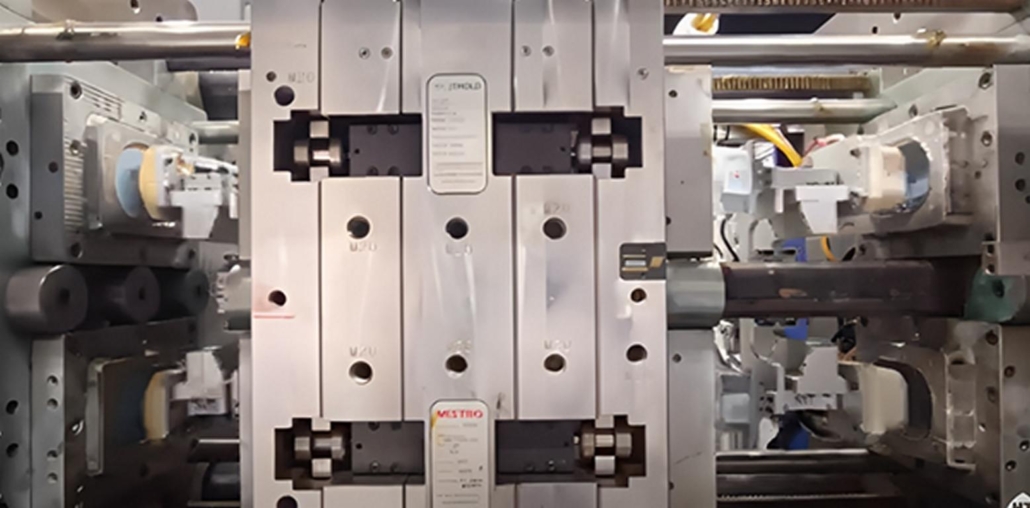
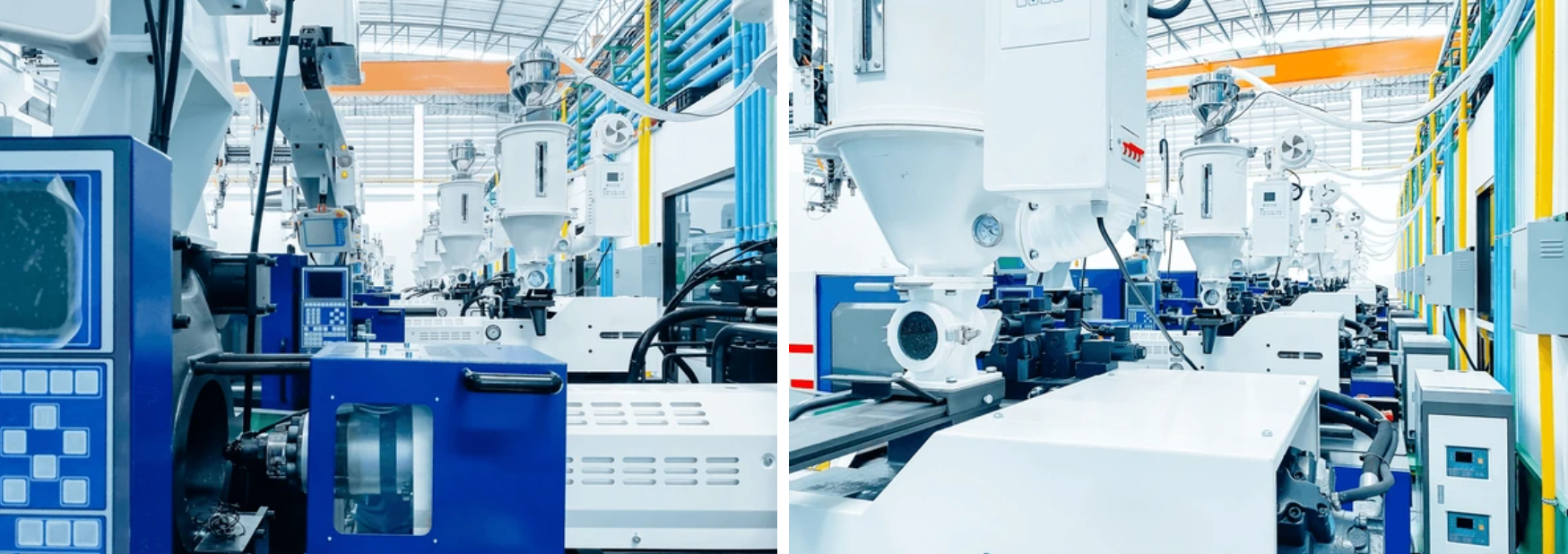
As a country with a clock-tower slogan: “Made in Germany,” Germany has developed itself into one of the highest innovative levels in engineering, production, and technology. Germany, the largest economy country in Europe and one of the largest exporting countries in the world, has a good reputation and a needy concept of quality and solidarity. Manufacturing is one of the major contributors to the overall performance of the country’s economy, and it focuses on efficiency, new ways of production, sustainability, and automation. Germany, as an exponent of precision engineering, has a lot of reputed companies in the automobile, electronic, and medical equipment segments. Research and development at the heart of the country promise constant innovations in material science, digitization, and automation as factors of industrial dominance. It also holds one more function of Industry 4.0 through implementing the IoT, AI, and Robotization in the production line. This integration enables Germany to set standards across the globe regarding quality and productivity rates.
