særlige teknikker for at installere messingindsatser, så de bliver holdbare og stærke. Trykmontering, varmestikning, ultralydsindsættelse og indstøbningsteknikker gør det muligt at integrere indsatser i plastdele, der er nødvendige for anvendelsen. Afhængigt af materialeegenskaber, belastningskrav og produktionsmængde er der en valgt metode. Der findes et stort udvalg af messingindsatser i forskellige gevindtyper som BSW, UNC, UNF, BSP, NPT og ISO-metrik til forskellige industrielle anvendelser. Af disse grunde er de vigtige komponenter i moderne produktion, og de er korrosionsbestandige og tilbyder overlegen ledningsevne og omkostningseffektivitet. Messingindsatser bruges i vid udstrækning af producenterne af elektroniske stik, medicinsk udstyr og bilkomponenter til at forlænge plastdelenes levetid og pålidelighed betydeligt og er vores bedste løsning til fastgørelse og gentagne samlinger.
Denne artikel handler om messingindsatser til plastsprøjtestøbning, typer af messingindsatser, funktioner, hvordan man installerer messingindsatser, fordele og deres industrielle anvendelser.
Hvad er messingindsatser til plastsprøjtestøbning?
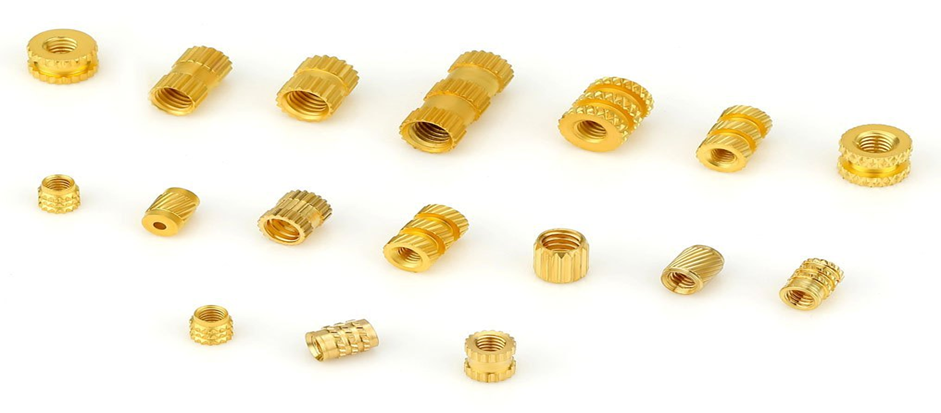

Messingindsatser til plastsprøjtestøbning har et lille, præcisionsfremstillet metal, der placeres i plastdele for sikre gevindforbindelser. Disse indsatse giver bedre udtræksmodstand end andre indsatse ved at gøre det muligt for plastkomponenter at modstå højere stress- og belastningsforhold.
Indsatserne kan være lavet af messing, et fremragende materiale, da det er let at bearbejde, modstandsdygtigt over for korrosion og har en høj varmeledningsevne. Messing er en meget god løsning, der kan tilbyde en perfekt balance mellem styrke og pris sammenlignet med andre metaller. Derfor er messing den bedste løsning til sprøjtestøbning af messingindsatser.
Typer af messingindsatser til sprøjtestøbning
Der findes flere forskellige designs og konfigurationer af messingindsatser, som er velegnede til en bestemt anvendelse. De mest almindeligt anvendte typer er dog:
1. Messingindsatser med gevind

De indvendige gevind på disse indsatser gør det muligt at skrue og montere skruer og bolte i plastkomponenter med en sikker fastgørelse. De bruges typisk i elektroniske kabinetter, bildele og forbrugerprodukter, hvor de ofte skal skilles ad og samles igen.
