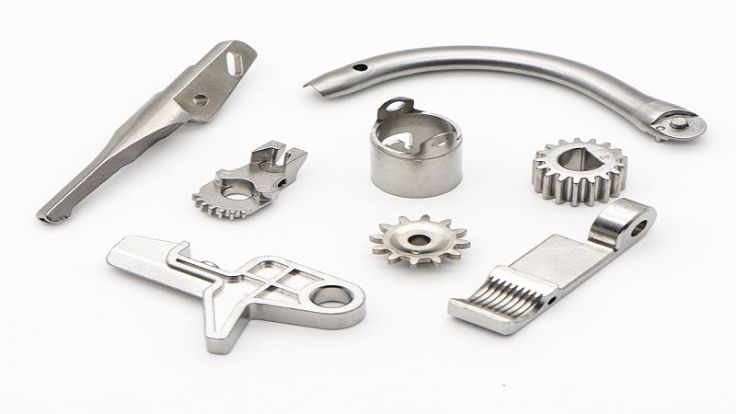
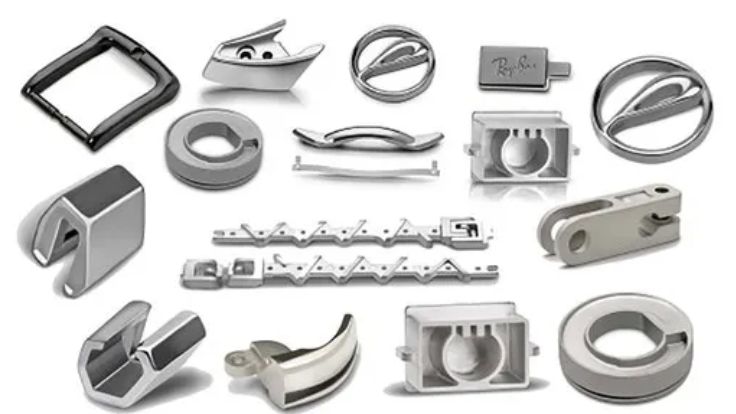
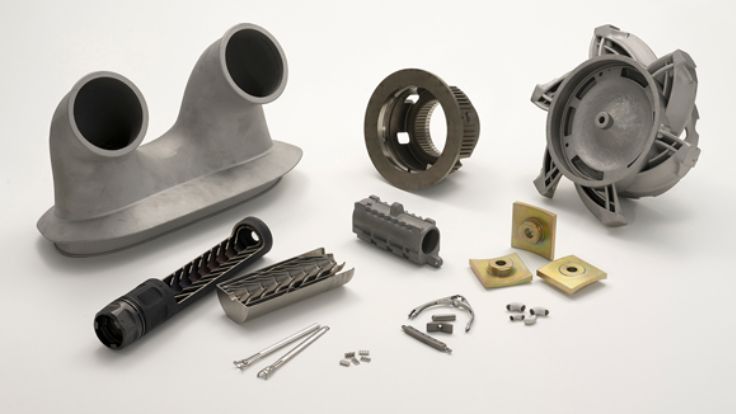
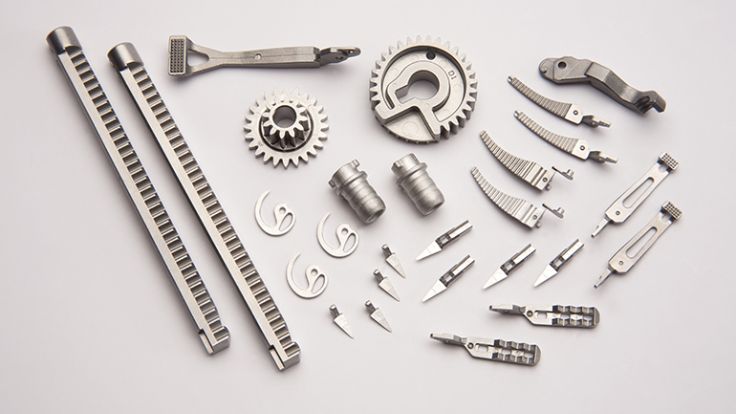
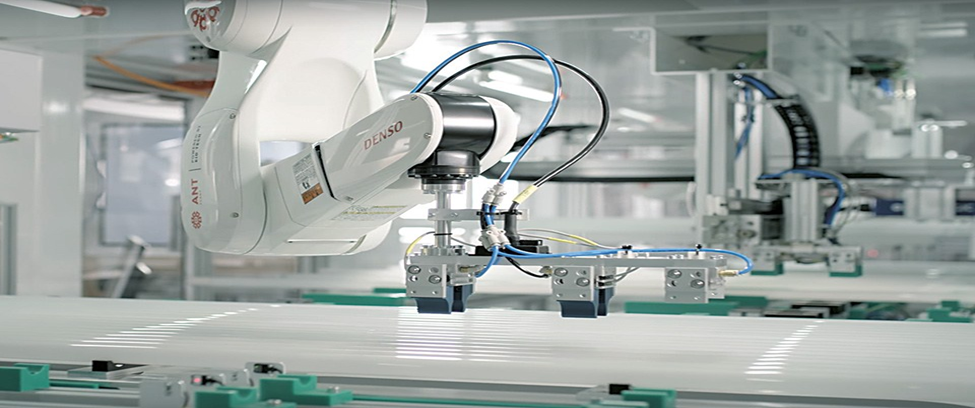
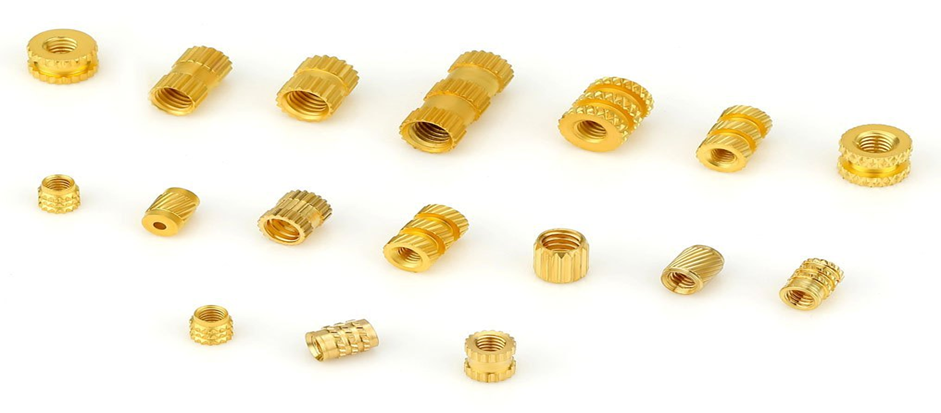
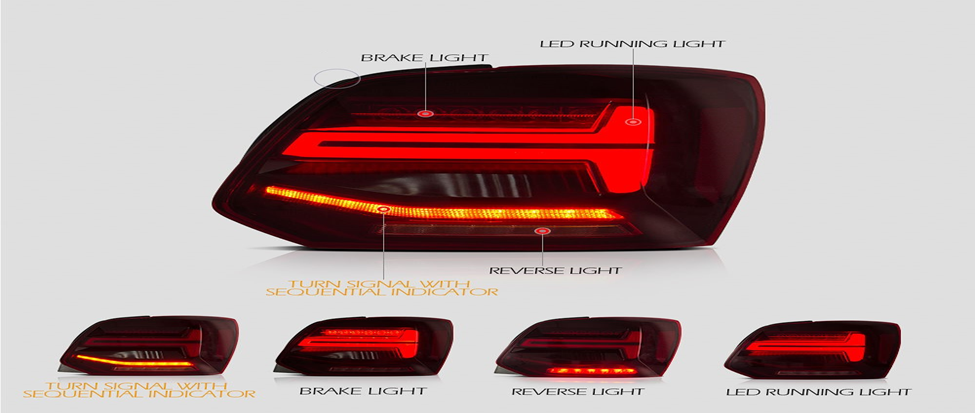
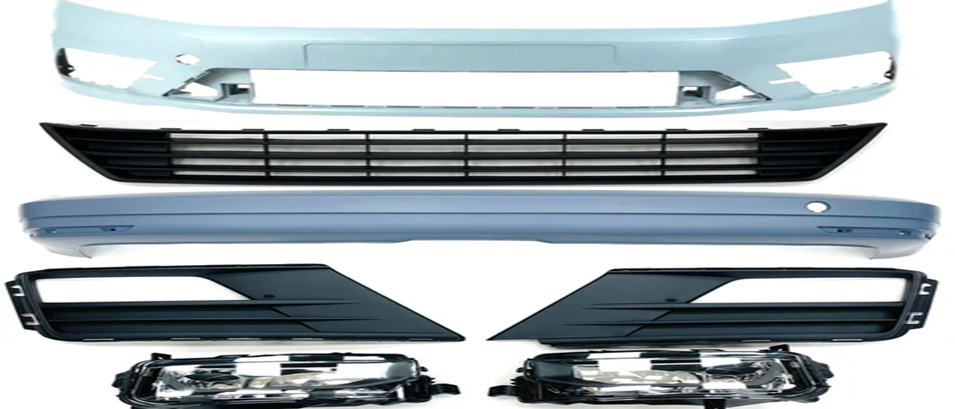
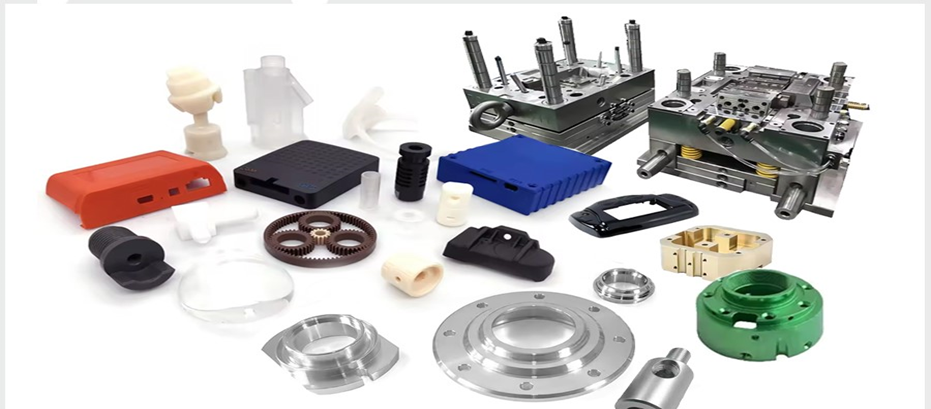
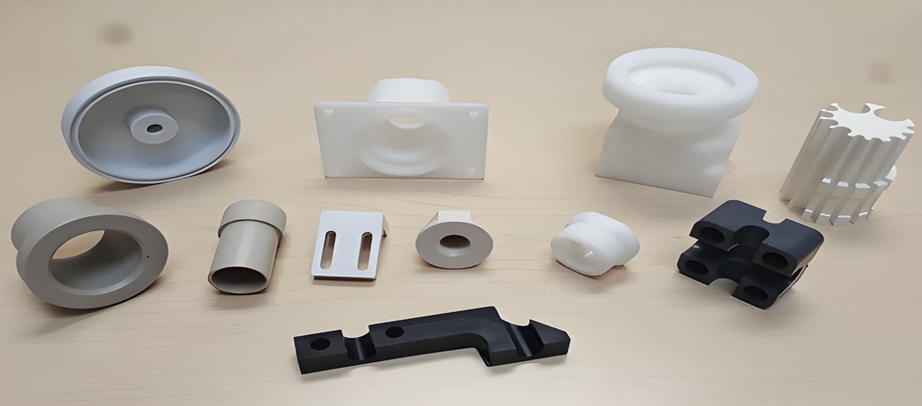
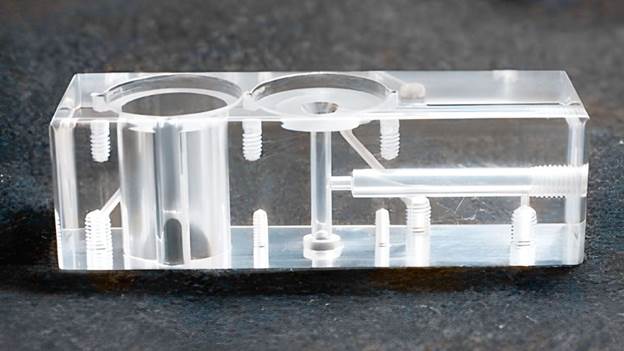
