Formowanie wtryskowe akrylu: Kluczowy proces w nowoczesnej produkcji
W dzisiejszych czasach czas ma kluczowe znaczenie w szybko zmieniającym się świecie produkcji, akryl formowanie wtryskowe zapewnia precyzję, trwałość i wydajność na najwyższym możliwym poziomie. Jak sugeruje powszechna nazwa, akryl (lub polimetakrylan metylu (PMMA)) jest wysoko ceniony za wyjątkową przezroczystość, wytrzymałość i wytrzymałość, i stał się podstawowym materiałem stosowanym w przemyśle motoryzacyjnym, lotniczym, medycznym i elektroniki użytkowej. Dzięki akrylowemu formowaniu wtryskowemu można konsekwentnie formować doskonałe właściwości optyczne, odporność na warunki atmosferyczne i wytrzymałość mechaniczną precyzyjnych komponentów. Od osłon świateł samochodowych i obudów medycznych po wysokiej klasy soczewki optyczne, a nawet niestandardowe oznakowanie, formowane produkty akrylowe zmieniają współczesne innowacje. Jednak proces ten można opanować tylko dzięki doświadczeniu w zakresie zachowania materiału, projektowania form i optymalizacji procesu, ponieważ proces ten wiąże się z wyzwaniami, które należy rozwiązać, takimi jak kruchość, skurcz i czas chłodzenia.
W tym artykule omówimy zawiłości procesu formowania wtryskowego akrylu, z jego procesem, zastosowaniem, zasadami projektowania, zaletami, a także przyszłymi trendami. Zastosowanie formowania opartego na sztucznej inteligencji, a także wykorzystanie zrównoważonych materiałów i form do druku 3D szybko kształtuje przyszłość produkcji akrylu w nowych obszarach zastosowań, jeśli chodzi o wysokowydajne rozwiązania z tworzyw sztucznych.
Zrozumienie formowania wtryskowego akrylu

Formowanie wtryskowe akrylu to proces podgrzewania żywicy akrylowej do stanu stopionego za pomocą ciepła, a następnie wtryskiwania jej pod wysokim ciśnieniem do formy, tworząc części. W przypadku produkcji wielkoseryjnej proces ten jest szeroko stosowany w celu uzyskania spójności projektu, dokładności i jakości.
Kluczowe etapy formowania akrylu

Przygotowanie materiałów: Wilgoć zawarta w granulacie akrylowym jest usuwana, dzięki czemu granulat wysycha i może być formowany bez wad.
Topienie i wtryskiwanie: W drugim przypadku granulki są wprowadzane do gniazda formy, gdzie są podgrzewane do temperatury 200-250°C.
Chłodzenie i krzepnięcie: Gdy akryl nabierze kształtu, forma jest schładzana.
Wyrzucenie produktu: Forma jest otwierana i uwalniana jest gotowa część.
Przetwarzanie końcowe: Nie jest to kształt produktu, ale raczej wykończenie powierzchni, polerowanie lub powlekanie, które poprawia wygląd i funkcjonalność produktu.
Różne właściwości akrylu
Wspomnieliśmy wcześniej o kilku ważnych cechach akrylu, takich jak odporność na ścieranie i udarność. W tej części zagłębimy się w jego właściwości, aby ich natura nie była zagadką dla osoby zainteresowanej poznaniem, dlaczego akryl jest tak przydatny w produkcji.
Ogólne właściwości akrylu
Gęstość: 1,19 g/cm³
Twardość Rockwella: M 102
Absorpcja wody: 0.2%
Klasa palności: UL94 HB, klasa 3 (BS 476 część 7)
Ten akryl jest lekki, ale jest bardzo wytrzymałym tworzywem sztucznym. Dobra odporność na uderzenia w porównaniu z tradycyjnym szkłem pozwala mu być mniej podatnym na rozbicie. Co więcej, akryl jest materiałem słabo przewodzącym ciepło, dzięki czemu może być stosowany jako doskonały izolator termiczny. Akryl jest nie tylko odporny na ciepło, ale także chroni przed promieniami UV, co oznacza, że byłby odpowiednim wyborem do zastosowań na zewnątrz, gdzie jest narażony na działanie promieni słonecznych.