2. Messingindsats til indpresning
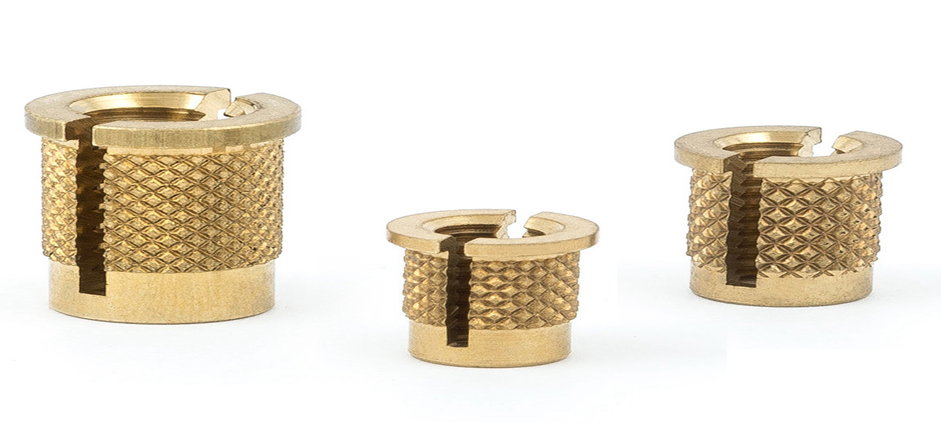

Indpresningsindsatsen anvendes med mekaniske kræfter til at presse indpresningsindsatsen ind i formstøbte eller forborede huller i plastkomponenter. De har en god fastholdelse og er en billig løsning til anvendelser, hvor der ikke kræves en høj udtræksmodstand.
3. Varmeforstærkede messingindsatser

Termisk energi bruges til at installere de varmeforstærkede indsatser, hvor installationen blødgør plasten omkring indsatsen, som derefter kan indlejres sikkert. Når plasten afkøles, bliver indsatsen hårdere og kæmper mod plasten og danner en meget stærk og permanent binding.
4. Ultralydsindsatser i messing
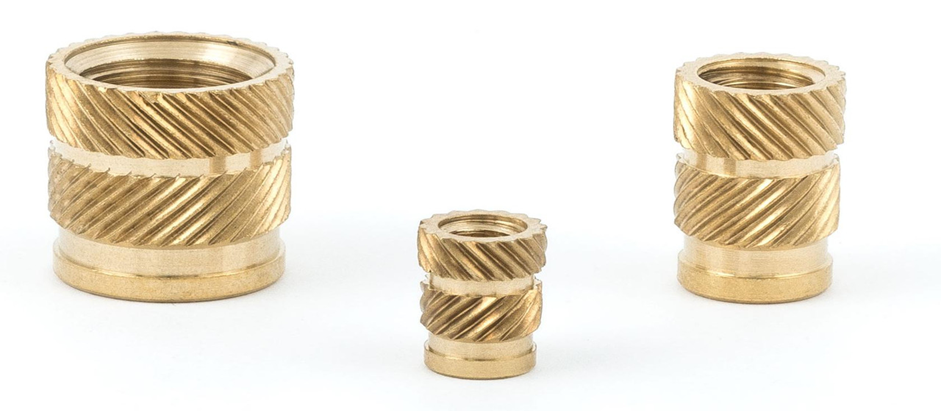

Ultralydsindsættelse bruger højfrekvente vibrationer til at generere varme, der smelter plasten og gør det muligt at indlejre messingindsatsen. Denne måde at danne bindingen på muliggør en meget nøjagtig positionering og et meget godt hold, hvilket især er velegnet til arbejde med høj præcision.
5. Indstøbte messingindsatser
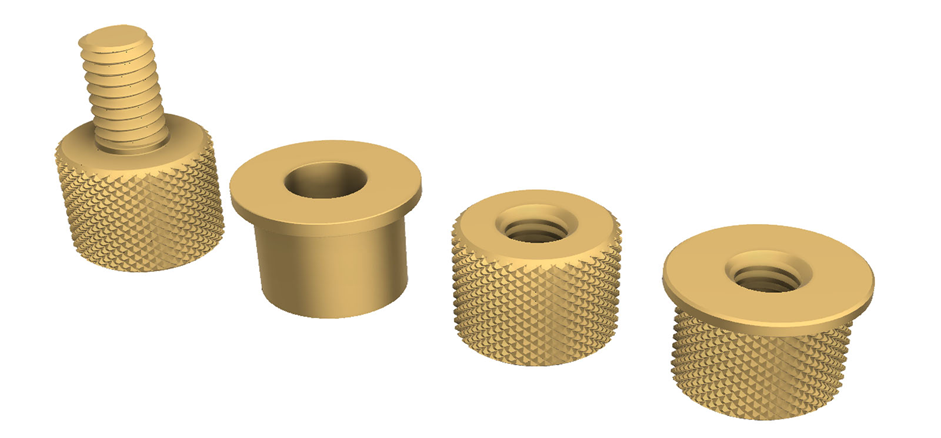
Indstøbte indsatser er placeret på plads inde i sprøjtestøbeformen, hvor plasten sprøjtes på plads. Indsatsen er helt indkapslet i plasten, hvilket giver den maksimal fastholdelse. Denne metode bruges ofte i applikationer til sprøjtestøbning af messingindsatser med den største styrke og holdbarhed.