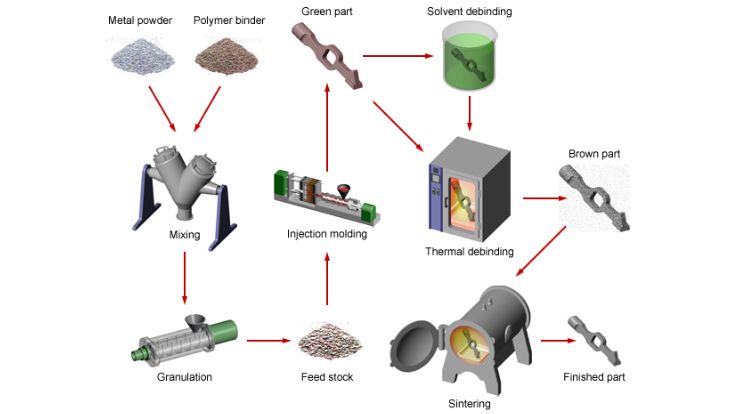
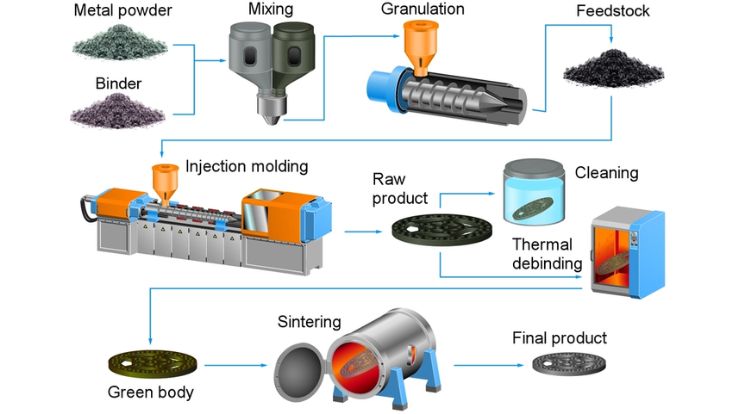
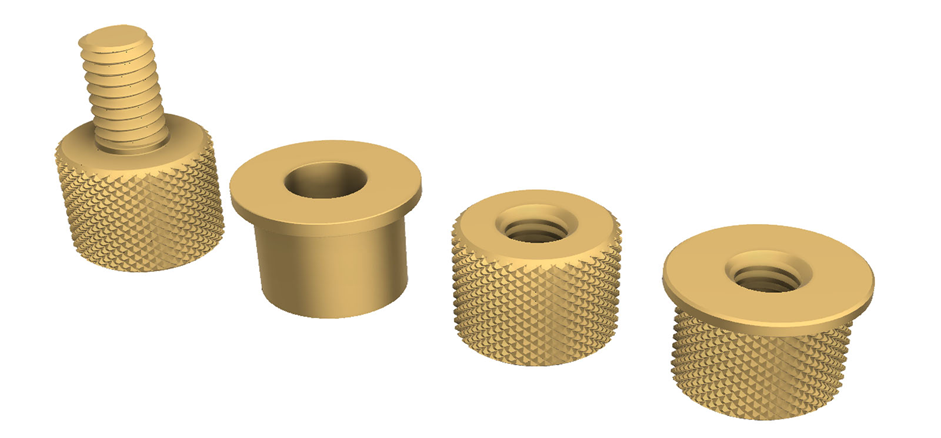
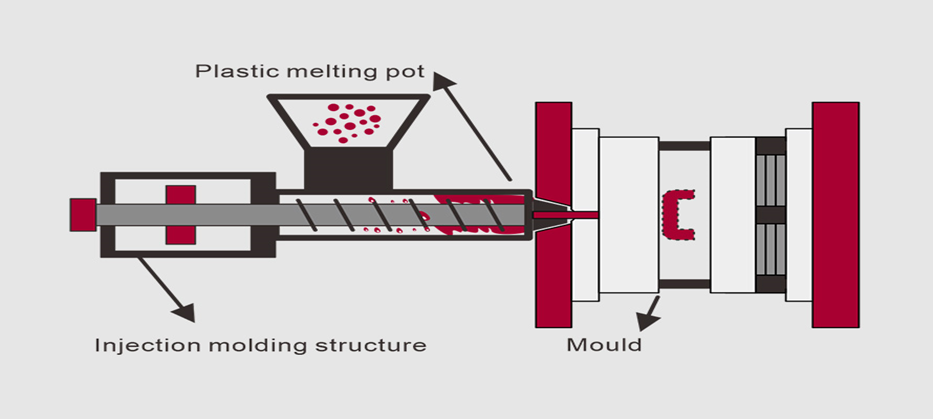
Injection molded parts production is a significant component of the contemporary industry. Injection molding is used to make many of the products surrounding us. This is a process that aids in the production of strong and accurate components. These are components that find their applications in numerous fields. The quality of molded products demanded goes up annually.
The reason behind the wide use of plastic injection molding parts is that they are durable and economical. They enable companies to manufacture large numbers of products that are of the same shape. Complex designs also work well in this process. Meanwhile, the injection molding mold parts are important in the shaping and forming of these products. The process cannot go on well without the right mold components.
