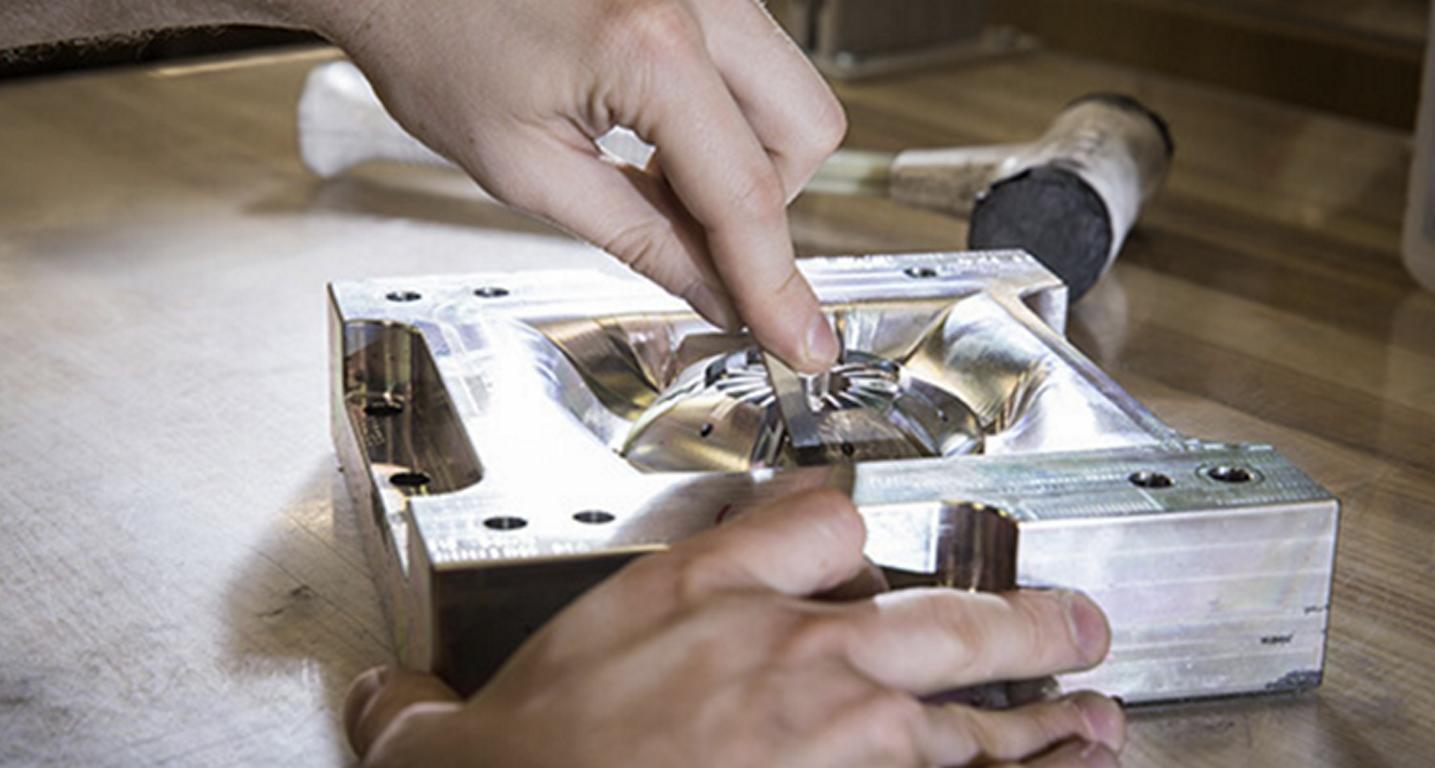
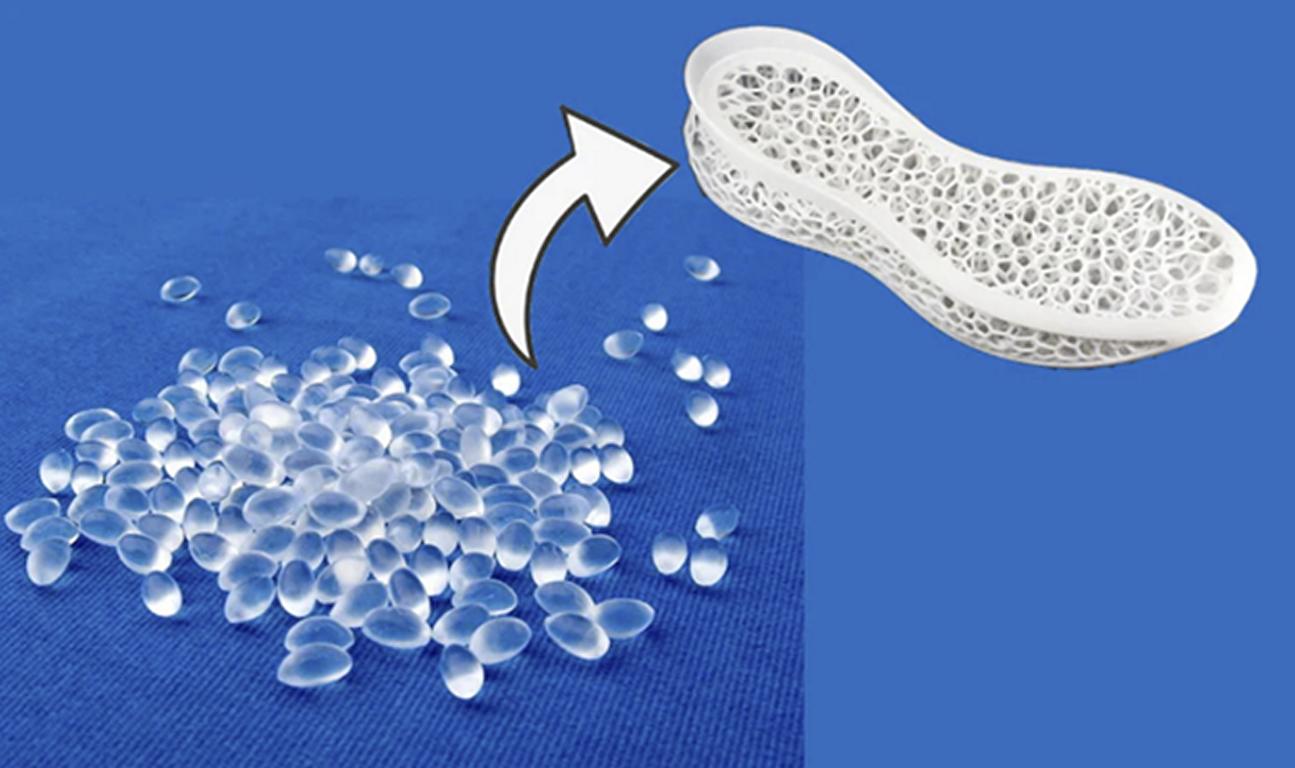
Clear plastic injection molding is a specialized manufacturing process also used in the production of high-quality, clear plastic components for multiple industries. This technique is different from standard plastic molding in that materials, mold design and all variables must be precisely controlled for this technique to provide exceptional optical clarity and durability. Clear plastic parts appear in medical instruments and automotive lenses, consumer electronics, and architectural lighting everywhere, and everywhere else too. The clear plastic injection molding succeeds depending upon the selection of such right material like acrylic, polycarbonate, and optical silicone rubber with their specific properties like impact resistance, UV stability, and light transmission.
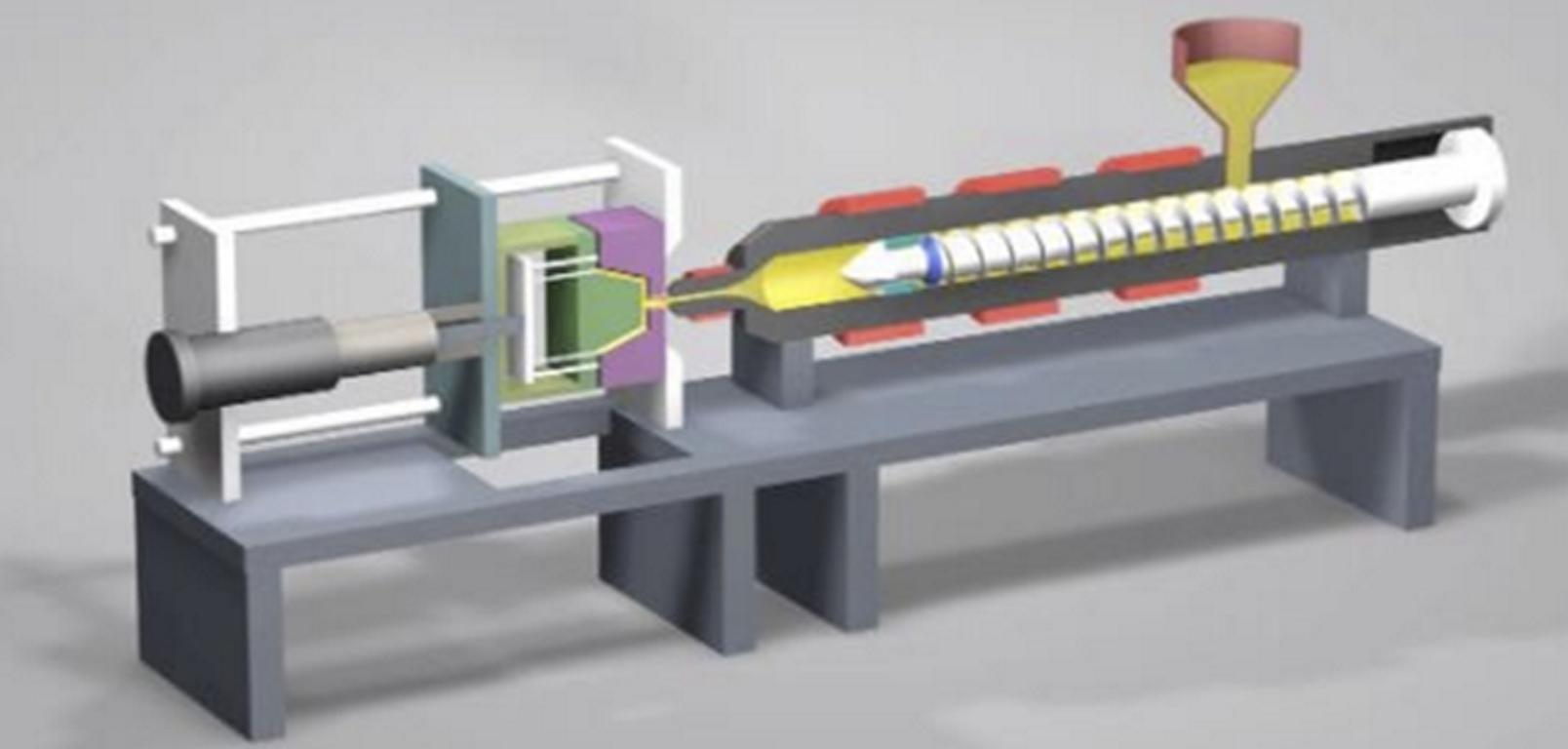
The process itself takes delicate preparation of mold, drying of the material, injecting in a controlled manner and then cooling slowly to avoid defects such as bubbles, streaks, and haze. Also, post-processing techniques and advanced coatings further enhance the optical performance of the optically clear plastic components. With all these things having advantages, clear plastic molding is facing challenges such as perfect transparency, surface defect avoidance, and material sensitivity. Nevertheless, the rate of progress in molding is increasing and those in the industry are taking advantage of innovations like AI-driven molding optimization, 3D print customizable molds and self-healing plastics to improve efficiency and the products produced.
The process of clear plastic injection molding is covered, the key materials used, challenges, applications, as well as their future advances in this article. If you are in the medical, automotive, electronics or lighting industry, if you need to know the mystery of how to make clear plastic tools, this knowledge can help you to choose a high performance and visually pleasing plastic component.
What is Clear Plastic Injection Molding?