6. Riflede indsatser

Messingindsatser med et mønster af riller på ydersiden for at forbedre grebet og fastholdelsen inde i plastdele kaldes riflede indsatser. Det er gevind, der i vid udstrækning kan bruges til sprøjtestøbning af plast, hvilket giver sikre, slidstærke indsatser. De er designet til at give bedre udtræksmodstand og er derfor velegnede til fastgørelse med høj styrke i mange industrier.
Trin-for-trin-proces til installation af messingindsatser i plastsprøjtestøbning

Ved sprøjtestøbning af plast er messingindsatser vigtige, da de tilbyder stærke, genanvendelige gevind til fastgørelse. Det er også vigtigt at vælge den rigtige installationsmetode, så installationen holder længe, strukturen bliver stærk, og funktionaliteten bliver passende. Nedenfor finder du en detaljeret trin for trin-guide til, hvordan du installerer messingindsatser ved hjælp af forskellige teknikker.
Metode 1: Installation med presfitting
Dette er den enkleste metode, hvor der bruges mekanisk kraft til at skubbe messingindsatsen ind i et forboret eller støbt hul.
Trin
1. Bor eller støb hullet: Bor eller støb hullet lidt mindre end messingindsatsen, så det sidder tæt.
2. Placer messingindsatsen over hullet, og juster indsatsen.
3. Brug en pressemaskine, en hammer eller en spindelpresse til at tvinge indsatsen på plads. Det fungerer bedst, når man bruger en god portion kraft.
4. Sikker pasform: Indsatsen skal sidde lige mod overfladen og ikke bevæge sig.
Anvendelser: Til hurtige, billige anvendelser, hvor der ikke kræves høj udtræksmodstand.
Yderligere tips
- Sørg for, at hullerne har den rette størrelse, så de ikke sidder løst.
- Brug ikke for stor kraft, da det kan beskadige plasten.
- Denne metode er velegnet til brug i applikationer med lav belastning i forbrugerelektronik og letvægtsplastdele.
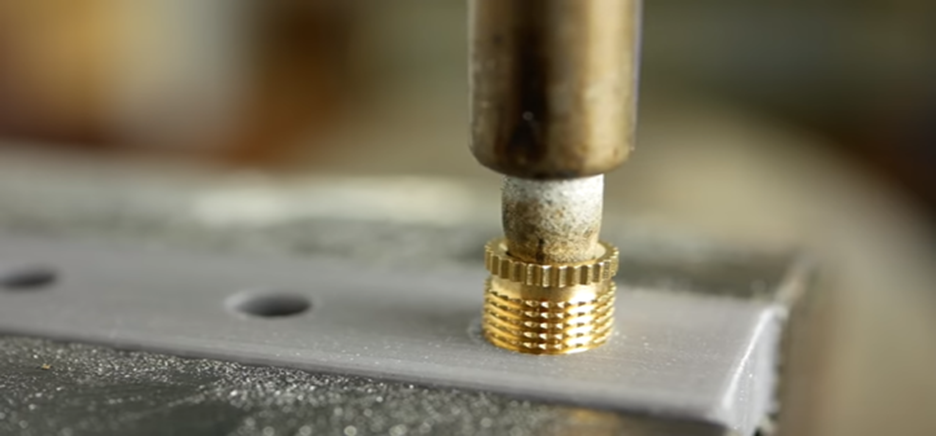
Metode 2: Installation med varmepæle
Varmen blødgør plasten, og messingindsatsen sidder godt fast.
Trin
1. Bor eller støb et hul: Hullets størrelse skal passe til indsatsens størrelse.
2. Varm messingindsatsen op: Man kan bruge en varmemaskine, loddekolbe eller varmepresse til at varme messingindsatsen op.
3. Tryk indsatsen på plads: Tryk forsigtigt den opvarmede indsats ind i den blødgjorte plast.
4. Afkøling: Lad plasten køle af omkring indsatsen for at binde plasten og indsatsen sammen og skabe en stærk, permanent binding.
Det egner sig bedst til opgaver, der kræver stærk fastholdelse og høj udtræksmodstand.