We have injection molding, which is the main foundation of German manufacturing equipment and serves automotive, packaging, and medical, amongst others. The German injection molding firms work in smart tool-equipped manufacturing houses and offer cheap, customized, accurate products. It emerges here how exact, economical, eco-friendly, innovation-oriented Germany is to ensure that the nation prevails in an industry where employment can be relocated globally.
The purpose of this article is to provide readers with an overview of 10 firms and their work in Germany’s injection molding industry to help our readers firstly understand the complexity and creativity behind those firms’ works, secondly, to get the opportunity to explore the firms’ roles and contributions to the manufacturing industry.
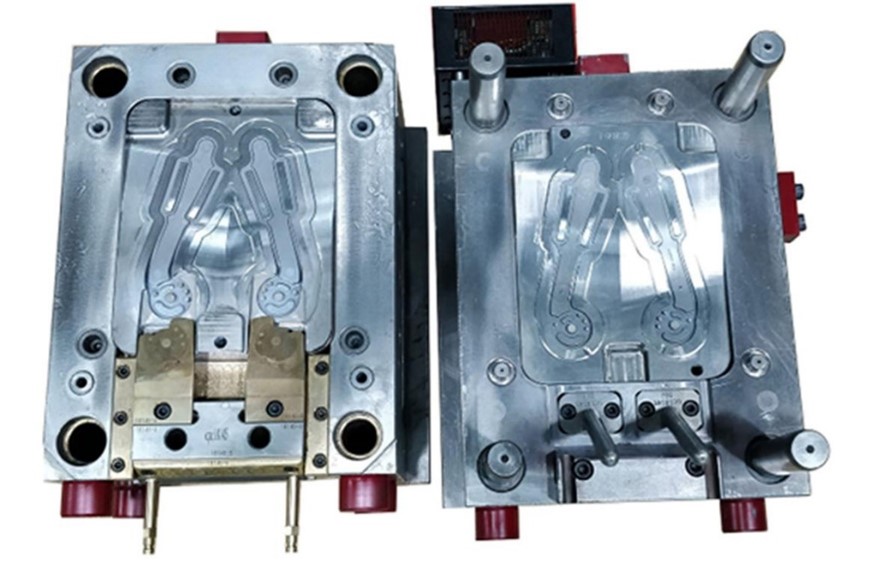
1. Foboha (Germany) GmbH
Year of establishment: 1995
Number of employees: 260
Business type: FOBOHA specializes in advanced injection molding tools, Cube Molds, and high-efficiency manufacturing solutions.
Website and Contact
Website: https://www.foboha.com
Email: info@foboha.com
Phone: +49 78 32 798 0
Fax: +49 78 32 798 988

Company Profile
FOBOHA was established in 1973 in Haslach, Germany, by Werner Bodmer. It is a company that produces injection molding technology products. The company is recognized for its unique Cube Mold, and it offers advanced, highly efficient molded systems for the automotive, medical, and packaging divisions. Purchased in August 2016 by Barnes Group Inc., FOBOHA currently utilizes the technologies and resources of an international manufacturing company to provide precision machinery, energy-saving solutions, and sustainable, high-performance manufacturing benchmarks.