Clear plastic injection molding is a type of manufacturing where plastic transparent or semi transparent material is melted and injected into a mold to create certain shapes lastly. Unlike regular injection molding this process is very sensitive to material selection (including selection of types of flows), to the mold design, and to cooling techniques to avoid such defects as cloudiness, bubbles and distortions.
It is widely used for manufacturing products that should possess excellent optical properties, such as medical instruments, automotive lighting and electronic displays.
Clear Plastic Injection Molding Process

It’s a very precise process to achieve clear plastic components. Here is a breakdown of some of the essential steps in this online course.
1. Mold Design and Preparation
Clear plastic injection molding requires a mold that is well-designed. The mold must have:
- Polished to very high levels to prevent marks or distortions of the sound.
- It can vent to remove air bubbles and avoid trapped gases.
- Mechanisms to control the temperature to regulate cooling rates
2. Material Drying
Plastic resins with too much moisture content are known to cause cloudiness, bubbles, or weak spots. Polycarbonate and acrylic materials need to be dried at controlled temperatures prior to injection to remove moisture.
3. Melting and Injection
The mold cavity is filled under high pressure with the dried resin heated to its melting point. Key considerations include:
- Prevents flow marks and stress fractures by injection speed and pressure
- Higher temperature helps in maintaining optical clarity
- Even cooling and prevents shrinkage: Uniform filling
4. Cooling and Solidification
The cooling must be slow and uniform to avoid warping or distortion of the material. Transparent plastics often require:
- Gradual cooling to maintain clarity
- Advanced cooling channels within the mold can be used.
- In some cases, post-mold annealing reduces internal stress.
5. Ejection and Post-Processing
The part is ejected carefully once solidified to avoid scratches or marks. Post-processing techniques such as:
Polishing
- UV coating for protection
- Laser cutting for precision
- This can also improve the appearance and durability of the product.
Clear Injection Molding Uses key materials.
Clear injection molded plastics require the choice of material, which is important to provide high strength and high clarity. The most commonly used materials are given below:
Acrylic (PMMA)

Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA), or as it is known scientifically as Acrylic, is one of the most widely used materials for clear plastic injection molding because of its excellent optical clarity. With a light transmission rate of approximately 92%, it is designed for applications that require high transparency like lighting fixtures, display cases and automotive components.
In addition to superior UV resistance resulting in no yellowing over time and high scratch resistance, acrylic is also nontoxic in a range of applications. Acrylic, however, is very brittle and is prone to cracks or cracks upon impact. Moreover, it is very sensitive to moisture and requires pre drying to be used in molding without defects.
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)

High-density polyethylene or HDPE is a relatively inexpensive and versatile material with translucent clarity making it suitable for those products that do not require full transparency. Because of its UV resistance, it is a good choice for use outdoors, since it can tolerate long exposure to the sun without degrading.
HDPE has more impact resistance compared to acrylic so is less likely to break. Mostly used in the production of bottles, pipes, and packaging containers as the low cost of manufacturing with amazing durability. On the other hand, HDPE is not rigid enough like other transparent plastics, which makes it unsuitable for applications involving high structural strength.
Polycarbonate (PC)

Polycarbonate (PC) is a high performing, transparent, plastic with good optics and very high mechanical strength. In applications that require transparency and durability, it is widely used, e.g. safety glasses, automotive headlights, bulletproof windows.
Contrary to acrylic, polycarbonate is extremely impact-resistant and will not shatter under severe forces. Moreover, this is a good UV resistant, the condition will not yellow for a long period of time. One downside though is that the surface of polycarbonate is prone to surface scratches and will usually need another coat of something to actually make it durable. PC also requires pre doping before injection molding to prevent moisture related defects (like acrylic).
Polyetherimide (PEI)

High-performance engineering plastic Polyetherimide (PEI) is an outstanding plastic that resists UV, heat, and chemicals. The application of the alloy is primarily in industries that demand high mechanical strength as well as high thermal stability, such as the aerospace, automotive, and medical equipment manufacturing industries.
As a result, PEI has excellent heat resistance for anything that will be exposed to extreme temperatures. Though more expensive and hard to mold onto the surface of a product, it is used occasionally in consumer products. In many cases, PEI injection molding requires the use of steel molds, in order to be precise and maintain durability.
Polypropylene (PP)