Yderligere tips
- Overophed ikke indsatsen, da for meget varme vil ødelægge plaststrukturen.
- Det er en god metode til bilkomponenter, plastikhylstre og fremstilling af apparater.
- Heat staking giver bedre styrke end pressfitting, men det kræver ekstra udstyr.
Metode 3: Ultralydsindføring
Ultralydsvibrationer bruges til at opvarme plasten til en smeltetemperatur, så plasten smelter og indlejres sikkert.
Trin
1. Forbered hullet: Bor eller støb et hul, der er lidt mindre end messingindsatsen.
2. Indsæt over hullet: Sæt messingindsatsen på hullet.
3. Ultralydsvibrationer anvendes: En ultralydssvejser bruges til at opvarme materiale gennem højfrekvente vibrationer.
4. Den blødgjorte plast indlejrer indsatsen: Plasten flyder rundt om indsatsen.
5. Hærd og afkøl: Når vibrationerne stopper, hærdes plasten for at sikre indsatsen.
Bedst til: Højpræcisionsanvendelser som elektronik, rumfart og medicinsk udstyr.
Yderligere tips
- Den ultrasoniske indsættelsesproces er hurtig og effektiv til produktion af store mængder.
- Det giver en tilsvarende og pålidelig binding til små og sarte dele.
- Frekvensen skal indstilles korrekt for at undgå skader på plasten og for at opnå en ensartet varmefordeling.
Metode 4: Indstøbt installation
Det er den mest sikre metode, da messingindsatser sættes i formen før plastindsprøjtning.
Trin
1. Sæt messingindsatsen i formen: Sæt messingindsatsen i formhulrummet, så indsatsen er placeret korrekt.
2. Plast: Indsatsen sprøjtes ind i plasten, som flyder rundt om den og omslutter den helt.
3. Maksimal fastholdelse: Plasten størkner omkring indsatsen og tillader afkøling.
4. Udskydning af den færdige del: Den færdige plastdel skubbes ud med indsatsen permanent indlejret.
Til: De mest krævende anvendelser, der kræver den højeste grad af fastholdelse.
Yderligere tips
- Justering af indsatsen i formen er kritisk og skal udføres korrekt.
- Den højeste styrke og udtræksmodstand opnås med indstøbte indsatser, men de øger formens kompleksitet.
- Denne metode bruges ofte i industrimaskiner, i luft- og rumfart og i bilindustrien.
Egenskaber ved sprøjtestøbeindsatser af messing
Messingindsatserne findes i flere gevindtyper, størrelser og riflede mønstre til forskellige industrielle anvendelser. Nogle af de vigtigste funktioner er:
- Fremstillet af messing af høj kvalitet: Fremstillet af messing af høj kvalitet for at gøre dem holdbare, endda modstandsdygtige over for korrosion og meget ledende til langvarig brug.
- Præcisionsgevind: Leveres i metriske, UNC, UNF, BSW, BA, BSP, metriske ISO- og DIN-standarder, så de passer perfekt til en række fastgørelsesspecifikationer.
- Alsidig til sprøjtestøbning, rotationsstøbning, PVC-sprøjtestøbning og gummistøbning.
- Tilpasning af design: Kan tilpasses kundens behov med hensyn til design, prøver og dimensionskrav i de forskellige brancher.
- Fine rifler, diamantmønstre, diagonal, omvendt kryds osv. - For at give en stærk fastholdelse og et godt greb har produkterne fine riller, diamantmønstre, diagonale og omvendte kryds osv.
- Udviklet med høj bæreevne - indsatsen kan modstå høj belastning, perfekt til barske miljøer, som bilindustrien og industrielle applikationer kræver.
Messingindsatser er det perfekte valg til sådanne anvendelser på grund af disse egenskaber.
Messingindsatser Gevindstørrelser
Denne tabel indeholder oplysninger om gevindstørrelser for messingindsatser.
| Trådtype | Imperiale størrelser (tommer) | Metriske størrelser (millimeter) |
| BSW (British Standard Whitworth) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| UNC (Unified National Coarse) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| UNF (forenet national bøde) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| BSP (britisk standardrør) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| NPT (nationalt rørgevind) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| NPS (National Pipe Straight) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
| ISO-metrisk (internationale standardgevind) | 1/8″, 5/32″, 3/16″, 1/4″, 5/16″, 3/8″, 1/2″, 3/4″ | 3 mm, 4 mm, 5 mm, 6 mm, 8 mm, 10 mm, 12 mm |
Tabellen viser messingindsatsens gevindstørrelser, som omfatter britiske og metriske målestandarder, i et klart struktureret format.