The popularity of injection molding is due to the fact that it is time-saving. It also reduces waste. The method allows short-cycle production. It is something that a number of industries cannot afford to do away with.
Plastic Injection Molding: What is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding refers to a production process. In large quantities, plastic products are produced with its assistance. It is also a fast and reliable procedure. It can be used to manufacture parts of the same shape and size in all cases.
In this process, plastic material is first heated. The plastic becomes soft and melts. The liquid plastic is then inserted into a mold. The mold has a specific shape. When the plastic cools down, it becomes solid. This entire part is removed from the mold.

Plastic injection molding is used to bring about simple and complex products. It allows high accuracy. It also reduces material wastefulness, too. The reason has to do with the fact that it is popular because less time and money are wasted.
Table 1: Injection Molding Mold Components
| Mold Component | Typical Material | Tolerance | Surface Finish | Typical Life Cycle | Function |
| Core & Cavity | Hardened Steel / Aluminum | ±0.01–0.03 mm | Ra 0.2–0.8 μm | >1 million shots | Shapes internal and external features |
| Runner | Steel / Aluminum | ±0.02 mm | Ra 0.4–0.6 μm | >500,000 shots | Channels molten plastic to the cavity |
| Gate | Steel / Aluminum | ±0.01 mm | Ra 0.2–0.5 μm | >500,000 shots | Controls plastic entry into the cavity |
| Cooling Channels | Copper / Steel | ±0.05 mm | Ra 0.4–0.6 μm | Continuous | Removes heat efficiently |
| Ejector Pins | Hardened Steel | ±0.005 mm | Ra 0.3–0.5 μm | >1 million shots | Ejects finished part without damage |
| Venting Slots | Steel / Aluminum | ±0.01 mm | Ra 0.2–0.4 μm | Continuous | Releases trapped air during injection |
Knowing the Injection Molding Process
A controlled and precise method of production is the injection molding technology. They are applied in the production of plastic components of high accuracy. It is a functional procedure that occurs in stages. Each step has some parameters and numerical values.
Selection and Preparation of Materials
It begins with plastic raw material. This is usually packed in the form of pellets or in the form of granules. Such material is normally ABS, polypropylene, polyethylene, and nylon.
- Pellet size: 2–5 mm
- Wet content before drying: 0.02% -0.05%
- Drying temperature: 80°C–120°C
- Drying time: 2–4 hours
Proper drying is critical. Bubbles and surface defects of molded parts may be brought about by moisture.
Melting and Plasticizing
The plastic pellets are dried and forced into the injection molding machine. They go through a screw that rotates and through a hot barrel.
- Barrel temperature zones: 180°C–300°C
- Screw speed: 50–300 RPM
- Screw compression ratio: 2.5:1 -3.5:1.
The plastic is melted by the turning of the screw. The substance turns into a homogenous mass of liquid. Even the melting offers consistency of the component.
Injection Phase
On completion of melting down the plastic, it is pushed into the molding cavity. The mold is filled with great pressure in a quick and regularized way.
- Injection pressure: 800–2000 bar
- Injection speed: 50–300 mm/s
- Injection time: 0.5–5 seconds
There is no use of short shots and flash due to appropriate pressure control. It is intended to fill the entire mold prior to the beginning of plastic cooling.
Packing and Holding Stage
The mold is filled, and pressure is applied to the mold. This is to overcome the process of material shrinkage at room temperature.
- Loading pressure: 30-70 percent flow of injection.
- Holding time: 5–30 seconds
- Typical shrinkage rate: 0.5%–2.0%
This process increases the part concentration and dimension. It also reduces internal stents.
Cooling Process
Injection molding is the process that takes the longest in cooling time. The plastic substance would then solidify and melt.
- Mold temperature: 20°C–80°C
- Cooling time: 10–60 seconds
- Heat transfer efficiency: 60%–80%
Elimination of heat is done by cooling channels in the mold. Proper cooling eliminates warping and defects of the surface.
Mold Opening and Ejection
After cooling, the mold opens. A section that has been completed is removed using ejector pins or plates.
- Mold opening speed: 50–200 mm/s
- Ejector force: 5–50 kN
- Ejection time: 1–5 seconds
Ejection: Careful ejection will not damage parts. The closing of the mold then commences the next cycle.
The Cycle Time and Production Output
The total cycle time will be different depending on the size of the parts and the material.
- Average cycle time: 20–90 seconds
- Output rate: 40 -180 parts/hour.
- Machine clamping force: 50–4000 tons
Reduced cycle times will boost productivity. However, quality must be maintained constantly.
Monitoring and Control of Process
In contemporary machines, sensors and automation are employed. Pressure flow rate and temperature are checked by these systems.
- Temperature tolerance: ±1°C
- Pressure tolerance: ±5 bar
- Dimensional accuracy: ±0.02 mm
Consistency of quality is ensured by monitoring the process. It also reduces scrap and downtimes.