Polypropylene (PP) is a broadly used thermoplastic having flexibility, chemical resistance as well as electrical conductivity. It is used widely in packaging materials, textiles and automotive components on account of its durability and versatility.
PP’s most significant benefit lies in its ability to be closed and re-opened several times without breaking. It is thus especially suited for such applications as flip-top bottle caps and living hinges. Nevertheless, polypropylene is not as transparent as acrylic or polycarbonate — it is more well suited being translucent than clear. Additionally, it is not rigid enough to be used as a structural or load bearing component.
Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR)

Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) is a high-performance elastomer and one that is known for being extremely well biocompatible, having excellent thermal stability and chemical resistance. Mechanically, it is quite strong and flexible and is widely used in medical, automotive, and electronic applications.
The outstanding advantage of LSR is its ability to maintain shape and properties under conditions of extreme thermal cycling, or of exposure to chemicals or solvents and heat. LSR have elasticity and durability which makes it suitable for seals, gaskets, medical tubing. This also further extends its uses in demanding environments thanks to its resistance to heat and chemicals.
Optical Silicone Rubber (OSLR)

This Optical Silicone Rubber (OSLR) is specifically developed for high light transmission, high optical clarity. In optical lens, LED lighting, medical imaging devices and other fields where higher light transmittance and extremely low distortion is necessary, such as in a CCTV.
OSLR has outstanding resistance to adverse weather conditions and does not yellow through the expected life. It is an appropriate choice for outdoor lighting fixtures and high precision optical components because of its ability to keep optical stability over time.
Polyethylene (PE)

Polyethylene (PE) is a thermoplastic that is created from petroleum-based materials through heat and pressure treatment. Used because of its cost-effectiveness and moldability, it is commonly used in bottles, pipes, packaging, and consumer goods.
It is well UV resistant, thus great for outdoor use. While it cannot come close to the optical clarity of acrylic or polycarbonate itself, it is better for translucent applications than fully transparent ones.
Elastomeric Resins (TPR)

Thermoplastic Rubber (TPR) is a flexible material that contains the characteristics of plastic and rubber. In medical, industrial and expendable consumer applications that require chemical resistance and elasticity, it is frequently used.
TPR is used in common applications such as fluid dispensers, medical catheters, and flex hoses. It is an ideal material for products that require resistance to acids and harsh chemicals due to the fact that it can withstand tough conditions.
Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU)

Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU) is a high-strength elastomer used frequently in sporting goods, automotive parts, and ergonomic handles. As a material it is notorious for its soft texture, superior elasticity, as well as its excellent tear resistance.
TPU gives a rubber feeling to its composition therefore it is widely used in grips and flexible parts. While this version of plastic is more expensive than standard plastics, its durability and ability to withstand impact make it a good choice of plastic for high performance applications.
Light transmissivity and its features and best use
There is this table that helps compare how different transparent and translucent materials perform in terms of light transmissivity and its features and best use case.
| Material | Light Transmission (%) | Key Features | Common Applications |
| Acrylic (PMMA) | ~92% | It is a clear, UV resistant, and scratch-resistant brittle | Lighting fixtures, display screens, optical lenses |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 88-90% | High impact resistance, UV resistance, slightly lower clarity than PMMA | Safety glasses, automotive headlights, bulletproof windows |
| Optical Silicone Rubber (OSLR) | ~90-94% | Glass-like clarity, flexible, high-temperature resistance | LED lighting, optical lenses, medical imaging devices |
| Liquid Silicone Rubber (LSR) | ~85-90% | Flexible, biocompatible, heat & chemical resistant | Medical devices, electronics, specialized lighting |
| Polypropylene (PP) | ~80-85% | Translucent, chemical-resistant, flexible, low cost | Frosted covers, containers, packaging solutions |
| High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) | ~75-85% | Translucent, durable, cost-effective, impact-resistant | Bottles, pipes, packaging, consumer goods |
Challenges in Clear Injection Molding