Właściwości optyczne akrylu
Transmisja światła: Ponad 92%
Współczynnik załamania światła: 1.49
Przejrzystość akrylu jest jednym z głównych powodów, dla których jest on tak szeroko wykorzystywany w zastosowaniach optycznych. Jeśli chodzi o przezroczystość dla światła, przepuszcza on ponad 92 procent światła widzialnego, co odpowiada doskonałemu szkłu. Stosowany w technikach polerowania mechanicznego lub parowego, staje się polerowany jak kryształy i staje się dobrym wyborem dla obiektywu, światłowodu, panelu wyświetlacza. Akryle o wysokiej przejrzystości to popularne marki akrylowe, takie jak Perspex, Rohm Plexiglas itp.
Właściwości mechaniczne akrylu
Wytrzymałość na rozciąganie: Około 8000 psi
Moduł rozciągania: 350 000 - 500 000 psi
Moduł sprężystości: Podobnie jak moduł sprężystości przy rozciąganiu
Akryl jest również mocnym i sztywnym tworzywem termoplastycznym, które może wytrzymać duże obciążenia mechaniczne. Jego wytrzymałość na rozciąganie wynosi około 8000 psi, więc pęknięcie materiału wymagałoby 8000 funtów na cal kwadratowy. Wysoka wartość modułu sprężystości wskazuje również, że akryl może być stabilny strukturalnie pod wpływem sił zginających i rozciągających. Jest również wodoodporny i odporny na promieniowanie UV, co czyni go lepszym wyborem do znaków zewnętrznych, osłon ochronnych i części samochodowych.
Właściwości termiczne akrylu
Minimalna temperatura pracy: -40°C
Maksymalna temperatura pracy: 80°C
Punkt zmiękczania: Powyżej 110°C
Liniowy współczynnik rozszerzalności: 7.7 × 10-⁵
Akryl ma temperaturę topnienia od 130° C do 140° C, a jego maksymalna temperatura pracy wynosi od 65° C do 93° C. Dzięki temu może wytrzymać umiarkowanie wysokie temperatury, ale pod wpływem nadmiernego ciepła ulegnie deformacji lub zmiękczeniu. Ze względu na niską przewodność cieplną, akryl działa jako skuteczny izolator termiczny. Jest również łatwo formowalny, gdy jest gorący i stosowany jako materiał termoformowany, a także jako materiał do formowania wtryskowego i procesu produkcji.
Zastosowania akrylowego formowania wtryskowego
Formowanie wtryskowe akrylu jest znaną metodą produkcji drobnych, trwałych i wysokiej jakości komponentów w różnych branżach. Producenci wtryskują stopiony akryl do formy, aby stworzyć części, które są zarówno bardzo przezroczyste, jak i mocne, a także odporne na warunki atmosferyczne. Poniżej przedstawiono niektóre kluczowe zastosowania formowania akrylowego.