Services
- Injection molding tools and Cube Molds
- Custom mold design
- Maintenance
- Repair technical support for molds
Pros
1. Innovative Technology Leader: Cube Mold technology is used in FOBOHA’s production line, which increases efficiency in its production capacity and lowers cycle times, making the company suitable for high-volume production.
2. High Precision and Reliability: The company provides only the latest mold technology that provides the best and long-lasting design that results in improved quality of produced products across various industries.
3. Sustainability Focus: FOBOHA solution focuses on environmental production, using efficient energy in the production process, and using green materials in production.
Cons
1. High Initial Costs: Newer technologies, such as Cube Molds, may be capital intensive initially, making it strongly advisable to only those businesses with large outlay.
2. Specialized Training Requirements: Many technologies that FOBOHA uses in operation and maintenance require additional training to perform, making operational issues even more challenging.
3. Industry-Specific Focus: Applied mainly to industries where high accuracy in molding is crucial, the company is unsuitable for other areas of the manufacturing industry, so it is frequently used by different companies.
For injection molding services in Germany, please refer to FOBOHA for product innovation.
2. H&K Müller
Year of establishment: 1934
Number of employees: 110
Business type: Thus, HK Müller is focused on implementing the technological process of plastic injection molding to create customized packaging for various sectors, such as cosmetics and medicine.
Website and Contact
Website: https://www.hk-mueller.de/en
Email: info@hk-mueller.de
Address: Alsbacher Eichen 1, 51766 Engelskirchen
Phone: +49 2263 89-0

Company Profile
HK Müller is a foremost company dealing with great precision plastic injection molding solutions and is concerned with manufacturing precision plastic parts and packaging. Some of its clients include cosmetics manufacturers, food processing firms, and medical-focused industries, and the company can provide a range of services from design to delivery. Because of its efficient tool-making, assembly, and rapid prototyping, HK Müller offers quality solutions that are dependable and innovative. Because of their concentration on strict quality assurance and customer satisfaction, they stand out as the solution provider in injection molding manufacturing.
Services
- Injection Molding
- Tool Making
- Assembly Services
- Packaging Solutions
- 3D Prototyping
- Quality Control
- Transportation and Operations Management
Pros
1. Covers and customized products for many verticals.
2. The molding by injection is of high quality and precise.
3. A full range of services includes prototyping and supply chain management.
Cons
1. Because specialized services are usually more expensive than general ones.
2. Some particular designs might need elaborate clothing to execute successfully.
3. Custom projects’ lead time concerns.
For injection molding services in Germany, you may turn to HK-Müller for sound manufacturing solutions and product development.
3. Weber GmbH & Co. KG
Year of establishment: 1949
Number of employees: 1400
Address: Industriestraße 14 , 35683 Dillenburg, Germany
Business Type: Weber Group deals with producing automatic systems for packaging, food, and industrial automation.
Website and contact
Website: https://www.weber-group.com/en/
Phone: +49 2771 394-0
Email: info(at)weber-group.com

Company Profile
Weber Group has expertise in automation systems; the company deals in packaging automation, food processing automation, and installation, among other services. specializations lie in specific contracts, processing techniques through injections, and incorporating a manufacturing system. Weber Group is also involved in design, consultation, supply, installation, maintenance, and servicing the finished product. Paying careful attention to product quality details, these vendors provide robust, accurate automation tools that promote efficiency for business or organizational applications that address various industries.
Services
- Automated Packaging Solutions
- Food Processing Systems
- Industrial Automation
- Custom Engineering and Design
- System Integration
- Sales & Service Support
- Robotics and AI Solutions
- Integrated management services of production lines
Pros
1. It specializes in automating packaging and food processing industry equipment.
2. Custom services for different sectors focusing on food and industrial robotics.
3. Services range from consultation, technical support in system implementation, and follow-up support after the sale of the software.
Cons
1. Initial costs are relatively high compared to standard, out-of-the-box automated systems.
2. For complex installations and integration procedures, leave it to an expert who deals with Windows server systems.
3. It mainly operates in an industry related to automation requirements, which confines its applicability to a certain extent.