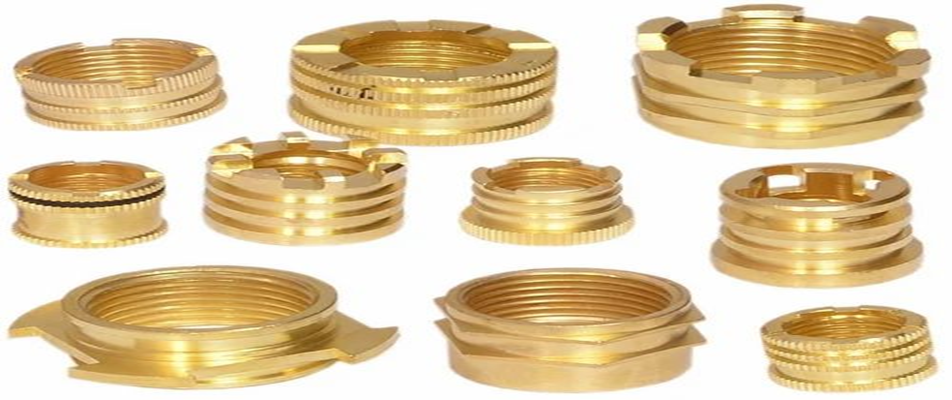
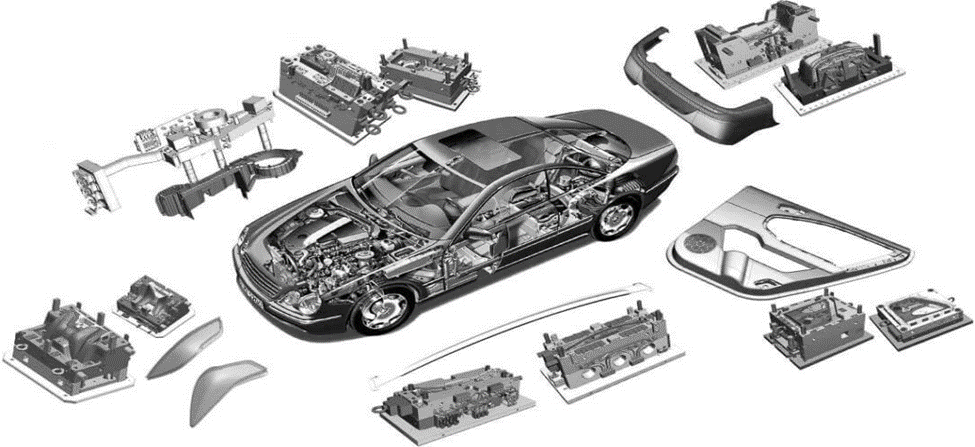
Importance of Components of Mold
Injection molding is dependent on the parts of the mold. Each of the elements of the mold has some role to play. These are the shaping, cooling, and ejecting.
The plastic injection molding parts are considered to be successful depending on the correct design of the mold. A poor mold can cause defects. These defects include cracks and unbalanced surfaces. Mold parts made by injection molding, on the other hand, help in ensuring accuracy. They also ensure that they go in good cycles.
High-quality protract parts are molded. They reduce the maintenance costs as well. This makes it more effective and dependable.
Mold Components Technical Information
Mold components are the most important elements of the injection molding system. They control the shape, accuracy, strength, and quality of the surface. Without mold components that are well-designed, there is no way that stable production can be achieved.

Core and Cavity
The core and the cavity are what determine the final shape of the product. The external surface consists of the cavity. The core makes up internal features.
- Dimensional tolerance: ±0.01–0.03 mm
- Surface finish: Ra 0.2–0.8 µm
- Typical steel hardness: 48–62 HRC
Precision in core and cavity is high, hence minimizing defects. It enhances the uniformity of the parts also.
Runner System
The system of the runner directs the molten plastic at the injection nozzle to the cavity. It has an influence on flow balance and filling speed.
- Runner diameter: 2–8 mm
- Flow velocity: 0.2–1.0 m/s
- Pressure loss limit: ≤10%
Reduction in material waste is done by proper runner design. It also has an even filling.
Gate Design
The gate regulates the flow of plastic in the cavity. Part quality depends on the size and type of gate.
- Gate thickness: 50 -80 of part thickness.
- Gate width: 1–6 mm
- Shear rate limit: <100,000 s⁻¹
Right gate design eliminates weld lines and burn marks.
Cooling System
Cooling tracks are used to cool down the mold. This system has a direct influence on cycle time and the stability of parts.
- Cooling channel diameter: 6–12 mm
- Distance of the channel to the cavity: 10-15mm.
- Maximum temperature difference permitted: < 5 °C.
Ease of cooling enhances dimensional accuracy. It also reduces the time of production.
Ejection System
When cooled, the part is ejected within the ejection system. It has to exert force in equal quantity to prevent harm.
- Ejector pin diameter: 2–10 mm
- Ejector force per pin: 200–1500 N
- Ejection stroke length: 5–50 mm
Even ejection eliminates cracks and deformation.
Venting System
The air can be trapped and escape through vents when injecting. Burns and incomplete filling are caused by poor venting.
- Vent depth: 0.02–0.05 mm
- Vent width: 3–6 mm
- Maximum air pressure: <0.1 MPa
Adequate venting enhances the quality of surfaces and the life of molds.
Base and Alignment Components Mold Base
The base of the mould bears all the parts. Bushings and guide pins are used to provide proper alignment.
- Guide pin tolerance: ±0.005 mm
- Mold base flatness: ≤0.02 mm
- Lifecycle alignment: more than 1M shots.
High alignment decreases the wear and flash.
