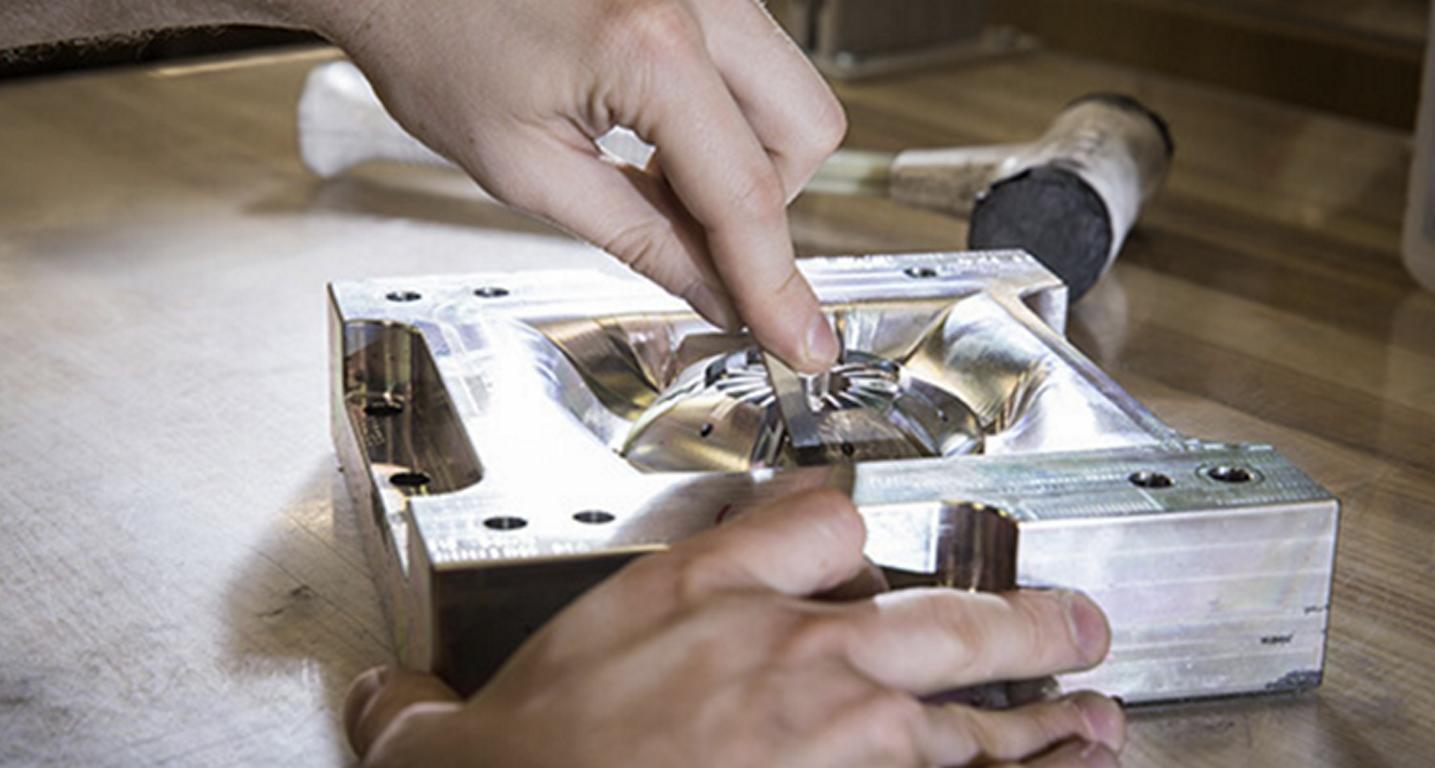
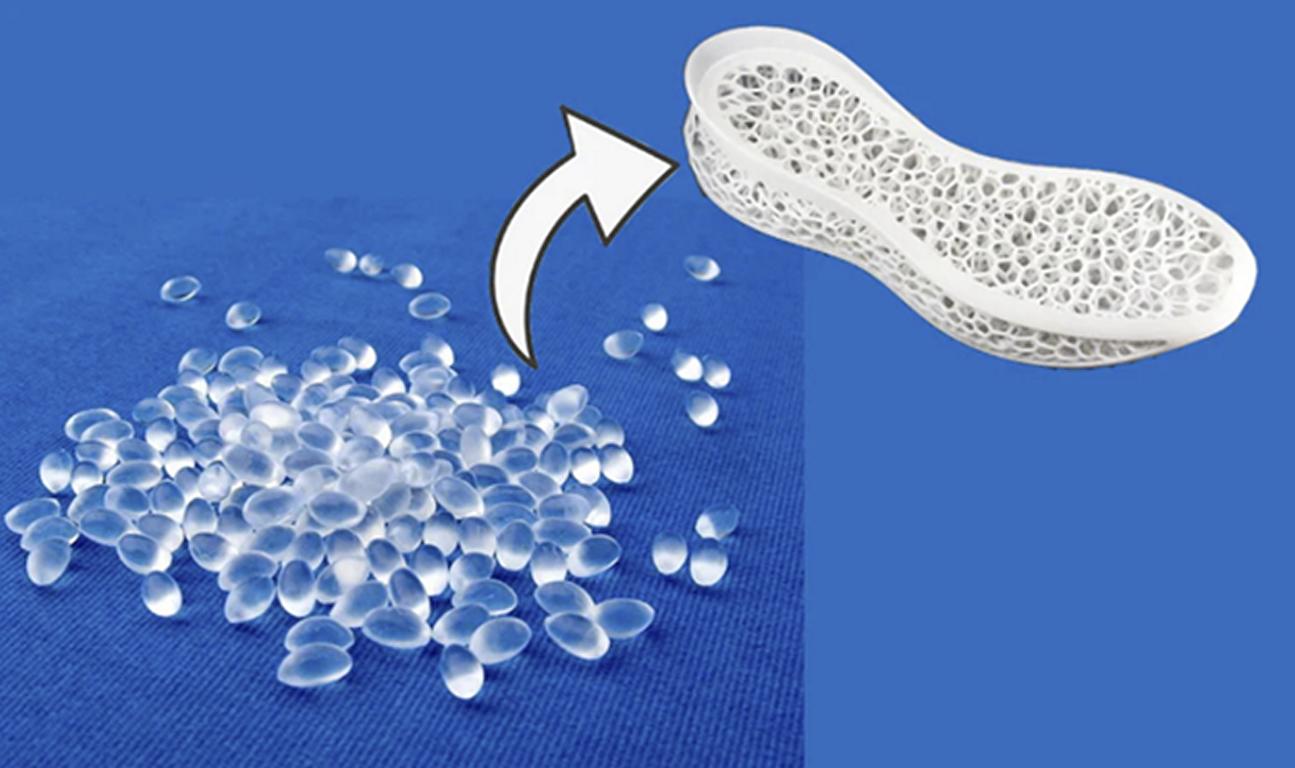
Formsprutning av klar plast är en specialiserad tillverkningsprocess som också används för att tillverka högkvalitativa, klara plastkomponenter för flera branscher. Denna teknik skiljer sig från standard plastgjutning genom att material, formdesign och alla variabler måste kontrolleras exakt för att denna teknik ska ge exceptionell optisk klarhet och hållbarhet. Klara plastdelar förekommer i medicinska instrument och fordonslinser, konsumentelektronik och arkitektonisk belysning överallt, och överallt annars också. Formsprutningen av klar plast lyckas beroende på valet av sådant rätt material som akryl, polykarbonat och optiskt silikongummi med sina specifika egenskaper som slagtålighet, UV-stabilitet och ljusöverföring.
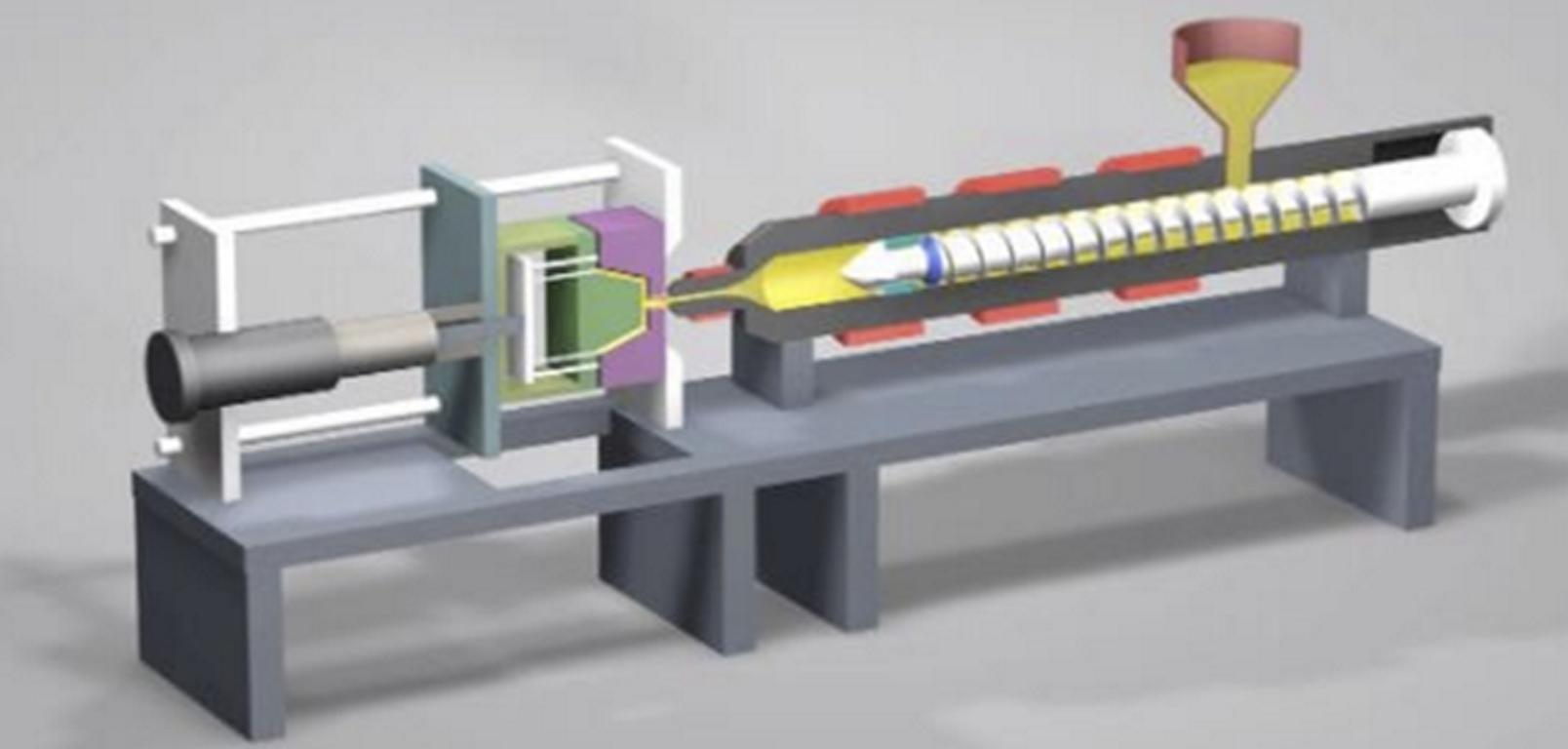
Själva processen kräver noggrann förberedelse av formen, torkning av materialet, kontrollerad injektion och sedan långsam kylning för att undvika defekter som bubblor, ränder och dis. Dessutom förbättrar efterbehandlingstekniker och avancerade beläggningar ytterligare den optiska prestandan hos de optiskt klara plastkomponenterna. Trots alla dessa fördelar står gjutning av klar plast inför utmaningar som perfekt transparens, undvikande av ytdefekter och materialkänslighet. Trots detta ökar framstegen inom gjutning och de som arbetar i branschen drar nytta av innovationer som AI-driven optimering av gjutning, anpassningsbara formar för 3D-utskrift och självläkande plaster för att förbättra effektiviteten och de produkter som produceras.
Processen för formsprutning av klar plast täcks, de viktigaste materialen som används, utmaningar, applikationer samt deras framtida framsteg i den här artikeln. Om du är inom medicin-, fordons-, elektronik- eller belysningsindustrin, om du behöver veta mysteriet med hur man gör klara plastverktyg, kan denna kunskap hjälpa dig att välja en högpresterande och visuellt tilltalande plastkomponent.
Vad är formsprutning av klar plast?