For more detailed information on the activities of consulting and project management specialists, visit the websites within this category’s links.
4. Meusburger Georg GmbH & Co KG
Year of establishment: 1964
No or employees: 1700
Business type: Meusburger offers precision, standard stocked parts, injection molding templates, and tools and services that meet specific requirements for tool-making companies.
Website and contact
Website: https://beta.meusburger.com/en-gb
Phone: +43 5574 67060
Email: office@meusburger.com
Address: Kesselstr.42, Wolfurt, Austria

Company Profile
Meusburger is a global company specializing in the manufacture of identified precision standard parts and providing customers with individual solutions relevant to the manufacture of tools and molds. One of the leading industries in their field, Meusburger focuses on injection molding tools and hot runner systems, offering a vast catalog of services with guaranteed quality and effectiveness. It offers clients innovation, technical support, and customer satisfaction. It enhances industrial sectors by providing services, rich CAD resources, complete training, and build—c—catalog industry benchmarks of precision engineering and manufacturing.
Services
- Standard Parts for Tool and Mold Making
- Sporting Mold Base Customizations
- Hot Runner Systems and Components
- Injection Molding Tools
- CNC Machining and Processing
- General Notes and Support
- CAD Data & Technical Resources
- Training and Workshops
- Spare Parts and Accessories
- Cooperation and Work Proposal
Pros
1. They also provide acceptable interchangeability and guarantee the required quality and reliability of the components.
2. Products and services offered include essential, various, and even specialized services.
3. Computer-aided design data as well as technical support and/or training.
Cons
1. These special-purpose solutions are also relatively expensive.
2. Complex projects may take more time to complete because of the time it takes to complete the project.
3. Lack of concentration on products other than tools and injection molded products.
Regarding injection molding in Germany, Meusburger should be the company of choice for accurate and high-quality injection mold tools and solutions.
5. Hofmann – Ihr Impulsgeber
Year of Establishment: 1958
Number of employees: 280
Business type: Hofmann is a leading injection molding, tool manufacturing, as well as automation expert for a broad range of manufacturing sectors.
Website and contact
Website: https://www.hofmann-impulsgeber.de/
Email: info@hofmann-impulsgeber.de
Address: An der Zeil 2 25339 Lichtenfels Germany

Company Profile
Originally a supplier of molds and tooling, Hofmann Impleader has emerged as a leading organization in tool making, injection molding, and additive manufacturing. The company is based in Germany and focuses on precision engineering for industries like automobiles, medicine, and consumers. With Höfmann, which provides prototype and serial production as well as 3D printing and advanced mold construction, their services range from initial equipment to high-volume production. Their commitment to quality, innovation, and sustainability guarantees dependable, efficient solutions that meet client requirements.
Services
- Toolmaking and Mold Construction
- Injection Molding Solutions
- (2) Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- Prototyping and Rapid Prototyping
- Large-Scale Manufacturing Flexibilities
- Custom Mold Design and Engineering
- Quality Assurance and Testing
- Maintenance and Repair Services
- Business Automation and Process Efficiently
- Consulting services and Technical Assistance
Pros
1. Core competencies in manufacturing precision tools, injection molding application, and industrial application of additive manufacturing.
2. Everything from concept prototyping to high production volume and for various industries.
3. Guarantee continuous improvement in innovation and sustainability with leading-edge technologies such as 3D printing.
Cons
1. Low-end user value of high initial investments in solutions and technologies.
2. Whereas specialized services always take longer lead times depending on the project, huge ones.
3. Concentrated mainly on sectors that require acceptable production levels, restraining market diversification.
To get professional injection molding in Germany, contact Hofmann Impulsgeber for accuracy and creativity.
6. EWIKON Heißkanalsysteme GmbH
Year of Establishment: 1978
Number of employees: 300-500
Business type: Ewikon is a supplier of hot runner systems and a comprehensive solution provider in the field of injection molding and plastics processing.