Table 2: Key Process Parameters
| Parameter | Recommended Range | Unit | Description | Typical Value | Notes |
| Barrel Temperature | 180–300 | °C | Heatis applied to melt the plastic | 220–260 | Depends on the material type |
| Injection Pressure | 800–2000 | bar | Pressure to push molten plastic into the mold | 1000 | Adjust for part size & complexity |
| Mold Temperature | 20–120 | °C | Temperature is maintained for proper cooling | 60–90 | Higher for engineering plastics |
| Cooling Time | 10–60 | seconds | Time for the plastic to solidify | 25–35 | Depends on wall thickness |
| Cycle Time | 20–90 | seconds | Total time per molding cycle | 30–50 | Includes injection, packing, and cooling |
| Ejector Force | 5–50 | kN | Force to remove part from the mold | 15–30 | Must prevent part damage |
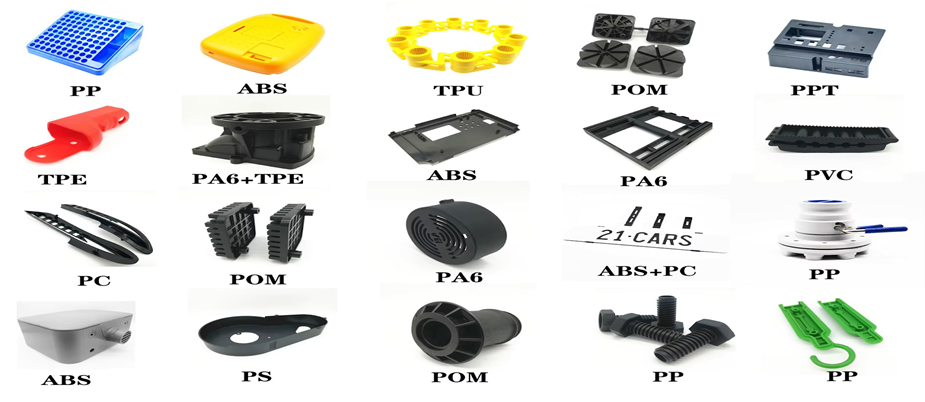
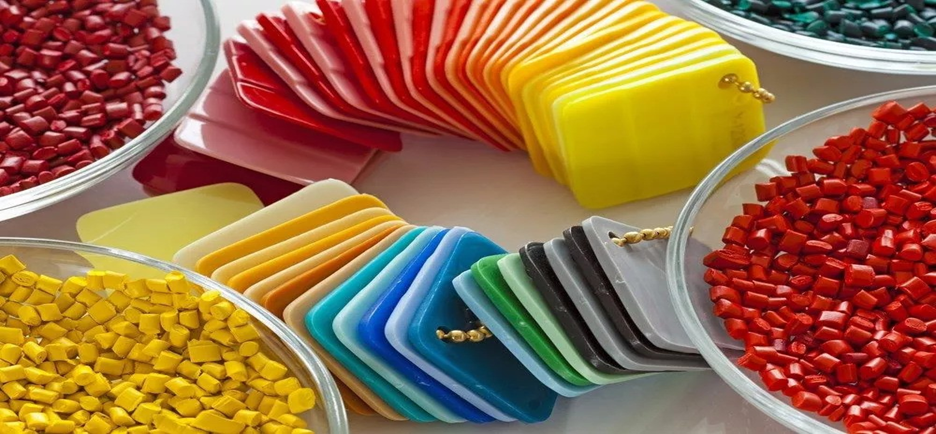
Raw Materials Injection Molding
Material selection is very important. It influences the quality, stability, outlook, and price of the end product. Selecting the appropriate plastic is necessary to guarantee that the parts will work and will be printed properly.

Thermoplastic Materials
The most widespread materials are thermoplastics due to the fact that they can be melted and reused several times. There is a wide use of ABS, polypropylene, polyethylene, and polystyrene. ABS is impact-resistant and strong, and melts at 200 to 240 °C. Polypropylene melts at temperatures of 160 °C or 170 °C; it is light in weight and resistant to chemicals. Polyethylene has a melting point of 120 °C to 180 °C and is suitable in moisture resistant products.
Engineering Plastics
High-strength parts or heat-resistant parts are made with engineering plastics such as Nylon, Polycarbonate (PC), and POM. Nylon melts at 220 °C -265 °C and is applied in gears and mechanical parts. Polycarbonate is a strong and transparent polymer that melts at 260 °C to 300 °C. POM has a melting temperature of 165 °C to 175 °C and is accurate in components.
Thermosetting Plastics
Plastics that are thermosetting are difficult to remelt after being molded because they harden permanently. They melt at 150 °C- 200 °C and are utilized in high-temperature applications such as electrical components.
Additives and Fillers