Formsprutning av klar plast är en typ av tillverkning där transparent eller semitransparent plastmaterial smälts och sprutas in i en form för att skapa vissa former till sist. Till skillnad från vanlig formsprutning är denna process mycket känslig för materialval (inklusive val av typer av flöden), för formens utformning och för kylningstekniker för att undvika defekter som grumlighet, bubblor och distorsioner.
Det används ofta för tillverkning av produkter som måste ha utmärkta optiska egenskaper, t.ex. medicinska instrument, fordonsbelysning och elektroniska displayer.
Formsprutningsprocess för klar plast

Det är en mycket exakt process för att uppnå klara plastkomponenter. Här är en sammanfattning av några av de viktigaste stegen i denna onlinekurs.
1. Formkonstruktion och beredning
Formsprutning av klar plast kräver en form som är väl utformad. Formen måste ha:
- Polerad till mycket höga nivåer för att förhindra märken eller förvrängningar av ljudet.
- Den kan ventileras för att avlägsna luftbubblor och undvika instängda gaser.
- Mekanismer för att kontrollera temperaturen för att reglera kylningshastigheter
2. Torkning av material
Plasthartser med för hög fukthalt är kända för att orsaka grumlighet, bubblor eller svaga punkter. Polykarbonat- och akrylmaterial måste torkas vid kontrollerade temperaturer före injektion för att avlägsna fukt.
3. Smältning och injektion
Formhålan fylls under högt tryck med det torkade hartset som värms upp till sin smältpunkt. Viktiga överväganden inkluderar:
- Förhindrar flödesmärken och spänningsfrakturer genom injektionshastighet och tryck
- Högre temperatur bidrar till att bibehålla den optiska klarheten
- Jämn kylning och förhindrar krympning: Enhetlig fyllning
4. Kylning och stelning
Kylningen måste vara långsam och jämn för att undvika att materialet vrids eller förvrängs. Transparenta plaster kräver ofta:
- Gradvis kylning för att bibehålla klarheten
- Avancerade kylkanaler i gjutformen kan användas.
- I vissa fall minskar den inre spänningen genom glödgning efter gjutning.
5. Utskjutning och efterbearbetning
När detaljen har stelnat matas den försiktigt ut för att undvika repor och märken. Efterbearbetningstekniker som t.ex:
Polering
- UV-beläggning för skydd
- Laserskärning för precision
- Detta kan också förbättra produktens utseende och hållbarhet.
Clear Injection Molding Använder viktiga material.
Klar formsprutad plast kräver val av material, vilket är viktigt för att ge hög hållfasthet och hög klarhet. De vanligast förekommande materialen anges nedan:
Akryl (PMMA)