Website and contact
Website: https://www.ewikon.com
Email: info@ewikon.com
Phone: +49 6451 5010
Address: Siegener Straße 35, Frankenberg, Germany

Company Profile
Ewikon is a world-class manufacturer and supplier of hot runner systems for injection molding, focusing on developing a range of hot runners to fit specific application requirements. Specializing primarily in design, installation, maintenance, repair, and technical consulting, Ewikon guarantees an improvement in the functionality of the systems. Due to their innovative technologies and the emphasis on customers’ needs, they are reliable industrial partners for enterprises of various branches interested in receiving accurate and qualitative injection molding and plastics processing.
Services
- Hot Runner System Design and Engineering
- Custom Injection Molding Solutions
- Installation and Commissioning Support
- Maintenance and Repair Services
- Technical Consulting and Troubleshooting
- Spare Parts and Optimization
- Training and Workshops
Pros
1. Offers superior, precision-designed hot runner injection molding systems for respective applications.
2. These capitalized service offerings include the scope’s installation, maintenance, and repair services.
3. Provides custom proposals for improvement of existing systems and their further optimization.
Cons
1. Upfront costs are relatively high for implementing the highest level of hot runner systems.
2. Specialized systems may be very complex and require technical personnel.
3.It also means that lead times can be longer if the product includes custom development work or if system-level optimizations are required.
EWIKON has wide experience in hot runner systems and sophisticated technologies, thus making it the ideal solution provider for injection molding in Germany. Get in touch with them for premium services.
7. Rosti GP Germany
Year of Establishment: 1944
Number of employees: 400-500
Business type: Rosti is a leading global supplier of technical plastic injection molding and contract manufacturing, together with product design for worldwide industries.
Website and contact
Website: https://rosti.com
Email: gdpr@rosti.com.
Phone: + 46 (0)40 204 701
Address: Västra Varvsgatan 19S211 77 Malmö, Sweden
Company Profile
Rosti Group, established in 1944 in Malmö, Sweden, is a prominent full-service contract manufacturing and injection molding company specializing in plastics. Founded in 1969 with 12 plants in Europe and Asia, Rosti offers turnkey solutions in the packaging, medical and automotive industries. To its commitment to sustainability, innovation, and excellence, Rosti uses core values of Passion, Integrity, Partnership, and Excellence to serve clients with the best sustainable, innovative solutions.
Service
· Plastic injection molding
· Surface finishing
· Over molding
· Metal to plastic conversion
· Contract Manufacturing
· Injection blow molding
Pros
1. Geographical Coverage – Rosti company currently has twelve manufacturing facilities; thus, Rosti’s global coverage can be guaranteed.
2. CP – Conducting business as a one-stop provider for design, tooling, assembly, or logistics needs.
3. NCD Focus Area – Company environmental awareness demonstrated through its adherence to the ISO 50001 energy management system.
Cons
1. Expensive – Sometimes, they may be expensive for a small business undertaking.
2. Limited customization – Integrating a company’s processes may limit product design.
3. Reliance on region – Business and operations may be problematic in very developing regions with fewer structures.
Rosti’s advanced technology and local experience make it an ideal company for plastic injection molding in Germany.
8. Otto Injection Molding GmbH & Co. KG
Year of Establishment: 1956
Number of employees: 400-500
Business type: Engineering, construction of molds, multi-component molding, hybrid technique, fluid injection, and high-performance plastics.
Website and contact
Phone: +493726/2649
Website: https://www.otto-im.de/en
Email: kontakt@otto-im.de
Address: Kurze Str. 14, 09577 Niederwiesa, Germany

Company Profile
Otto Injection Molding GmbH & Co. KG was established in 1956 in Niederwiesa, Germany, and the company deals with high-quality injection molds and injection molded parts. Target industries include medical, aerospace, and automotive; they provide multi-component molding, hybrid technology, and fluid injection. Boasting its expertise in engineering, tooling, and production, Otto has remained committed to delivering quality innovation. With sound financial performance and dependable stability, it remains one of the top suppliers of superior plastic products worldwide.
Services
· Injection molding
· Mold construction
· Engineering
Pros
1. Injection molding and Advanced Technologies – Over Sixty years and going strong.
2. Multiple Types of Solutions – It provides solutions to various industries such as healthcare, aerospace, and automotive.