1. Komponenty optyczne
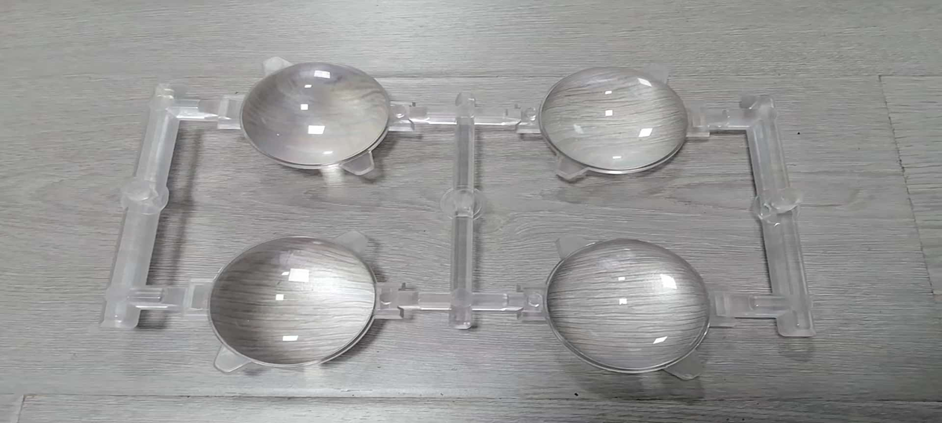

Ponieważ akryl charakteryzuje się wysoką przepuszczalnością światła i przejrzystością optyczną, jest przydatny w produkcji soczewek, filtrów optycznych i osłon świetlnych. Stanowi on tanią alternatywę dla szkła i jest trwały, a także odporny na uderzenia w różnych zastosowaniach optycznych.
2. Oznakowanie i wyświetlacze

Formowanie akrylowe jest rodzajem plastiku używanym w wielu reklamach i produkcji wyświetlaczy. Ze względu na jego zdolność do formowania złożonych kształtów i przenoszenia światła, są one powszechnie stosowane w podświetlanych znakach, panelach wystawowych i elementach oznakowania ozdobnego.
3. Produkty konsumenckie

Akrylowe formowanie wtryskowe jest często stosowane w przedmiotach codziennego użytku, takich jak akcesoria domowe, przedmioty dekoracyjne i zabawki. Z punktu widzenia trwałości, estetyki i odporności na zużycie jest to preferowany materiał w branży dóbr konsumpcyjnych.
4. Komponenty motoryzacyjne

W przemyśle motoryzacyjnym wewnętrzne dopasowanie i wykończenie elementów wykończenia wnętrza, paneli deski rozdzielczej, osłon świateł i akcentów zewnętrznych odbywa się za pomocą akrylowego formowania wtryskowego. Jest to wspaniały materiał do pracy ze względu na jego odporność na ciepło, promieniowanie UV i uderzenia oraz jest idealnym materiałem funkcjonalnym i projektowym.
5. Sprzęt medyczny
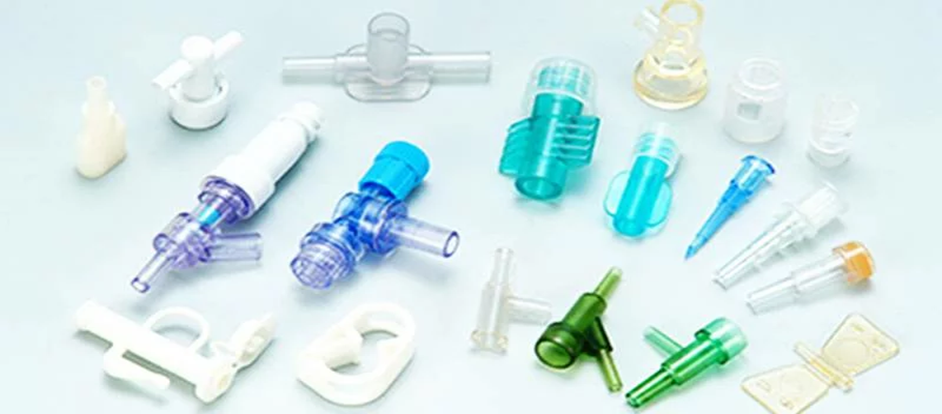

Obudowy medyczne, sprzęt diagnostyczny i osłony ochronne mogą być wykonane z akrylu ze względu na jego przejrzystość, biokompatybilność i odporność na ataki chemiczne. W zastosowaniach medycznych, gdzie wytrzymałość i przezroczystość współistnieją, jest on używany.