Polymetylmetakrylat (PMMA), eller som det är känt vetenskapligt som akryl, är ett av de mest använda materialen för formsprutning av klar plast på grund av dess utmärkta optiska klarhet. Med en ljusöverföringshastighet på cirka 92% är den utformad för applikationer som kräver hög transparens som belysningsarmaturer, vitriner och bilkomponenter.
Förutom överlägsen UV-beständighet, vilket innebär att den inte gulnar med tiden, och hög reptålighet är akryl också giftfri i en rad olika tillämpningar. Akryl är dock mycket sprött och har en tendens att spricka eller spricka vid stötar. Dessutom är den mycket känslig för fukt och kräver förtorkning för att kunna användas i gjutning utan defekter.
Polyeten med hög densitet (HDPE)

Högdensitetspolyeten eller HDPE är ett relativt billigt och mångsidigt material med genomskinlig klarhet som gör det lämpligt för de produkter som inte kräver full transparens. Tack vare sin UV-beständighet är det ett bra val för användning utomhus, eftersom det tål långvarig exponering för solen utan att försämras.
HDPE har högre slagtålighet jämfört med akryl och är därför mindre benägna att gå sönder. Används mest vid tillverkning av flaskor, rör och förpackningsbehållare eftersom den har låg tillverkningskostnad och fantastisk hållbarhet. Å andra sidan är HDPE inte tillräckligt styvt som andra transparenta plaster, vilket gör det olämpligt för applikationer som kräver hög strukturell styrka.
Polykarbonat (PC)

Polykarbonat (PC) är en högpresterande, transparent plast med god optik och mycket hög mekanisk hållfasthet. Den används ofta i tillämpningar som kräver transparens och hållbarhet, t.ex. skyddsglasögon, billyktor och skottsäkra fönster.
I motsats till akryl är polykarbonat extremt slagtåligt och splittras inte under svåra krafter. Dessutom är det en bra UV-resistent, vilket gör att den inte gulnar under en längre tid. En nackdel är dock att ytan på polykarbonat är benägen att få ytliga repor och vanligtvis behöver en ny beläggning av något för att faktiskt göra den hållbar. PC kräver också fördopning före formsprutning för att förhindra fuktrelaterade defekter (som akryl).
Polyeterimid (PEI)

Högpresterande teknisk plast Polyeterimid (PEI) är en enastående plast som står emot UV, värme och kemikalier. Legeringen används främst inom industrier som kräver hög mekanisk hållfasthet och hög termisk stabilitet, t.ex. flyg-, bil- och medicinteknikindustrin.
PEI har därför en utmärkt värmebeständighet för allt som utsätts för extrema temperaturer. Även om det är dyrare och svårare att forma på ytan av en produkt, används det ibland i konsumentprodukter. I många fall kräver formsprutning av PEI att man använder stålformar för att kunna vara exakt och bibehålla hållbarheten.
Polypropylen (PP)

Polypropylen (PP) är en vanligt förekommande termoplast som har flexibilitet, kemisk resistens och elektrisk ledningsförmåga. Tack vare sin hållbarhet och mångsidighet används den i stor utsträckning i förpackningsmaterial, textilier och fordonskomponenter.
PP:s största fördel är att den kan stängas och öppnas flera gånger utan att gå sönder. Den är därför särskilt lämpad för applikationer som kapsyler och gångjärn. Polypropen är dock inte lika genomskinligt som akryl eller polykarbonat - det passar bättre som genomskinligt än som klart. Dessutom är det inte tillräckligt styvt för att användas som en strukturell eller bärande komponent.
Flytande silikongummi (LSR)

Flytande silikongummi (LSR) är en högpresterande elastomer som är känd för att vara extremt väl biokompatibel, ha utmärkt termisk stabilitet och kemisk resistens. Mekaniskt sett är det ganska starkt och flexibelt och används ofta i medicinska, fordons- och elektroniska applikationer.
Den främsta fördelen med LSR är dess förmåga att bibehålla form och egenskaper under extrema värmeväxlingar eller vid exponering för kemikalier, lösningsmedel och värme. LSR har elasticitet och hållbarhet vilket gör den lämplig för tätningar, packningar och medicinska slangar. Tack vare sin värme- och kemikaliebeständighet kan den även användas i krävande miljöer.
Optiskt silikongummi (OSLR)

Detta optiska silikongummi (OSLR) är speciellt utvecklat för hög ljusgenomsläpplighet och hög optisk klarhet. I optiska linser, LED-belysning, medicinsk bildutrustning och andra områden där högre ljusgenomsläpplighet och extremt låg distorsion är nödvändig, t.ex. i en CCTV.
OSLR har enastående motståndskraft mot ogynnsamma väderförhållanden och gulnar inte under den förväntade livslängden. Det är ett lämpligt val för utomhusbelysningsarmaturer och optiska komponenter med hög precision på grund av dess förmåga att bibehålla den optiska stabiliteten över tiden.
Polyeten (PE)