Although clear plastics offer several benefits, they still come with disadvantages:
1. Achieving High Optical Clarity
Transparency may be reduced by any imperfection in the mold or the cooling. The mold has to be smooth and highly polished and processing has to be done at precise temperatures.
2. Avoiding Bubbles and Flow Lines
Bubbles or flow lines of air trapped during the injection process can be seen in the final product. To prevent this:
Proper venting in the mold is needed. It helps to maintain smooth flow by slow, controlled injection speeds.
3. Material Sensitivity
Polycarbonate and acrylic are clear plastics that are very sensitive to moisture, heat, and UV exposure. If drying and storage are done appropriately, the output is quality.
4. Scratches and Surface Defects
That’s because because imperfections show clearly in clear plastics, so manufacturers must use:
- Anti-scratch coatings
- Protective packaging during transportation
Common Defects in Clear Plastic Parts and Their Solutions

For the manufacture of clear plastic parts, perfect transparency and smoothness is required. There are, however, many defects that can affect the final product’s clarity and overall quality. Here are some common problems in clear plastic injection molding and how to resolve them.
1. Bubbles
Cause
Trapped air or gas that cannot escape during the molding process is usually the cause of bubbles. This can happen due to:
- Incomplete filling of the mold.
- Rapid cooling at the condensation surface.
- Resin with moisture causing vapor formation.
Solution
- Make sure that the mold is vented properly so that gases escape.
- Increase the injection pressure to improve the material flow.
- Excess moisture should be removed from the plastic resin before molding.
2. Silver Streaks
Cause
Internal stress variations during material flow cause silver streaks. By applying pressure to the resin, the resin is pushed into different directions, creating an array of uneven refractive index and resulting in a streaky or silk-like effect. If this stress is allowed to build up, it will eventually lead to cracking.
Solution
- To promote even cooling, mold temperature should be optimized.
- Increase injection speed and pressure to minimize stress buildup.
- Prevent directional material alignment during molding with low-stress molding techniques.
3. Seismic Patterns
Cause
This defect is characterized by grooved or wavy patterns on the surface resulting from high melt viscosity. If the resin does not flow smoothly and condenses too early in the cavity, it ruins the homogeneity of the material.
Solution
- Increase the melt temperature to increase material flow.
- Viscosity is reduced by adjusting plasticizing conditions.
- Change the sprue and runner design to have better material distribution.
4. Poor Surface Gloss
Cause
The cause of a dull or uneven surface finish is typically rough mold surfaces, or the resin fully solidifying too soon before it totally conforms to the mold.
Solution
- To achieve a smoother finish, polish the mold cavity.
- Increase the mold temperature to improve the material flow.
- High-quality resins with better flow characteristics should be used.
5. White Smoke / Black Spots
Cause
The resin degradation inside the injection molding barrel due to excessive heat is the reason for causing these defects. Black spots can occur when overheated material can burn and white smoke can occur when gas is emitted from degraded resin.
Solution
- Prevent the overheating of the barrel by lowering the temperature.
- Finningers are to regularly clean and maintain the injection machine to avoid resin buildup.
- Guarantee consistent cycle times so that the material is not getting degraded.
6. Whitening / Haze
Cause
When moisture or dust particles contaminate the plastic material, there is haze or cloudiness. Light diffraction due to improper drying or airborne impurities will reduce transparency.
Solution
- Process raw materials after thoroughly drying them.
- Contamination can be avoided by keeping stored materials in a clean, controlled environment.
- Keep dust off the air with the use of filters and air purifiers in the production area.
Advantages of Clear Plastic Injection Molding
However, there are many benefits to clear plastic injection molding despite its downsides.
1. Excellent Optical Transparency
High light transmission lends itself well to clear injection molded plastics used in items such as lenses, medical equipment and display screens.
2. Precision and Consistency
Injection molding is highly accurate and repeatable resulting in identical parts having very few defects in each.
3. Cost-Effective Mass Production
Once the mold is created, production costs plummet significantly compared to the subsequent ones, thus being an effective way when it comes to manufacturing in bulk.
4. Lightweight and Durable
Because clear plastic parts are lighter than most glass, shatter resistant and more impact resistant, they are excellent for use in safety applications.
Applications of Clear Injection Molded Plastics
Plastics with clear injection molds are commonly used in industries because they have optical clarity, durability, chemical resistance, and less weight. Plastics that can create transparent, high-precision components increasing functionality and aesthetics are these. Some of the main industries that clear plastic injection molding applies are stated below.
1. Medical Industry