Fordele ved at bruge messingindsatser til sprøjtestøbning

1. Forbedret styrke og holdbarhed
Levetiden for plastgevind reduceres med tiden, indtil det forårsager driftssvigt. Den stærke, holdbare gevindløsning fra sprøjtestøbte plastindsatser kan fungere gentagne gange og samtidig bevare sin oprindelige kvalitet.
2. Overlegen korrosionsbestandighed
Messing har en naturlig korrosionsbestandighed, som gør det velegnet til enheder, der skal fungere under fugt- og kemikalieeksponering og barske miljøforhold. Materialet forbliver pålideligt, mens det præsterer på høje kvalitetsniveauer på grund af dets holdbarhedsegenskaber.
3. Forbedret termisk og elektrisk ledningsevne
Behovet for elektrisk og termisk ledning i produktionen får producenterne til at bruge messingindsatser som deres foretrukne materiale under sprøjtestøbning. Messingens elektriske og termiske ledningsegenskaber gør det til et optimalt materialevalg til fremstilling af digitale elementer og sensorer til biler samt industrielle systemer.
4. Reduceret stress på plastkomponenter
Messingindsatser fordeler plastdelens stress jævnt og beskytter derfor mod lokale skader, der kan forårsage revner. Komponenten får en længere levetid, samtidig med at den opretholder en ensartet ydeevne takket være messingindsatserne.
5. Nem montering og demontering
Kombinationen af messingindsatser skaber et sikkert fastgørelsessystem, som beskytter plastmaterialet mod skader. Applikationerne drager fordel af denne metode, fordi de har brug for konstant samling af komponenter og vedligeholdelsesopgaver eller procedurer for udskiftning af komponenter.
6. Omkostningseffektivitet
Omkostningerne ved at bruge messingindsatser til sprøjtestøbning er fortsat overkommelige, selv om deres ydeevne overgår forventningerne. Kombinationen giver en overkommelig forbedring af produktstyrken, samtidig med at de fleste produktionsomkostninger bevares.
Installationsmetoder til sprøjtestøbning af messingindsatser
Proceduren for installation af messingindsatser afhænger af flere faktorer, der omfatter de nødvendige anvendelser sammen med materialets egenskaber og produktionsmængder. Du kan finde tre grundlæggende installationsmetoder, der bruges til sprøjtestøbning af messingindsatser.
1. Varmestakning
En forvarmet messingindsats presses ind i en forboret åbning i plastkomponenten. Messingindsatserne opnår i sidste ende en stærk binding med plasten gennem nedkøling, og processen skaber en høj fastholdelsesstyrke.
2. Ultralydsindføring
Ultralydsindsættelse anvender højfrekvente lyde til at skabe begrænsede termiske effekter, som blødgør plastmaterialet, før messingindsatsen placeres i plastkomponenten. Indsættelsesteknikken muliggør nøjagtig positionering, og den har mange anvendelser inden for sprøjtestøbning af messingindsatser til elektronik og medicinsk udstyr.
3. Press-fitting
Ved presmontering skal operatørerne bruge manuel kraft til at drive messingindsatser ind i de ønskede huller, som er forberedt på forhånd. Denne enkle procedure er både budgetvenlig og velegnet, da den ikke kræver kraftig udtræksmodstand.
4. Støbt indføring
Indstøbning er den mest sikre metode, da messingindsatsen placeres inde i formen, før plastindsprøjtningen begynder. Når indsætningsmetoden anvendes, dækker plastmaterialet og omgiver indsatsen fuldstændigt for at opnå den stærkeste holdeevne.
Valg af messingindsatser til sprøjtestøbning af plast
Valget af den rigtige messingindsats til din applikation er et ret komplekst valg, og du skal have flere ting i tankerne, når du vælger.
1. Design af gevind
Vælg en indsats med den korrekte gevindtype og stigning til din anvendelse. Da fine gevind giver bedre greb, giver grove gevind bedre installation.
2. Indsatsens størrelse og form
Indsatsen skal have en størrelse og form, der passer til plastkomponenten og til installationsmetoden. Forestil dig, at du skal tage hensyn til faktorer som vægtykkelse, huldiameter og delgeometri.