Polyeten (PE) är en termoplast som skapas av petroleumbaserade material genom värme- och tryckbehandling. På grund av sin kostnadseffektivitet och formbarhet används den ofta i flaskor, rör, förpackningar och konsumentvaror.
Det är UV-beständigt och lämpar sig därför utmärkt för utomhusbruk. Även om det inte kan komma i närheten av den optiska klarheten hos akryl eller polykarbonat är det bättre för genomskinliga applikationer än helt genomskinliga.
Elastomeriska hartser (TPR)

Termoplastiskt gummi (TPR) är ett flexibelt material som innehåller egenskaper från plast och gummi. Det används ofta i medicinska, industriella och konsumentapplikationer som kräver kemisk beständighet och elasticitet.
TPR används i vanliga applikationer som vätskedispensrar, medicinska katetrar och flexslangar. Det är ett idealiskt material för produkter som kräver motståndskraft mot syror och hårda kemikalier eftersom det tål tuffa förhållanden.
Termoplastisk polyuretan (TPU)

Termoplastisk polyuretan (TPU) är en höghållfast elastomer som ofta används i sportartiklar, bildelar och ergonomiska handtag. Materialet är känt för sin mjuka textur, överlägsna elasticitet och utmärkta rivhållfasthet.
TPU ger en gummikänsla till sin sammansättning och används därför ofta i handtag och flexibla delar. Den här plastvarianten är visserligen dyrare än standardplast, men dess hållbarhet och förmåga att motstå stötar gör den till ett bra val för högpresterande applikationer.
Ljustransmissivitet och dess egenskaper och bästa användning
I den här tabellen kan du jämföra hur olika transparenta och genomskinliga material fungerar när det gäller ljusgenomsläpplighet och deras egenskaper och bästa användningsområden.
| Material | Ljusöverföring (%) | Viktiga funktioner | Vanliga tillämpningar |
| Akryl (PMMA) | ~92% | Det är en klar, UV-beständig och reptålig spröd | Belysningsarmaturer, bildskärmar, optiska linser |
| Polykarbonat (PC) | 88-90% | Hög slagtålighet, UV-beständighet, något lägre klarhet än PMMA | Skyddsglasögon, strålkastare för bilar, skottsäkra fönster |
| Optiskt silikongummi (OSLR) | ~90-94% | Glasliknande klarhet, flexibel, motståndskraftig mot höga temperaturer | LED-belysning, optiska linser, medicinsk bildutrustning |
| Flytande silikongummi (LSR) | ~85-90% | Flexibel, biokompatibel, värme- och kemikaliebeständig | Medicintekniska produkter, elektronik, specialbelysning |
| Polypropylen (PP) | ~80-85% | Genomskinlig, kemikalieresistent, flexibel, låg kostnad | Frostat lock, behållare, förpackningslösningar |
| Polyeten med hög densitet (HDPE) | ~75-85% | Genomskinlig, hållbar, kostnadseffektiv, slagtålig | Flaskor, rör, förpackningar, konsumentvaror |
Utmaningar inom klar formsprutning

Även om genomskinlig plast erbjuder flera fördelar finns det fortfarande nackdelar med den:
1. Uppnå hög optisk klarhet
Genomskinligheten kan minskas av eventuella brister i formen eller kylningen. Formen måste vara slät och högpolerad och bearbetningen måste ske vid exakta temperaturer.
2. Undvika bubblor och flödeslinjer
Bubblor eller flödeslinjer av luft som fångats upp under injektionsprocessen kan ses i slutprodukten. För att förhindra detta:
Korrekt avluftning i formen är nödvändig. Det hjälper till att upprätthålla ett jämnt flöde genom långsamma, kontrollerade insprutningshastigheter.
3. Materialkänslighet
Polykarbonat och akryl är klara plaster som är mycket känsliga för fukt, värme och UV-exponering. Om torkning och förvaring sker på rätt sätt blir resultatet av hög kvalitet.
4. Repor och ytdefekter
Det beror på att ojämnheter syns tydligt i genomskinlig plast, så tillverkarna måste använda:
- Anti-repbeläggningar
- Skyddande förpackning under transport
Vanliga defekter i genomskinliga plastdelar och deras lösningar