Materials are enhanced by additives. Glass fibers (10% -40 percentage) add strength, mineral fillers (5%-30 percentage) lower shrinkage, and UV stabilizer (0.1-1 percentage) shield against the sun. These assistive components are longer-lasting and work better.
Material Selection Requirements
The material selection is factor-driven in terms of temperature, strength, chemical confrontation, moisture, and cost. Adequate selection will result in long-lasting, precise, and quality products and lessen the mistakes and waste.
Table 3: Material Properties
| Material | Melt Temp (°C) | Mold Temp (°C) | Injection Pressure (bar) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Shrinkage (%) |
| ABS | 220–240 | 60–80 | 900–1500 | 40–50 | 0.5–0.7 |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 160–170 | 40–70 | 800–1200 | 30–35 | 1.0–1.5 |
| Polyethylene (PE) | 120–180 | 20–50 | 700–1200 | 20–30 | 1.5–2.0 |
| Polystyrene (PS) | 180–240 | 50–70 | 800–1200 | 30–45 | 0.5–1.0 |
| Nylon (PA) | 220–265 | 80–100 | 1200–2000 | 60–80 | 1.5–2.0 |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | 260–300 | 90–120 | 1300–2000 | 60–70 | 0.5–1.0 |
| POM (Acetal) | 165–175 | 60–80 | 900–1500 | 60–70 | 1.0–1.5 |
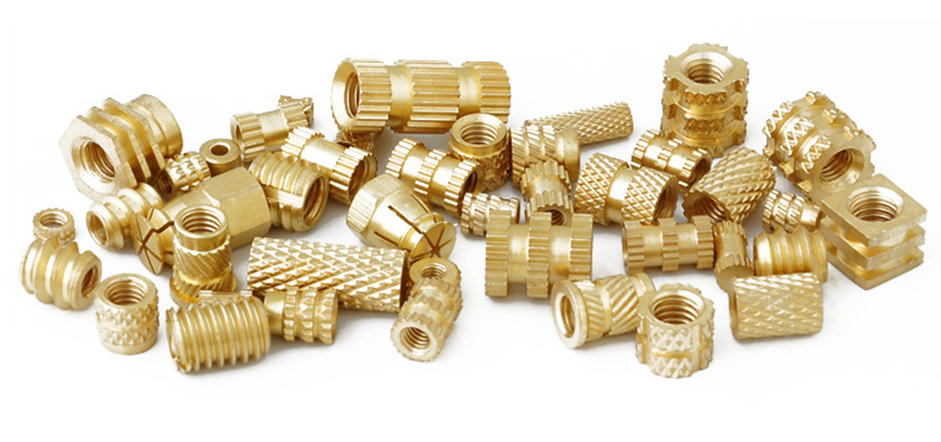
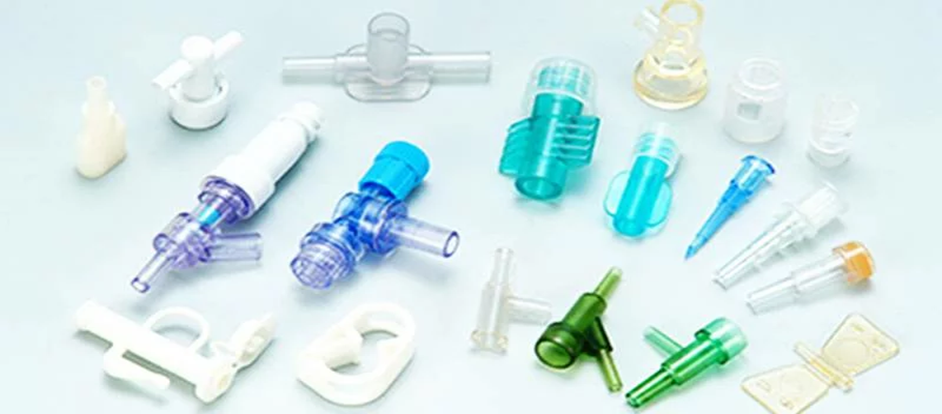
Components that are manufactured under the Plastic Injection Molding Process
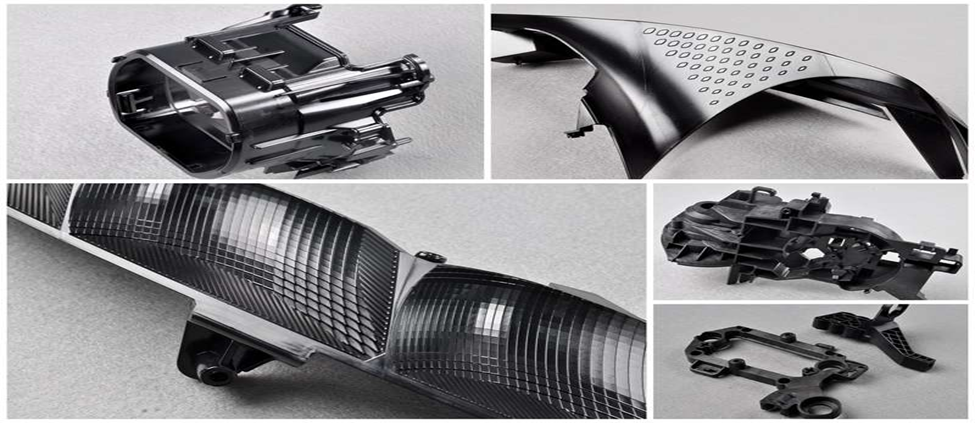
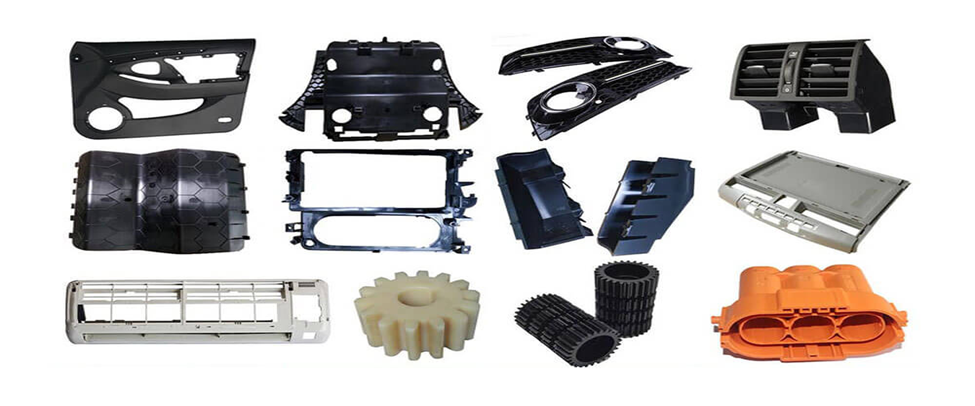
Plastic injection molding is a process that creates a large number of components applicable in various sectors. The process is precise, durable, and of large volume production. Examples of typical components produced in this manner are shown below.

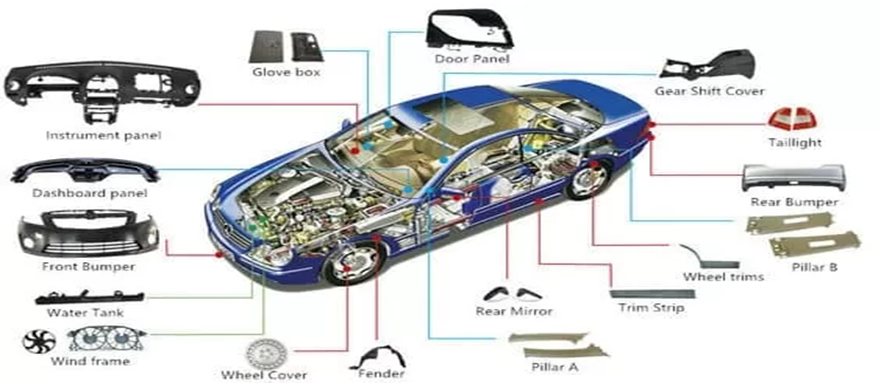
Automotive Parts
- Dashboards
- Bumpers
- Air vents
- Door panels
- Gearshift knobs
- Fuel system components
- Interior trims
Medical Parts
- Syringes
- Tubing connectors
- Surgical instruments
- IV components
- Medical device housings
- Disposable medical tools
Electronics Parts
- Housings for devices
- Switches and buttons
- Cable clips and wire holders
- Connectors and plugs
- Keyboard keys
- Circuit board enclosures
Packaging Products
- Bottles and jars
- Bottle caps and closures
- Food containers
- Cosmetic containers
- Lids and seals
- Storage boxes
Consumer and Industrial Goods
- Toys and figurines
- Household tools
- Appliance components
- Construction fittings
- Accurate clips and fasteners.