Formowanie wtryskowe akrylu nadal pozostaje ważnym procesem ze względu na wszechstronność, koszt i precyzję, jaką oferuje.
Zarządzanie temperaturą w formowaniu wtryskowym akrylu
- Zmienność powłoki w akrylowym formowaniu wtryskowym zależy od właściwego zarządzania temperaturą. Akryl ma zakres topnienia 130-140°C i może pracować w krótkich okresach temperatury od 65-93°C. Jako izolator jest znany z łatwego formowania na gorąco i niskiej przewodności cieplnej.
- Kolejną ważną kwestią jest suszenie materiału przed obróbką. Współczynnik absorpcji wody dla akrylu wynosi 0,3-0,4%, a nadmiar wilgoci może tworzyć pęcherzyki, linie gazowe i zmniejszać przejrzystość produktu końcowego. Następnie akryl jest suszony, aby utrzymać poziom wilgotności poniżej 0,1 lub jeszcze lepiej poniżej 0,04%.
- Jakość produktu i czas cyklu w dużym stopniu zależą od temperatury topnienia. Akryl, podobnie jak inne tworzywa termoplastyczne, topi się w zakresie 130-140°C, a dokładna temperatura powinna być ściśle kontrolowana, aby pozostać po właściwej stronie wydajności formowania w stosunku do trwałości części matrycy.
Co więcej, stabilność wymiarowa i jakość powierzchni gotowego produktu zależy również od temperatury formy. Poniżej przedstawiono trzy najlepsze praktyki dotyczące optymalnej temperatury formy.
Używaj systemu kontroli temperatury: Forma otrzymuje precyzyjny system sterowania, który zapewnia stałą dystrybucję ciepła do całej formy.
Regularnie monitoruj temperaturę: Pomaga w przypadku wypaczenia, skurczu lub niedoskonałości powierzchni, sprawdzając i dostosowując temperaturę formy.
Optymalizacja kanałów chłodzenia: Dzięki odpowiednio zaprojektowanym kanałom chłodzącym dostępne są wysokie wydajności cieplne do usuwania ciepła, skracania czasów cykli, a także zapewniania równomiernego chłodzenia.
Dodatkowe uwagi dotyczące formowania akrylu

Oprócz kontroli temperatury, należy wziąć pod uwagę temperaturę ugięcia ciepła, spawanie ultradźwiękowe i koszt formy, aby jeszcze bardziej poprawić jakość produktu i wydajność produkcji.
Temperatura ugięcia cieplnego (HDT)
HDT akrylu mieści się w zakresie od 80 do 100°C, co oznacza, że odkształcenie rozpoczyna się w tym punkcie temperatury, ale pod obciążeniem. Jednak prawa wymiany ciepła ograniczają maksymalne dopuszczalne temperatury przetwarzania poniżej HDT w celu uzyskania dokładności wymiarowej i przejrzystości optycznej.
Spawanie ultradźwiękowe
Spawanie ultradźwiękowe to niezawodny proces w przypadku wielu części akrylowych. Aby wytworzyć ciepło, proces ten wykorzystuje fale dźwiękowe o wysokiej częstotliwości do łączenia komponentów, z niewielkimi lub żadnymi widocznymi śladami, co czyni go idealnym do stosowania na częściach LFT.
Koszt pleśni
Akrylowe formy wtryskowe są drogie ze względu na złożoność, dobór materiałów i wymagania projektowe. Harmonizacja tego ogólnego celu polega na zmniejszeniu kosztów, które producenci mogą osiągnąć, projektując lub wybierając uproszczone projekty części, używając komponentów formy więcej niż jeden raz i wykorzystując odpowiednie materiały formy.