3. Kompatibilitet mellem materialer
Messingindsatsen skal være egnet til brug med den type plast, der bruges til støbning. Plast med lavt smeltepunkt kan også få lavet indsatser for at beskytte denne plast mod at blive beskadiget under installationen.
4. Bærende kapacitet
Messingindsatsens mekaniske egenskaber fra udtræksstyrke, momentmodstand til forskydningsstyrke vil blive vurderet. Vælg en indsats, der opfylder applikationens strukturelle krav.
5. Miljømæssige forhold
Vurder plastkomponentens omgivelser. Hvis komponenten f.eks. er udsat for fugtige kemikalier eller høje temperaturer, skal du vælge korrosionsbestandige messingindsatser med en passende belægning.
Anvendelser af messingindsatser i sprøjtestøbning
Messingindsatser til plastsprøjtestøbning er vigtige elementer, da de giver forbedret styrke, korrosionsbestandighed og holdbarhed til det endelige produkt. Indsatserne finder bred anvendelse i de industrier, hvor der er brug for sikre, langsgående gevindforbindelser. De er uundværlige på grund af deres evne til at styrke plastkomponenter ved at give dem stærke fastgørelsesløsninger. Længere nede diskuterer jeg nogle anvendelser i forskellige brancher.
1. Bilindustrien
I BilindustrienMessingindsatser har mange anvendelsesmuligheder og indgår i strukturelle såvel som funktionelle plastkomponenter. Høj styrke, vibrationsmodstand og pålidelighed gør disse indsatser til højtydende dele til bilindustrien.
Almindelige anvendelser
- Paneler til instrumentbræt: For at give en fast montering af digitale displays og instrumentgrupper.
- Sensorhuse: Leverer stabile, vibrationsresistente monteringspunkter til bilsensorer i motor- og sikkerhedssystemer.
- Motordæksler: Forbedrer holdbarheden og varmebestandigheden af plastmotorkomponenter.
- Indvendige trimkomponenter: bruges til at skrue indvendige paneler, betjeningsenheder og knapper sammen, så de holder længe.
- Sørg for, at fittings på brændstofpumper, filterhuse og injektorens komponenter sidder godt fast.
2. Elektronik og elektriske komponenter
Fordi messingindsatser har en fremragende ledningsevne med høj slidstyrke, bruges de i vid udstrækning i elektronik og elektriske applikationer. De giver stærk mekanisk støtte og giver også mulighed for pålidelige elektriske forbindelser i plastkabinetter.
Almindelige anvendelser
- Circuit Board Mounts, som fastgør printkort til plastikhuse, så de ikke kan bevæge sig eller blive beskadiget.
- Stikkontakter: Nogle elektriske stik giver stabile og ledende forbindelser.
- Huse til elektriske kontakter: Leverer stærk støtte til elektriske kontakter, der kan modstå hård brug.
- Batterirum: Disse er skabt til at lave en stærk batteriboks i fjernbetjeninger og elværktøj.
- Sikker fastgørelse af plastkabinetter til elektriske distributionssystemer som f.eks. strømfordelingsenheder.
3. Medicinsk udstyr
Messingindsatser lavet af plastkomponenter vil blive brugt til styrke, præcision og holdbarhed i den medicinske industri. Disse indsatser gør det muligt for designet at opfylde strenge sikkerheds- og hygiejnestandarder som i medicinske applikationer.
Almindelige anvendelser
- Kirurgiske værktøjer: Opnå sikre gevindforbindelser, der anvendes i kirurgiske plastinstrumenter, som skal steriliseres og genbruges.
- Diagnostisk udstyr: Bruges i ultralydsmaskiner, CT-scannere og laboratorieudstyr til sikker montering.
- Proteser: Sikrer stærke forbindelser i plastikproteser og medicinske implantater.
- Medicinsk følsom elektronik, som skal placeres i forskellige kabinetter, der kræver en holdbar fastgørelse, f.eks. EKG-monitorer og infusionspumper.
- Sikring af plastkomponenter, der hjælper med at holde på centrifuger, mikroskoper og udstyr til prøvetestning.
4. Forbrugerprodukter
Forbrugsvarer er i høj grad afhængige af brugen af messingindsatser, som giver langvarige, pålidelige fastgørelsesløsninger for at forhindre, at plastkomponenter bliver påvirket med tiden. Derudover har de god korrosionsbestandighed og holdbarhed til hverdagsprodukter.
Almindelige anvendelser
- Plastkabinetter: Bruges i elektroniske gadgets, beskyttelsesetuier og værktøjshuse af plast.