För tillverkning av klara plastdelar krävs perfekt transparens och jämnhet. Det finns dock många defekter som kan påverka slutproduktens klarhet och övergripande kvalitet. Här är några vanliga problem vid formsprutning av klar plast och hur man löser dem.
1. Bubblor
Orsak
Innesluten luft eller gas som inte kan komma ut under gjutningsprocessen är vanligtvis orsaken till bubblor. Detta kan hända på grund av:
- Ofullständig fyllning av gjutformen.
- Snabb avkylning vid kondensationsytan.
- Resin med fukt som orsakar ångbildning.
Lösning
- Se till att formen är ordentligt ventilerad så att gaser släpps ut.
- Öka insprutningstrycket för att förbättra materialflödet.
- Överflödig fukt bör avlägsnas från plasthartset före gjutning.
2. Silver Streaks
Orsak
Variationer i inre spänningar under materialflödet orsakar silverstrimmor. Genom att applicera tryck på hartset trycks hartset i olika riktningar, vilket skapar en rad ojämna brytningsindex och resulterar i en randig eller silkesliknande effekt. Om denna stress tillåts byggas upp kommer den så småningom att leda till sprickbildning.
Lösning
- För att främja jämn kylning bör formtemperaturen optimeras.
- Öka insprutningshastighet och tryck för att minimera spänningsuppbyggnad.
- Förhindra riktningsjustering av materialet under gjutning med gjutningstekniker med låg belastning.
3. Seismiska mönster
Orsak
Denna defekt kännetecknas av räfflade eller vågiga mönster på ytan till följd av hög smältviskositet. Om hartset inte flyter jämnt och kondenserar för tidigt i hålrummet förstör det materialets homogenitet.
Lösning
- Höj smälttemperaturen för att öka materialflödet.
- Viskositeten minskas genom att justera plastifieringsförhållandena.
- Ändra utformningen av granen och löparen för att få bättre materialfördelning.
4. Dålig ytglans
Orsak
Orsaken till en matt eller ojämn ytfinish är vanligtvis grova formytor eller att hartset stelnar för tidigt innan det helt anpassar sig till formen.
Lösning
- För att uppnå en jämnare yta, polera formhålan.
- Höj temperaturen i gjutformen för att förbättra materialflödet.
- Högkvalitativa hartser med bättre flödesegenskaper bör användas.
5. Vit rök / svarta prickar
Orsak
Hartsnedbrytningen inuti formsprutningsröret på grund av överdriven värme är orsaken till att dessa defekter orsakas. Svarta fläckar kan uppstå när överhettat material kan brinna och vit rök kan uppstå när gas släpps ut från nedbrutet harts.
Lösning
- Förhindra överhettning av cylindern genom att sänka temperaturen.
- Finjusterare ska regelbundet rengöra och underhålla insprutningsmaskinen för att undvika hartsuppbyggnad.
- Garantera konsekventa cykeltider så att materialet inte bryts ned.
6. Vitare / dimma
Orsak
När fukt eller dammpartiklar förorenar plastmaterialet blir det dis eller grumlighet. Ljusdiffraktion på grund av felaktig torkning eller luftburna föroreningar minskar transparensen.
Lösning
- Bearbeta råmaterial efter att ha torkat dem ordentligt.
- Kontaminering kan undvikas genom att förvara lagrat material i en ren och kontrollerad miljö.
- Håll dammet borta från luften genom att använda filter och luftrenare i produktionsområdet.
Fördelar med formsprutning av klar plast
Det finns dock många fördelar med formsprutning av klar plast trots dess nackdelar.
1. Utmärkt optisk transparens
Hög ljusgenomsläpplighet lämpar sig väl för klara formsprutade plaster som används i t.ex. linser, medicinsk utrustning och bildskärmar.
2. Precision och konsekvens
Formsprutning är mycket exakt och repeterbar, vilket resulterar i identiska delar med mycket få defekter i varje.
3. Kostnadseffektiv massproduktion
När formen väl är skapad sjunker produktionskostnaderna avsevärt jämfört med de efterföljande, vilket är ett effektivt sätt när det gäller tillverkning i bulk.
4. Lätt och tålig
Eftersom klara plastdelar är lättare än glas, splitterfria och mer slagtåliga är de utmärkta för användning i säkerhetsapplikationer.
Användningsområden för klar formsprutad plast
Plast med tydliga formsprutningsformar används ofta i industrier eftersom de har optisk klarhet, hållbarhet, kemisk resistens och mindre vikt. Plaster som kan skapa transparenta komponenter med hög precision som ökar funktionaliteten och estetiken är dessa. Några av de viktigaste branscherna som formsprutning av klar plast gäller anges nedan.
1. Medicinsk industri

Den medicinska marknaden kräver klara plastkomponenter där sterilitet och precision är avgörande, liksom behovet av synlighet. Vanliga användningsområden inkluderar:
- Omfattar genomskinliga sprutor och IV-slangar eller kirurgiska instrument som gör det möjligt för personalen att övervaka eller kontrollera vätskeflödet och förhindra överdosering.
- Styvhet hos det genomskinliga skyddsskalet över ansiktsmasken eller de medicinska skyddsglasögonen för att skydda utan att försämra sikten.
- Höljen för diagnostisk utrustning för röntgen-, MR- och ultraljudsapparater där tydligheten är så viktig.
2. Fordonsindustrin