Kwestie środowiskowe i zdrowotne
Nowoczesne wtryskarki zużywające od 20 do 50 procent mniej energii elektrycznej niż starsze maszyny są energooszczędne, ale zużycie energii elektrycznej nadal stanowi zagrożenie dla środowiska. Formowanie akrylowe może wytwarzać niebezpieczne opary, jeśli nie jest odpowiednio zarządzane, i nie kończy się w szafce, jeśli nie zostanie wypłukane, a tył nie zostanie odcięty, dzięki czemu cząsteczki pyłu mogą potencjalnie zostać wepchnięte do płuc. Systemy wentylacyjne, środki kontroli oparów i odpowiednie zabezpieczenia powinny być również stosowane w celu zapewnienia bezpieczeństwa pracowników w zakładach produkcyjnych.
Alternatywne materiały w formowaniu wtryskowym
Akryl jest jednym z materiałów, które są powszechnie stosowane ze względu na przejrzystość optyczną i trwałość, ale nie jest to jedyny materiał.
Poliwęglan (PC)
Bardziej odporny na uderzenia niż akryl, dzięki czemu idealnie nadaje się do sprzętu ochronnego i części samochodowych. Nie jest jednak przezroczysty jak akryl.
ABS (Akrylonitryl-butadien-styren)
Tworzywo sztuczne o dobrej wytrzymałości i podatności na formowanie, ale o niskiej przejrzystości optycznej, które jest zarówno tanie, jak i łatwe w obróbce. Powszechnie stosowany w częściach samochodowych, zabawkach i urządzeniach.
Polipropylen (PP)
Odporny na chemikalia i elastyczny, jest popularną opcją do zastosowań w opakowaniach i towarach konsumpcyjnych. Po drugie jednak, nie jest przezroczysty jak akryl.
ASA (akrylonitryl styrenu)
Odporność na promieniowanie UV i warunki atmosferyczne zapewnia możliwość stosowania na zewnątrz.
COC (cykliczny kopolimer olefin)
Niska absorpcja wody; odporność chemiczna; znany z zastosowań medycznych i optycznych.
PCT (politereftalan cykloheksylenodimetylenu)
Oferuje wysoką odporność na ciepło i przejrzystość optyczną, która jest powszechnie stosowana w oświetleniu samochodowym.
Każdy z tych materiałów ma unikalną wytrzymałość, przezroczystość i czynniki środowiskowe, a właściwy wybór zależy od tego, który z nich ma być używany w zamierzonym zastosowaniu.
Wytyczne projektowe dotyczące formowania wtryskowego akrylu
Niemniej jednak, podczas projektowania z wykorzystaniem akrylu ważne jest przestrzeganie standardowych zasad projektowania, aby uniknąć wad części akrylowych i osiągnąć maksymalną wydajność produkcji. Wysokiej jakości trwałe komponenty opierają się na odpowiedniej grubości ścianek, promieniach, kątach pochylenia i tolerancjach. Poniżej przedstawiono szereg kluczowych kwestii związanych z projektowaniem form akrylowych.
Grubość ścianki
Grubość ścianek części akrylowych powinna wynosić od 0,025 cala (0,635 mm) do 0,150 cala (3,81 mm), zgodnie z zaleceniami. Nie ma tolerancji dla niespójności w grubości ścianek, ponieważ zmiana (nagła lub stopniowa) może powodować wady, takie jak wypaczenia, ślady zatopienia lub naprężenia wewnętrzne.
Promienie i narożniki
Szybkie spojrzenie na akryl pokazuje, że jest on podatny na koncentrację naprężeń w ostrych narożnikach. Narożniki o minimalnym promieniu 25% grubości ścianki powinny być stosowane w celu poprawy formowalności i integralności strukturalnej. Najlepszym promieniem dla zwiększenia wytrzymałości jest 60% grubości ścianki.
Kąty zanurzenia
Zanurzenie między 0,5° a 1° jest niezbędne do uzyskania płynnego wyrzutu z formy. Jeśli część ma polerowane lub optycznie przezroczyste powierzchnie, może być potrzebny większy kąt zanurzenia, aby zachować jakość.