- Industrial machine parts
Design and Precision
Design is a significant contributor to success. An effective mold enhances the quality of a product. It minimizes errors during production as well.
The parts of the process of plastic injection molding require strict dimensions. Performance can be influenced by small mistakes. This is the reason why the creation of the injection molding mould parts is designed with close tolerances. State-of-the-art software is often employed in design.

Strength is also enhanced through good design. It enhances appearance. It guarantees superior fitting in end assemblies.
Industrial Applications
Many industries also use injection molding, which is fast, exact, and it is economical. It enables mass production of identical parts with very high precision.
Automotive Industry
In the auto sector, dashboards, bumpers, air vents, and interior panels are made using plastic injection molding parts. These components should be powerful, light, and heat-resistant. Particularly, it is done by molding, whereby the shapes are exact and uniform to prevent any safety and quality issues.
Medical Industry
In medicine Syringes, tubing connectors, and surgical instruments are made by injection molding. Much precision and hygiene areas needed. Particularly, plastic injection molding parts can be made of medical-grade plastics, and injection molding mold parts can be used to ensure accuracy and smoothness.
Electronics Industry
Housings, connectors, switches, and cable clips are all produced in the electronics industry through injection molding. Plastic injection molding parts secure the fragile circuits, and the injection molding mold parts are necessary to make the parts fit perfectly.
Packaging Industry
Injection molding is also applied in the packaging of bottles, containers, caps, and closures. The parts of the plastic injection molding are used to give the required shapes and sizes, whereas the parts of injection molding are used to produce in large quantities within the shortest amount of time by creating minimum wastage.
Other Industries
Consumer goods, toys, construction, and aerospace are also injected. Its flexibility and accuracy give it the ability to fit nearly any plastic product, be it the simple householder the complicated technical parts.
Quality Control and Testing
In manufacturing, quality control is required. All the parts should be desiccated to meet design requirements. Testing is a measure of safety and performance.
The plastic injection molding parts are subjected to visual and mechanical inspections. Defects are spotted at an early stage through these checks. Simultaneously, the inspection of the wear and damage of the injection mold parts is conducted. Frequent inspections eliminate the failure of production failures.
Good quality management enhances customer confidence. It also minimizes wastage and expenditure.
Pros of the Injection Molding
There are numerous advantages of injection molding. It permits a rapid production rate. It also guarantees repetition.
Plastic injection molding parts are dynamic and light. They are capable of mass production. In the meantime, automation is supported by the use of injection molding of the mold parts. This lowers the cost of labour and mistakes.

Also, the process is environmentally friendly. The scrap material may be reutilized. This will contribute to environmental mitigation.
Challenges and Solutions
Injection molding, just like any process, is challenging. These are material problems as well as wear of moulds. Unfavorable environments lead to flaws.
Part flaws may be assessed in the absence of proper handling of “plastic injection molding parts. These risks can be minimized by appropriate training. Simultaneously, mold parts that are used in injection molding must be maintained on a regular basis. This assures long life.
Modern technology will be useful in addressing a lot of issues. The efficiency is enhanced through automation and monitoring.
Future of Injection Molding
The injection molding future is solid. There is a development of new materials. Smart manufacturing is becoming a reality.
Injection molding parts that are produced out of plastic will be improved. They will be more significant and lighter. At the same time, better materials and coatings will be applied to the injection mold part. This will enhance longevity.
The industry will still be characterized by innovation. Competitive firms will be those that change.
China’s Role
China contributes significantly to the injection molding market in the world. It is among the biggest manufacturers of plastic injection molding parts and the distributor of injection molding mold parts. The manufacturing sector is very diversified in the country; small-scale production is available as well as large-volume industrial production.

The factories of China have high-precision machines and skilled labor that are used to manufacture parts. The reliance of many international companies on Chinese manufacturers is because they offer cost-effective solutions without reducing on quality.
Besides, China is an Innovation leader. It creates new materials, molds, and automation methods to enhance efficiency. It has a good supply chain and high production capacity that contribute to its status as a major player in satisfying global demand for injection molded products.
Why Choose Sincere Tech
We are Sincere Tech, and we deal with supplying high-quality plastic injection molding parts and injection molding mold parts to our clients in different industries. We have years of experience and a passion to do things in the best way, hence all our products are of the best quality in terms of precision, durability, and performance.
We have a group of experienced and qualified engineers and technicians who offer quality and affordable solutions through the application of modern machinery and new methods. We have ensured close attention to all the details, such as the choice of material, the design of molds, etc., so that we have the same quality in each batch.
Clients prefer Sincere Tech due to the fact that we appreciate trust, professionalism, and customer satisfaction. We collaborate with individual clients to get to know their special needs and offer solutions to their needs. We are also committed to the concept of on-time delivery, technical assistance, and constant improvement, which make us stand out inthe injection molding industry.
Sincere Tech is the company with which you can find excellence in plastic injection molding when you require either minor, detailed parts or large-volume production. You do not just get parts with us, you also get a team dedicated to your success and growth.
To learn more about our services and products, go to plas.co and see why we are the right choice for the clients of the world.
Conclusion
Injection molding is a solid process of production. It is the backbone of numerous industries in the world. Its main strengths are precision, speed, and quality.
Plastic injection molding parts are still very vital in everyday life. They are useful in serving various needs, from the simplest to the complex components. Meanwhile, injection molding mold parts guarantee the efficient flow of manufacturing and the same outcome.
Injection molding will only continue to increase with the right design and maintenance. It will also continue to form a vital aspect of modern production.