The medical market requires clear plastic components where sterility and precision are crucial, as well as the need for visibility. Common uses include:
- Comprise transparent syringes and IV tubes, or surgical instruments that allow staff to monitor or check fluid flow and prevent overdosing.
- Rigidness of clear protective shield over the face mask or medical goggles to protect without compromising one’s view.
- Diagnostic equipment housings for X-ray, MRI, and ultrasound scanner devices where clarity is so important.
2. Automotive Industry

Injection molded plastics can make vehicles more functional and design-friendly. They are used in:
- High optical transparency and durability lenses for headlight and taillight that withstand harsh weather conditions.
- Transparent top dash covers and speedometer panels to make controls and displays visible.
- Mention is made of impact-resistant clear plastics in some lightweight automotive designs which require sunroofs and side windows.
3. Consumer Electronics

Clear molded plastics, for manufacture of lightweight, durable and aesthetically pleasing parts, are used in the electronics industry.
- For protective and cost-sensitive touch applications on smartphone screens and display covers.
- Also including transparent TV and laptop screens with scratch resistance and high clarity.
- Screen components of wearable tech such as smartwatches and fitness tracker screens are also flexible and have impact resistance.
4. Packaging Industry

In packaging, clear plastics are commonly used as they are washable, lightweight, and aesthetically pleasing. Some key applications include:
- A selection of food-grade clear containers and bottles to keep foods fresh and to see contents.
- The type of transparent cosmetic and pharmaceutical packaging, so that customers can see the product safely while storing.
- Tamper-proof and airtight clear packaging, as used for medications, supplements, or more premium food products.
5. Lighting Industry