Formsprutad plast kan göra fordon mer funktionella och designvänliga. De används i:
- Linser med hög optisk transparens och hållbarhet för strålkastare och bakljus som tål tuffa väderförhållanden.
- Genomskinliga instrumentbrädor och hastighetsmätarpaneler för att göra reglage och displayer synliga.
- Det nämns att slagtåliga genomskinliga plaster används i vissa lätta fordonskonstruktioner som kräver takluckor och sidofönster.
3. Konsumentelektronik

Klargjutna plaster för tillverkning av lätta, hållbara och estetiskt tilltalande delar används inom elektronikindustrin.
- För skyddande och kostnadskänsliga touchapplikationer på smartphoneskärmar och displayskydd.
- Även transparenta TV- och laptopskärmar med reptålighet och hög klarhet.
- Skärmkomponenter i bärbar teknik, t.ex. smartklockor och träningsarmband, är också flexibla och har slagtålighet.
4. Förpackningsindustrin

I förpackningar används ofta genomskinlig plast eftersom den är tvättbar, lätt och estetiskt tilltalande. Några viktiga tillämpningar inkluderar:
- Ett urval av klara behållare och flaskor i livsmedelskvalitet för att hålla maten fräsch och för att se innehållet.
- Typ av genomskinliga kosmetiska och farmaceutiska förpackningar, så att kunderna kan se produkten på ett säkert sätt under förvaringen.
- Tamper-säkra och lufttäta genomskinliga förpackningar, som används för mediciner, kosttillskott eller mer exklusiva livsmedelsprodukter.
5. Belysningsindustrin