- Hvidevarer til hjemmet: Vaskemaskine, køleskab, støvsuger for at sikre kontrolpaneler og delbevægelser.
- De kan bruges til at samle batterirum og bevægelige dele i børnelegetøj.
- Beslag til møbler: Sørg for stærke forbindelser i plastdele af modulære møbler og skabe.
- Sportsudstyr: Forbedrer styrken af plastkomponenter i træningsudstyr og beskyttelsesudstyr.
5. Luft- og rumfartsindustrien
I luft- og rumfartsapplikationer bruges de lette, stærke og vibrationsresistente fastgørelsesløsninger, messingindsatser. De hjælper med at forbedre sejheden af plastkomponenter, der bruges i højtydende flysystemer.
Almindelige anvendelser
- Flyets indvendige komponenter: Fastgørelser, der er låst gennem indvendige plastpaneler, sæder og kabinebeslag.
- Kontrolpaneler: Disse leverer gevind-/trykforbindelser til knapper, kontakter og paneler til instrumentering.
- Kommunikationsudstyr: Bruges i radio- og satellitkommunikationssystemer til stærke elektriske og mekaniske forbindelser.
- GPS og flyvekontrol: Stabil montering af plastkomponenter i GPS- og flystyringsenheder.
- Satellitkomponenter: Bruges i lette, men holdbare plastkomponenter i rumforskningssystemer.
Konklusion
Blandt de vigtige elementer i plastsprøjtestøbning er messingindsatserne, som forbedrer styrken, giver mere sejhed mod korrosion og viser lang levetid. Ved at tilbyde sikre og genanvendelige gevind forhindrer de plastdele i at blive slidt, hvilket muliggør forlænget produktlevetid og pålidelige produkter. Der findes forskellige former for messingindsatser, f.eks. med gevind, riflede, indpressede, varmeforstærkede og indstøbte, så producenten kan vælge det, der passer bedst til deres anvendelse.
Fastholdelse og udtrækningsmodstand mod mekanisk svigt opnås ved at installere messingindsatser ved hjælp af presmontering, varmestikning, ultralydsindsættelse eller indstøbte metoder. Disse indsatser aflaster plastdele ved at sprede dem bedre og mindske risikoen for revner eller deformation. Desuden har de en fremragende termisk og elektrisk ledningsevne, som gør dem velegnede til brug i elektronik, medicinsk udstyr og rumfartsindustrien.
Når industrier er i hastig forandring, bliver behovet for højere ydeevne og prisvenlige løsninger ikke mindre. Den perfekte kombination af omkostningsejerskab og styrke gør messing til de foretrukne indsatser for producenter verden over. Messingindsatser bruges stadig i applikationer med høj præcision eller stor belastning, hvilket gør dem til en vigtig del af moderne produktion.
Ofte stillede spørgsmål
1. Messingindsatser bruges til sprøjtestøbning af plast.
Brug af messingindsatser giver stærke genanvendelige gevind i plastkomponenter, der forbedrer deres levetid og sikrer fastgørelse i bilindustrien, elektronikindustrien og industrien for medicinsk udstyr.
2. Hvad er den anvendte nomenklatur for messingindsatser?
Der findes flere typer messingindsatser, f.eks. gevindindsatser, indpresningsindsatser, varmeindsatser, ultralydsindsatser, indstøbte indsatser og riflede indsatser, der bruges til specialiserede anvendelser og installationsmetoder.
3. Hvad er grundene til at bruge messingindsatser i stedet for plastgevind?
Overlegen styrke, korrosionsbestandighed og slidstyrke tilbydes af messingindsatser i modsætning til plastgevind, hvilket gør det holdbart at holde længe uden at kræve gentagen montering og demontering.
4. Hvordan indsættes messingindsatser i plastdele?
Forskellige teknikker til at installere messingindsatser er presmontering, varmestikning, ultralydsindsættelse og støbning af dem i plastdele under sprøjtestøbningsprocessen.
5. Hvornår bruges messingindsatser i industrien?
Stærke og pålidelige gevindforbindelser er efterspurgt i mange industrier, herunder bilindustrien, elektronik, rumfart, medicinsk udstyr og forbrugerprodukter, hvor messingindsatser er meget udbredte.












Skriv en kommentar
Vil du deltage i diskussionen?Du er velkommen til at bidrage!