Plastics which are most often used as electrically insulating materials, called clear plastics or plastics, are essential to modern lighting applications, providing increased efficiency and functionality. They are used in:
- LED covers and lamp diffusers for uniform light distribution, besides protecting LED components.
- Transparent panels for architectural lighting such as transparent panels can be used as customized lighting solutions for interior and exterior design.
- High-performance optical lenses are used in streetlights, stadium lightning, and automotive headlights for the flexibility of light direction and focus.
6. Aerospace and Defense
Moreover, lightweight, impact-resistant clear materials are required for many aerospace and defense industry applications such as:
- High optical clarity with resistance against pressure changes that are required for aircraft windows and cockpit panels.
- Transparency visors for helmets, which protect as much as the eyes can see.
- Optical lenses for defense equipment, such as night vision goggles and rangefinders.
7. Optical and Scientific Equipment
Clear plastics are needed for high-precision optical applications for accurate light transmission without distortion. Examples include:
- Congruently, their lenses have been used in microscopes and telescopes, giving rise to high clairvoyance magnification.
- Optical sensors and laser components are used in scientific research in industrial automation.
- Laboratory instrument preventive shields to safeguard the handling of dangerous materials.
Clear injection molded plastics are irreplaceable, due to their versatility and advanced properties, for many industries such as the medical, automotive, electronics, packaging, lighting, aerospace, and scientific fields where innovation is aided by the availability of these plastics.
Future Trends in Clear Plastic Injection Molding
The clear plastic injection molding industry will see major advancement as technology advances. Over the coming years it will be necessary to improve the durability of the materials, their sustainability and manufacture as well as the performance of the product. The industry will be defined by a few key trends which are enumerated below.
1. Enhanced Material Innovations
The field of clear plastics is advancing at a fast pace to develop more durable, sustainable, and functional plastic. Key innovations include:
- Automatic repairs of minor scratches made in self-healing clear plastics enhancing the life of products like automotive lenses and smartphone screens.
- High-strength, lightweight composites that are highly transparent and have a combination of good impact resistance and allow for resistance shock when thermoplastic materials are impossible or difficult to use.
2. Advanced Molding Technologies
Clear plastic injection molding undergoes various new manufacturing techniques that enable greater efficiency and precision:
- Integration to 3D printing for customizing the mold for rapid prototyping and low cost and mass production of complex parts such as the transparent one.
- Real-time molding optimization with AI, capable of dynamically adapting to cause fewer defects, producing more consistent products and shorter cycle time.
- Utilized for Nanotechnology enhanced injection molding in creating plastics that were better able to impact optical clarity, scratch resistance, and heat tolerance.
3. UV-Resistant and Anti-Fog Coatings
To produce future clear plastics with better functionality in various applications, plastics will be equipped with specialized coatings.
- Improved UV protection, so it will not cause yellowing or degradation of materials exposed to sunlight like car headlights or panels for outdoor lighting.
- Provides Anti-fog properties improving visibility on automotive windshields, medical appliances, and optical devices.
- Scratch-resistant coatings to increase the durability of smartphone screens, eyeglasses, industrial protective gear, etc.
4. Smart and Functional Clear Plastics
As clear plastic becomes more demanded as multi-functional material, smart technologies such as mesh will be integrated into it.
- Also embedded sensors in clear plastics for industrial and medical applications for real-time temperature, pressure, and chemical exposure monitoring.
- Cuts that allow for conductive clear plastics to be formed for transparent electronic displays and touch-sensitive surfaces in next-generation devices.
- And self-cleaning coatings that need less maintenance in medical, optical, and automotive product uses.
If these advancements are met, we will be guaranteed clearer plastic injection molding that will surely meet the growing demands of today’s industries in an even smarter and more sustainable way among other features.
Conclusion
Clear plastic injection molding is an important function that has transformed manufacturing industries that demand high transparency and accuracy. Advanced materials such as polycarbonate, acrylic, and optical silicone rubber, enable the manufacturer to design components that are lightweight, durable, and optically clear while replacing the older glass solutions. This has all led to a growing demand for clear plastics because of their use in medical devices, automotive lighting, electronics, and packaging. However, despite issues like moisture sensitivity, defects on the surface of the object, and strict processing requirements, molding technology has progressed greatly in increasing efficiency and improving product quality. AI, 3D printing, and nanotechnology continue to advance the technology, integrating the process at a cheaper and more precise level and carrying UV-resistant coatings and self-healing plastics have further increased the durability of the clear molded products.
Ahead, the clear plastic injection molding future is aimed at sustainability, smart materials and greater functional ability. Biodegradable and recyclable transparent plastics will be increasingly demanded by the industries looking for eco friendly alternatives to their regular products. Moreover, applications in the medical and the electronic fields may be realized with smart plastics which have embedded sensors and conductive properties. All in all, clear plastic injection moulding remains a very important technology that still develops and gives creative solutions to such industries as those that require transparency, strength and aesthetic appeal.
FAQs
1. What are the most commonly used materials in clear plastic injection molding?
PMMA is a high optical clarity material, used most often, PC for high impact resistance, OSLR for highest light transmission available, and PP for translucent, least costly applications. The choice of each material is made with respect to its corresponding properties and industrial need.
2. What are the main difficulties in clear plastic injection molding?
The main issues are in making sure the material is high optical clarity, no defects of bubbles or streaks, dealing with moisture sensitivity and scratch resistant surfaces. To overcome these challenges, precise molding conditions, good drying and very good molds are required.
3. Which industries use clear plastic injection molding most?
Clear plastic injection molding is one of the essential parts in manufacturing industries such as medical applications (syringes, IV tubes, diagnostic equipment) and automotive (headlight lenses, dashboard covers), consumer electronics (smartphone screens, display panels), packaging (food grade containers, cosmetic bottles), and lighting (LED covers, lamp diffusers).
4. What role is technology playing in clear plastic injection molding?
AI boosting of process, 3D Printing for customizing of mold, self healing plastics, improved UV resistant coatings are improving efficiency of production and the durability of the product. These reductions are enabling more reliable processes, better material performance and more sustainable processes.
5. Are clear plastic materials nature-friendly?
Traditional transparent plastics from petroleum appear to have improved in terms of sustainability, although biodegradable and recycled transparent plastics have developed in recent years. Bio–based alternatives and eco–friendly production techniques are also explored by manufacturers to cut down the environmental impact.