Plaster som oftast används som elektriskt isolerande material, så kallade klara plaster eller plast, är viktiga för moderna belysningsapplikationer, vilket ger ökad effektivitet och funktionalitet. De används i:
- LED-skydd och lampdiffusorer för jämn ljusfördelning och skydd av LED-komponenter.
- Transparenta paneler för arkitektonisk belysning, t.ex. transparenta paneler, kan användas som skräddarsydda belysningslösningar för interiör och exteriör design.
- Högpresterande optiska linser används i gatubelysning, stadionbelysning och bilstrålkastare för flexibilitet när det gäller ljusets riktning och fokus.
6. Flyg- och rymdindustrin samt försvar
Dessutom krävs lätta, slagtåliga klara material för många tillämpningar inom flyg- och försvarsindustrin, t.ex:
- Hög optisk klarhet med motståndskraft mot tryckförändringar som krävs för flygplansfönster och cockpitpaneler.
- Genomskinliga visir för hjälmar, som skyddar så mycket som ögonen kan se.
- Optiska linser till försvarsmateriel, t.ex. mörkerglasögon och avståndsmätare.
7. Optisk och vetenskaplig utrustning
Klar plast behövs för optiska applikationer med hög precision för exakt ljusöverföring utan distorsion. Exempel på detta är:
- På motsvarande sätt har deras linser använts i mikroskop och teleskop, vilket ger upphov till hög förstoring för klärvoajans.
- Optiska sensorer och laserkomponenter används inom vetenskaplig forskning och industriell automation.
- Skyddande sköldar för laboratorieinstrument för att skydda hanteringen av farliga material.
Klar formsprutad plast är på grund av sin mångsidighet och sina avancerade egenskaper oersättlig för många branscher, t.ex. medicin-, fordons-, elektronik-, förpacknings-, belysnings-, flyg- och vetenskapsbranschen, där innovation underlättas av tillgången till denna plast.
Framtida trender inom formsprutning av klar plast
Industrin för formsprutning av klar plast kommer att se stora framsteg i takt med att tekniken utvecklas. Under de kommande åren kommer det att vara nödvändigt att förbättra materialens hållbarhet, deras hållbarhet och tillverkning samt produktens prestanda. Branschen kommer att definieras av några nyckeltrender som räknas upp nedan.
1. Förbättrade materialinnovationer
Utvecklingen inom området för transparenta plaster går snabbt framåt för att ta fram mer hållbara, hållbara och funktionella plaster. Viktiga innovationer inkluderar:
- Automatiska reparationer av mindre repor i självläkande genomskinlig plast förlänger livslängden på produkter som fordonslinser och smarttelefonskärmar.
- Höghållfasta, lätta kompositer som är mycket transparenta och har en kombination av god slagtålighet och möjliggör motståndskraft mot stötar när termoplastiska material är omöjliga eller svåra att använda.
2. Avancerad gjutningsteknik
Formsprutning av klar plast genomgår olika nya tillverkningstekniker som möjliggör större effektivitet och precision:
- Integration med 3D-printing för anpassning av gjutformen för snabb prototyptillverkning och lågkostnads- och massproduktion av komplexa delar som den genomskinliga.
- Formningsoptimering i realtid med AI, som kan anpassas dynamiskt för att orsaka färre defekter, producera mer konsekventa produkter och kortare cykeltid.
- Används för nanoteknologiskt förbättrad formsprutning för att skapa plaster som bättre kan påverka optisk klarhet, reptålighet och värmetolerans.
3. UV-beständiga och antireflexbehandlade ytskikt
För att i framtiden kunna producera klara plaster med bättre funktionalitet i olika applikationer kommer plasterna att förses med specialiserade ytskikt.
- Förbättrat UV-skydd, så att det inte orsakar gulning eller nedbrytning av material som utsätts för solljus, t.ex. billyktor eller paneler för utomhusbelysning.
- Ger anti-fog-egenskaper som förbättrar sikten på vindrutor i bilar, medicinsk utrustning och optiska apparater.
- Reptåliga beläggningar för att öka hållbarheten på smartphoneskärmar, glasögon, industriell skyddsutrustning etc.
4. Smarta och funktionella genomskinliga plaster
I takt med att genomskinlig plast blir alltmer efterfrågad som ett multifunktionellt material kommer smarta tekniker som mesh att integreras i den.
- Även inbyggda sensorer i genomskinlig plast för industriella och medicinska tillämpningar för övervakning av temperatur, tryck och kemisk exponering i realtid.
- Skärningar som gör det möjligt att forma ledande klara plaster för transparenta elektroniska displayer och beröringskänsliga ytor i nästa generations enheter.
- Och självrengörande beläggningar som kräver mindre underhåll inom medicin, optik och fordonsindustrin.
Om dessa framsteg uppfylls kommer vi att garanteras tydligare formsprutning av plast som säkert kommer att möta de växande kraven från dagens industrier på ett ännu smartare och mer hållbart sätt bland andra funktioner.
Slutsats
Formsprutning av klar plast är en viktig funktion som har förändrat tillverkningsindustrier som kräver hög transparens och noggrannhet. Avancerade material som polykarbonat, akryl och optiskt silikongummi gör det möjligt för tillverkaren att designa komponenter som är lätta, hållbara och optiskt tydliga samtidigt som de ersätter de äldre glaslösningarna. Allt detta har lett till en växande efterfrågan på klara plaster eftersom de används i medicintekniska produkter, fordonsbelysning, elektronik och förpackningar. Trots problem som fuktkänslighet, defekter på objektets yta och strikta bearbetningskrav har gjutningstekniken gjort stora framsteg när det gäller att öka effektiviteten och förbättra produktkvaliteten. AI, 3D-utskrift och nanoteknik fortsätter att utveckla tekniken och integrerar processen på en billigare och mer exakt nivå och UV-beständiga beläggningar och självläkande plaster har ytterligare ökat hållbarheten hos de klargjutna produkterna.
Framtiden för formsprutning av transparent plast är inriktad på hållbarhet, smarta material och större funktionell förmåga. Biologiskt nedbrytbara och återvinningsbara transparenta plaster kommer att efterfrågas alltmer av de industrier som söker miljövänliga alternativ till sina vanliga produkter. Dessutom kan applikationer inom det medicinska och elektroniska området realiseras med smarta plaster som har inbyggda sensorer och ledande egenskaper. Sammantaget är formsprutning av genomskinlig plast en mycket viktig teknik som fortfarande utvecklas och ger kreativa lösningar till industrier som kräver genomskinlighet, styrka och estetik.
Vanliga frågor
1. Vilka är de vanligaste materialen vid formsprutning av klar plast?
PMMA är ett material med hög optisk klarhet och används oftast tillsammans med PC för hög slagtålighet, OSLR för högsta möjliga ljusgenomsläpplighet och PP för genomskinliga tillämpningar till lägsta kostnad. Valet av varje material görs med hänsyn till dess motsvarande egenskaper och industriella behov.
2. Vilka är de största svårigheterna med formsprutning av klar plast?
De viktigaste frågorna är att se till att materialet har hög optisk klarhet, inga defekter i form av bubblor eller ränder, att det är fuktkänsligt och att ytan är reptålig. För att klara dessa utmaningar krävs exakta gjutförhållanden, god torkning och mycket bra formar.
3. Vilka branscher använder formsprutning av klar plast mest?
Formsprutning av klar plast är en av de viktigaste delarna i tillverkningsindustrin, t.ex. medicinska tillämpningar (sprutor, droppslangar, diagnostisk utrustning) och fordonsindustrin (strålkastarglas, instrumentbrädor), konsumentelektronik (smartphoneskärmar, displaypaneler), förpackningar (livsmedelsbehållare, kosmetikaflaskor) och belysning (LED-lampor, lampdiffusorer).
4. Vilken roll spelar tekniken vid formsprutning av klar plast?
AI-styrda processer, 3D-printing för anpassning av gjutformar, självläkande plaster och förbättrade UV-beständiga beläggningar förbättrar produktionseffektiviteten och produktens hållbarhet. Dessa minskningar möjliggör mer tillförlitliga processer, bättre materialprestanda och mer hållbara processer.
5. Är genomskinliga plastmaterial naturvänliga?
Traditionella transparenta plaster från petroleum verkar ha förbättrats när det gäller hållbarhet, även om biologiskt nedbrytbara och återvunna transparenta plaster har utvecklats under de senaste åren. Biobaserade alternativ och miljövänliga produktionstekniker utforskas också av tillverkarna för att minska miljöpåverkan.