Tolerancje części
Tolerancje formowania wtryskowego akrylu dla rozmiaru części i wymagań dotyczących precyzji są następujące:
- Dla części do 160 mm tolerancje handlowe wynoszą od 0,1 mm do 0,325 mm.
- Dokładne tolerancje: 0,045 mm do 0,145 mm dla części 100 mm lub mniejszych.
Przestrzeganie tych zasad projektowania zapewnia precyzję, trwałość i optymalną wydajność formy do formowania tworzyw akrylowych.
Rodzaje form akrylowych i ich znaczenie
Formy jednogniazdowe vs. formy wielogniazdowe
Formy jednokomorowe: Niskonakładowa produkcja jest odpowiednia dla dobrej precyzji i możliwości dostosowania.
Formy wielokomorowe: Aby spełnić wymóg masowej produkcji w krótszym czasie i przy niższych kosztach dla każdej wyprodukowanej jednostki.
Formy gorącokanałowe a zimnokanałowe
Formy do gorących kanałów: Minimalizacja odpadów i poprawa wydajności dzięki utrzymywaniu stopionego akrylu wewnątrz systemu.
Formy do pracy na zimno: Bardziej opłacalna, ale nadmierna produkcja materiałów, co wymaga przycinania i recyklingu.
Niestandardowe formy akrylowe do produkcji specjalistycznej
Producenci mogą jednak wykorzystywać niestandardowe formy do produkcji złożonych projektów o wąskich tolerancjach, gwarantując, że elementy akrylowe są wytwarzane zgodnie z określonymi specyfikacjami wymaganymi w sektorze lotniczym i medycznym.
Zalety i wyzwania związane z formowaniem tworzyw akrylowych
Zalety formowania akrylowego
Wyjątkowa przejrzystość: Doskonałym substytutem szkła jest akryl, który charakteryzuje się nawet 92-procentową przezroczystością.
Lekki i wytrzymały: Szkło jest dwa razy cięższe niż akryl, ale nadal jest bardzo wytrzymałe.
Odporność na warunki atmosferyczne i promieniowanie UV: Chociaż niektóre tworzywa sztuczne żółkną lub ulegają degradacji, akryl tego nie robi.
Konfigurowalne właściwości: Poza tym akryl może być barwiony, powlekany lub modyfikowany do różnych zastosowań.
Wyzwania związane z formowaniem akrylu
Kruchość w porównaniu do poliwęglanu: Chociaż PC jest mniej odporny na uderzenia niż akryl, wytrzyma znacznie większy nacisk przed pęknięciem.
Kontrola skurczu: Jeśli zarządzanie temperaturą nie jest bardzo precyzyjne, mogą wystąpić wypaczenia i defekty.
Dłuższy czas chłodzenia: Stosunkowo niska przewodność cieplna akrylu prowadzi do wydłużenia czasu cyklu, a tym samym zmniejsza wydajność i produkcję.
Formowanie akrylu a inne procesy formowania tworzyw sztucznych
| Nieruchomość | Akryl (PMMA) | Poliwęglan (PC) | Tworzywo ABS |
| Przejrzystość | Przejrzystość 92% (przypominająca szkło) | Przejrzystość 85% | Słaby |
| Odporność na uderzenia | Umiarkowany | Wysoki | Wysoki |
| Odporność na ciepło | Umiarkowany (80-100°C) | Doskonały (120-140°C) | Dobry |
| Odporność na zarysowania | Wysoki | Umiarkowany | Niski |
| Koszt | Przystępna cena | Drogie | Tani |
Poliwęglan jest najlepszy pod względem odporności na uderzenia, podczas gdy akryl jest wybierany ze względu na swoje właściwości optyczne. W tanich zastosowaniach, gdzie elastyczność i wytrzymałość jest priorytetem, można użyć ABS.
Przyszłe trendy w formowaniu akrylu do zastosowań przemysłowych

- Formowanie akrylowe staje się kolejną wielką rzeczą i napędza przyszłość w następujących aspektach:
- Formy akrylowe drukowane w 3D mogą z jednej strony poprawić szybkość prototypowania i zaoszczędzić pieniądze na wytwarzaniu form.