3. Innovation and Quality – It targets high-performance plastics, an environmentally friendly approach, and the most recent molding techniques.
Cons
1. There is another disadvantage: High costs. Premium-quality services may not fit small business organizations with a small budget.
2. Small International Access – Most are based in Germany and thus can only be accessed internationally to a small degree.
3. High integration – Some products or systems involve many components, which may take longer to produce due to sophisticated technologies.
When looking for injection molding services in Germany, trust Otto Injection Molding because they are the best.
9. Braunform GmbH
Year of establishment: 1977
Number of employees: 200-300
Business type: Engineering, construction of molds, multi-component molding, hybrid technique, fluid injection, and high-performance plastics.
Website and contact
Website: https://www.braunform.com/de
Email: info@braunform.com
Phone: +49 7663 93200
Address: Industriestraße 25,79353 Bahlingen am Kaiserstuhl,,Germany.
Company Profile
Braunform GmbH & Co, KG was established in Germany in 1977 and specializes in High Precision Injection Molds and Clean Room Products. Targeting customers include the manufacturing sector, including the pharmaceuticals, automobiles, and Electronics sectors; it possesses technological solutions like multi-component and MED Mold solutions, ticals, automotive, and electronics. It also offers advanced technologies such as multi-component and MED Mold solutions. Braunform aims at quality, sustainability, and innovation; the company has ISO certifications today. Employees: 380, accolades: for its winning expertise, it offers customized products that are energy efficient and developmental to cater to the dynamic industry needs.
Services
- Product development collaboration
- Mold design optimization with Moldflow analysis
- Efficient production through intelligent mold design
- Integration of new technologies
- High-performance injection mold construction
Pros
1. Mold Manufacturing – Over 45 years of experience providing injection mold and clean room products.
2 . Wanshida is positioned to create reiterative and original technologies, including multi-component, MED Mold, and stack mold systems.
3. GRI Sustainable Development – Uses natural energy; has recognition for international standards on quality management.
Cons
1. Higher Price – Sophisticated service options attract high prices due to the service offered to start-ups and other businesses.
2. Geographical Specialization – Most operations in Germany may discourage access to international Markets.
3. Persistence of Fragmentation –there exists a wind that with new technologies, the current complicated process of production will be made even more complex, resulting in more time being spent on the actual development and manufacturing of the products themselves.
If you are searching for the most competent plastic injection molding service providers in Germany, the best one to contact is Braunform GmbH.
10. DONGGUAN SINCERE TECH CO.LTD
Year of establishment: 2005
Number of employees:80-100
Business type: Plas.co offers accurate plastic injection molding to distinct sectors of operation and solutions to their global production processes.
Website and contact
Website: https://plas.co/
Email: sales@cnm-mold.com
Phone: +86 (0)769-3388 9978
Fax: +86 (0)769-3388 9978
Address: 2nd industry area, TianTou Cun, HengLi Town, DongGuan City, Guangdong Province.China,523460

Company Profile
Plas.co is an established company that manufactures plastic injection molding and all-around manufacturing solutions for the electronics, automotive, and consumer goods industries. Their competency includes product design, prototyping, tool making, 2K molding, and over-molding. They also deal with PCB design services, CNC machining, die-casting molding, and high-volume manufacturing. Due to quality assurance, innovation in manufacturing services, and focus on customer expectations, Plas.co offers solutions for various manufacturing requirements.
Services
- Product design and manufacturing
- Prototyping and testing
- Plastic mold design and manufacturing
- 2K molding and overmolding
- PCB design and die-casting tooling
- CNC machining
- Certification services
- Mass production and assembly
- Inspection and packing solutions
Pros
1. Full process services from design to manufacturing allow clients to get everything they need in one place.
2. Properly applying 2K molding and over-molding improves product quality.
3. Increased concern with preventing failure growth via inspection and certification services to guarantee satisfactory results.
Cons
1. High set-up cost in services such as machining through computer numeric control and tooling for die casting.
2. The specialized process might take longer for custom jobs than for routine jobs.
3. In simple terms, this made it suitable for precision industries alone while lacking the flexibility needed for this market.
If you want a one-stop plastic injection molding, prototyping, and assembly services provider, go for Plas.co.