- Producenci sięgają po nadający się do recyklingu i ekologiczny akryl, aby zmniejszyć ilość odpadów.
- Integracja AI i IoT sprawia, że kontrola procesu produkcyjnego i zapewnienie jakości stają się inteligentniejsze, optymalizując w ten sposób inteligentne wtryskarki.
- Akryl z nanopowłoką - zwiększa odporność na zarysowania i ochronę przed promieniowaniem UV, zapewniając długotrwałą wytrzymałość.
Sincere Tech - Zaufane usługi formowania wtryskowego akrylu
Sincere Tech jest biegły w formowaniu wtryskowym tworzyw sztucznych i formowaniu wtryskowym akrylu o wysokiej jakości, która jest odpowiednia dla przemysłu motoryzacyjnego, medycznego i elektronicznego. Dzięki zaawansowanej technologii i wykwalifikowanym inżynierom tworzą bardzo przejrzyste i trwałe precyzyjne części akrylowe.
Dzięki niestandardowemu projektowaniu form i doświadczeniu w produkcji, zapewnia opłacalne rozwiązania zarówno do prototypowania, jak i produkcji masowej. Sincere Tech wykorzystuje wysokiej jakości materiały do produkcji naszych wysoce odpornych na promieniowanie UV, odpornych na uderzenia i optycznie przezroczystych elementów akrylowych.
Sincere Tech jest dostawcą tanich form akrylowych ze względu na swoją reputację w zakresie jakości, wydajności i innowacji. Skontaktuj się z nimi już dziś, aby uzyskać dostosowane usługi formowania tworzyw sztucznych z najwyższą precyzją!
Wnioski
Formowanie wtryskowe akrylu umożliwia produkcję wytrzymałych, lekkich i optycznie przejrzystych komponentów. Kruchość i kurczliwość akrylu nie zostały jeszcze rozwiązane, niemniej jednak okazał się on niedrogim zamiennikiem szkła, gdy wymagana jest precyzja i trwałość. Zgodnie ze zmianami w produkcji, inteligentne technologie formowania, automatyzacja i zrównoważone rozwiązania akrylowe również będą wiodły prym. Niemniej jednak materiał ten z pewnością nadal będzie znajdował swoje miejsce w nowoczesnych zastosowaniach przemysłowych, ponieważ rosnące zapotrzebowanie na spersonalizowane, wysokowydajne produkty akrylowe gwarantuje, że materiał ten będzie nadal służył jako rozwiązanie zarówno do produkcji masowej, jak i do specjalistycznych celów produkcyjnych.
Najczęściej zadawane pytania
1. Dlaczego wykorzystuje się akryl w formowaniu wtryskowym?
Akryl zapewnia wysoką przejrzystość (92%), odporność na promieniowanie UV, trwałość i przystępną cenę, będąc jednocześnie odpowiednim wyborem dla przezroczystych i odpornych na warunki atmosferyczne przedmiotów.
2. Gdzie można stosować formowanie akrylowe?
Akryl jest powszechnie stosowany w branży motoryzacyjnej, medycznej, towarów konsumpcyjnych i oznakowań ze względu na swoją wytrzymałość, przejrzystość i wszechstronność.
3. Dlaczego formowanie akrylu jest trudne?
Może być kruchy, może się wypaczać i wymaga bardzo ścisłej kontroli temperatury, aby nie powstawały wady.
Jakie są różnice między akrylem a poliwęglanem i ABS?
Akryl jest mniej przezroczysty, ale bardziej odporny na zarysowania w porównaniu do PC, podczas gdy tańszy ABS nie jest przezroczysty.











Dodaj komentarz
Chcesz się przyłączyć do dyskusji?Zapraszamy do udziału!